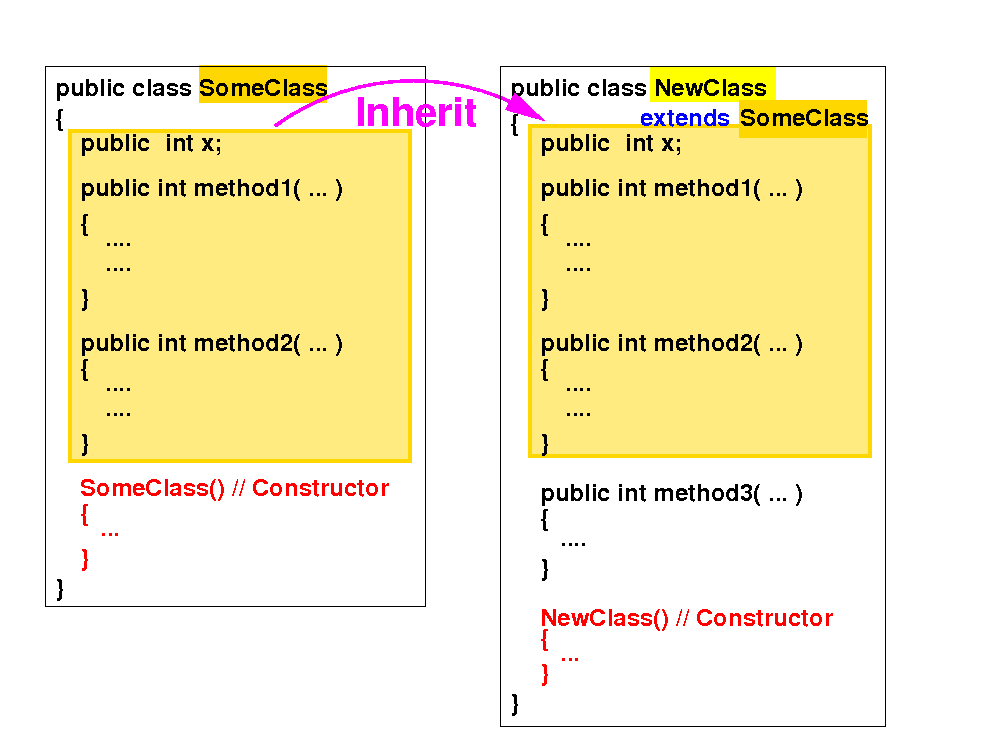
(1) A subclass inherits all variables and the normal methods from its superclass:
(2) A subclass do not inherit any constructor method from its superclass:
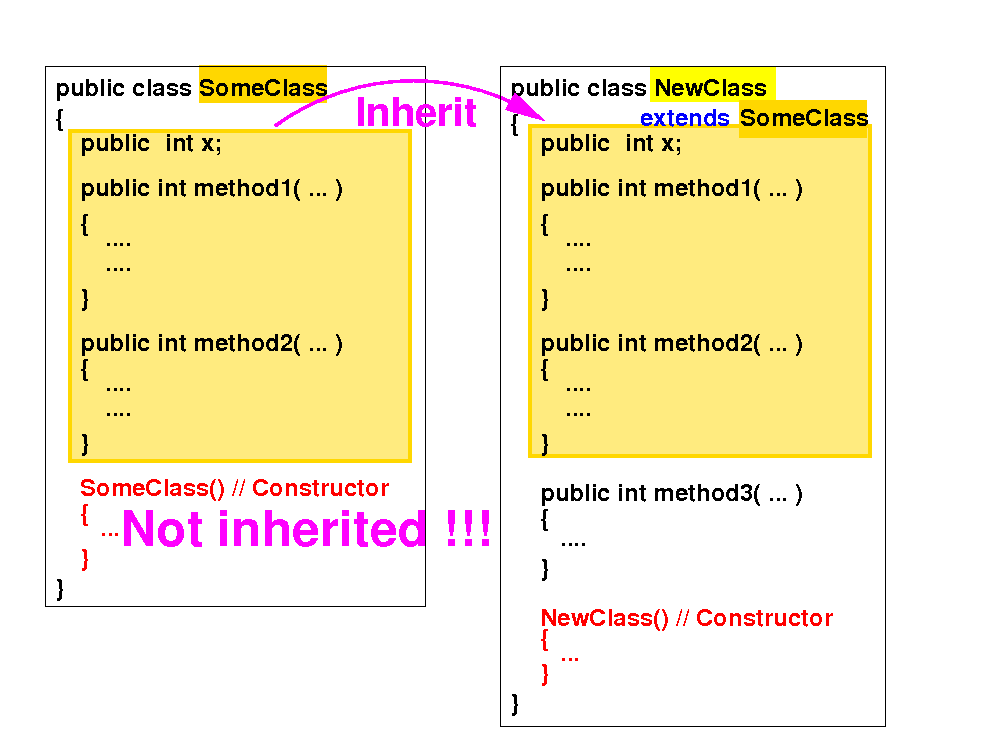
But instead: a constructor in the subclass