Data representation
|
Problem analysis
|
Problem analysis
why is this counting problem recursive
|
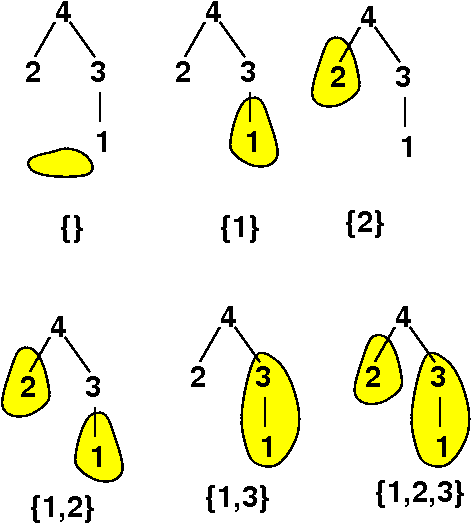
Finding the recursive relationship
|
Finding the recursive relationship
|
(I included the universe set in red because it will be important as shown next)
Finding the recursive relationship
|
Finding the recursive relationship
|
Finding the recursive relationship
|
Finding the recursive relationship
|
Finding the recursive relationship
|
Finding the recursive relationship
|
Finding the recursive relationship
|
A larger example to show the recursive relationship of subsets
# subsets (including the universe set) = k1*k2*...*kN + 1
Sets to remove How to form
==================================== ==============
7 {} {1} {2} {12} {126} (R1=T(6)+{ }+{ })
/ | \ {5} {15} {25} {125} {1265} (R2=T(6)+{5}+{ })
6 5 4 {3} {13} {23} {123} {1263} (R3=T(6)+{ }+{3 })
/ \ | {53} {153} {253} {1253} {12653} (R4=T(6)+{5}+{3 })
1 2 3 {34} {134} {234} {1234} {12634} (R5=T(6)+{ }+{34})
{534} {1534} {2534} {12534} {126534} (R6=T(6)+{5}+{34})
{1234567}
Total = 5 * 2 * 3 + 1
6 {} {1} {2} 5 {} 4 {} {3}
/ \ {12} {5} | {34}
1 2 {126} 3
Total = 2*2+1 = 5 Total = 2 Total = 2+1 = 3
1 {} 2 {} 3 {}
{1} {2} {3}
Total = 2 Total = 2 Total = 2
|
where: k1, k2, k3 are the size of the subsets in the subtrees
Data representation
4 <---- Mark = 4 4
3 <---- 3 invited 1 / \
4 <---- 4 invited 2 2 3
4 <---- 4 invited 3 \
1
Data repr:
invited[4] = {2,3}
invited[3] = {1}
invited[2] = {}
invited[1] = {}
Use: (variable length array)
vector<int> invited[10]; // Because N <= 6
|
Data representation
4 <---- Mark = 4 4
3 <---- 3 invited 1 / \
4 <---- 4 invited 2 2 3
4 <---- 4 invited 3 \
1
Data repr:
invited[4] = {2,3}
invited[3] = {1}
invited[2] = {}
invited[1] = {}
|
J5 solution
int countComb( vector |