must invoke some constructor in the superclass -- discussed next
Notice that a subclass object always contains a superclass object:
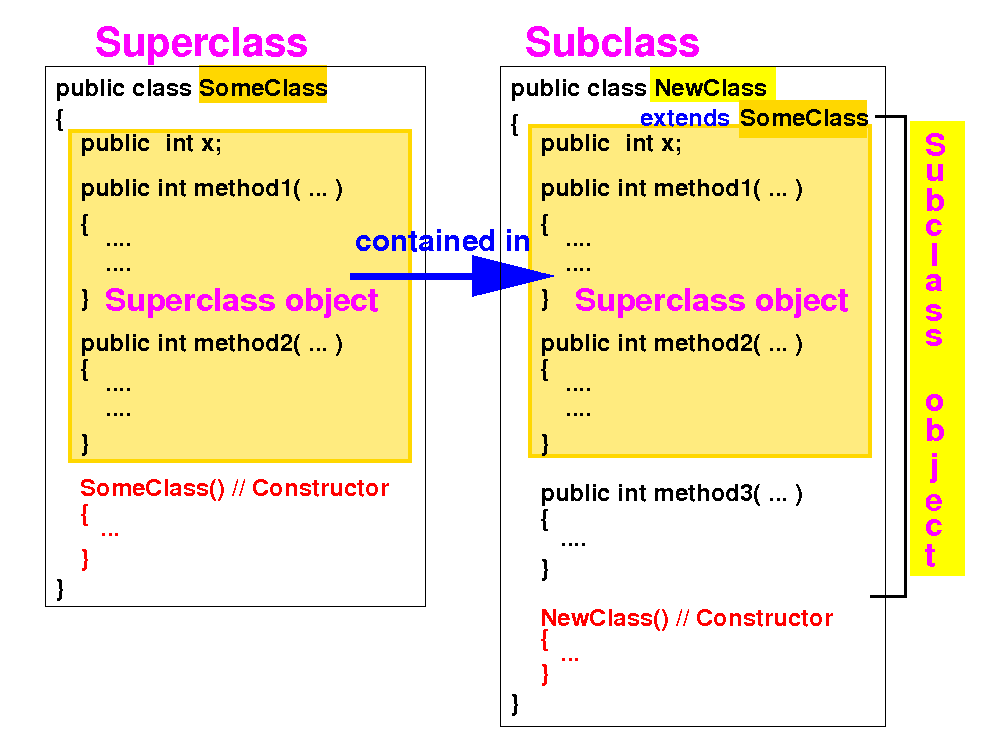
Recall: objects are initialized using a constructor -- how to makes sure that a subclass object is initialized ?
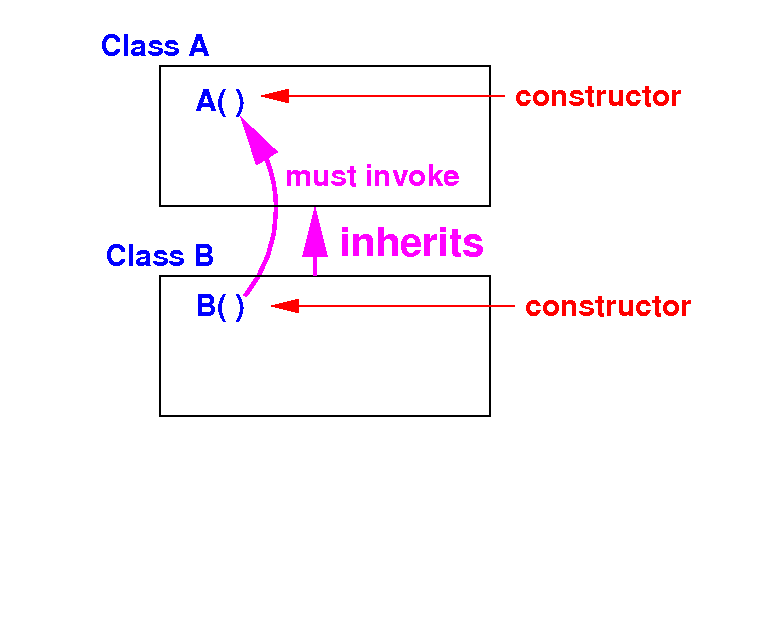
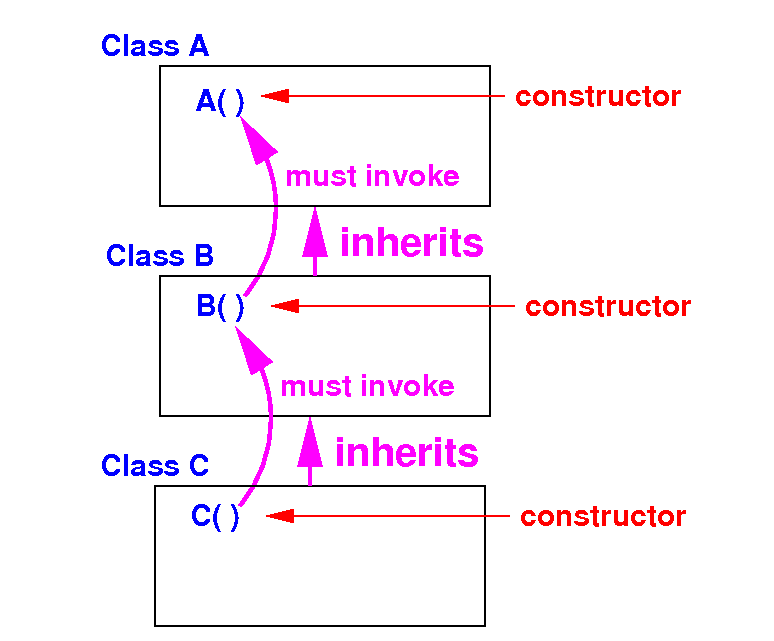
(3) Rule: a constructor of the subclass must invoke some constructor of its superclass as the first statement
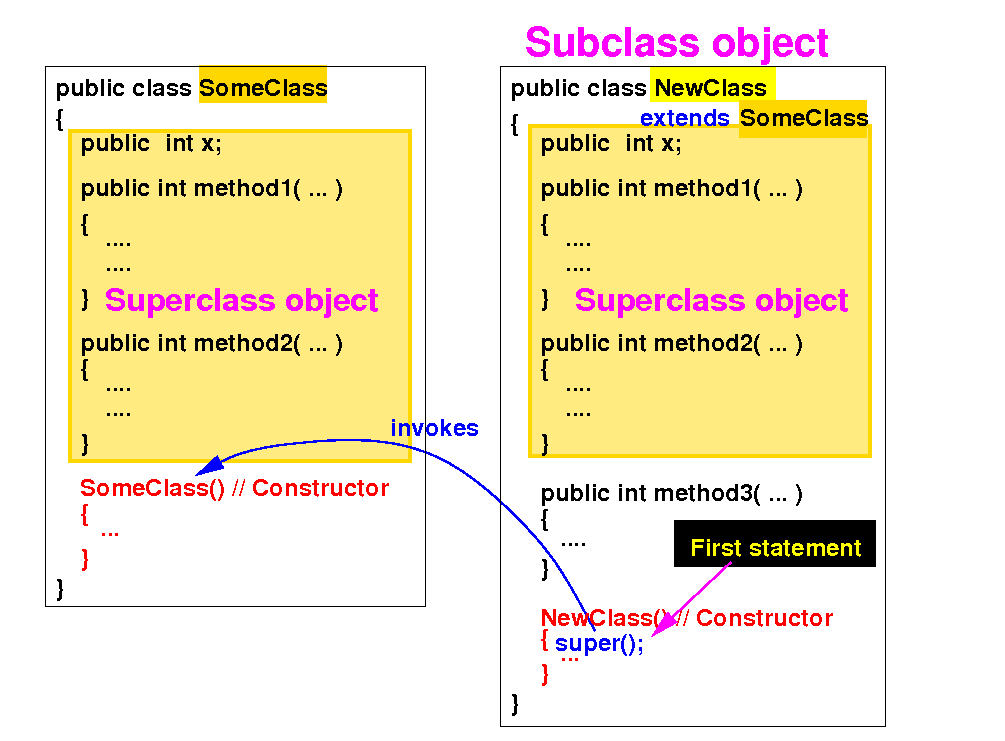
The syntax super( parameters ) is used to invoke a constructor in its superclass
public class myProg
{
public static void main()
{
NewClass a = new NewClass();
NewClass b = new NewClass(44);
}
}
|
public class NewClass
extends SomeClass
{
public NewClass()
{
super(); //Calls: SomeClass()
}
public NewClass(int a)
{
super(a); //Calls: SomeClass(a)
}
}
|
public class SomeClass
{
public int x;
public SomeClass()
{
x = 99;
}
public SomeClass(int a)
{
x = a;
}
}
|
DEMO: demo/13-inheritance/06-super
DEMO: trace the execution in BlueJ
(4) Compliance rule: if a constructor in the subclass does NOT invoke any constructor in its superclass:
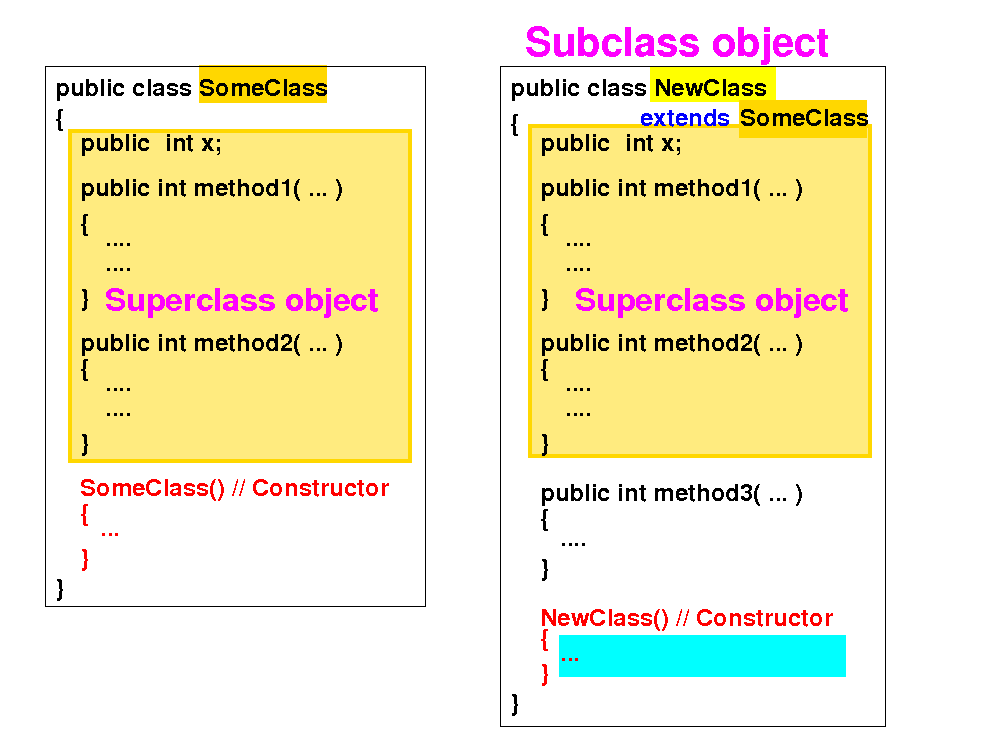
Then... (can you guess what will happen ??? Remember the rules about default constructors ?
(4) Then: the Java compiler will automatically insert the call super( ) as the first statement:
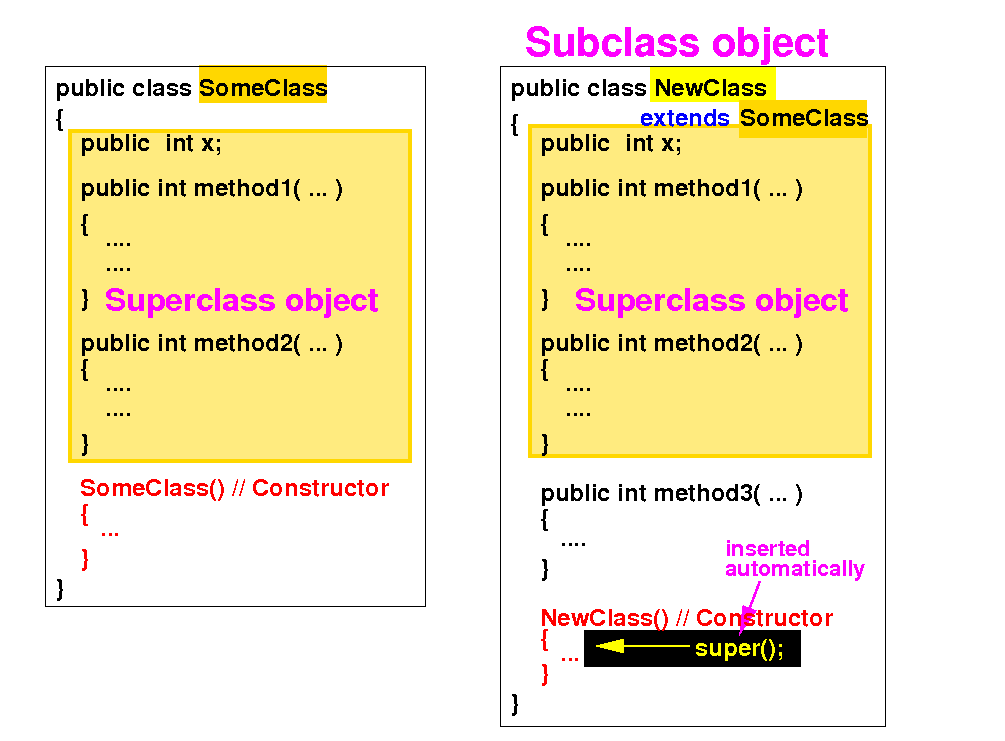
I.e.: if the first statement in a constructor is not super(...), the Java compiler will call the default constructor!
public class myProg
{
public static void main()
{
NewClass a = new NewClass();
}
}
|
public class NewClass
extends SomeClass
{
public NewClass()
{
// No super( ) call
// Java will insert super()
}
public NewClass(int a)
{
super(a);
}
}
|
public class SomeClass
{
public int x;
public SomeClass()
{
x = 99;
}
public SomeClass(int a)
{
x = a;
}
}
|
DEMO: demo/13-inheritance/07-super
DEMO: trace the execution in BlueJ
|
|
DEMO: demo/13-inheritance/09-chaining/
public class SomeClass
{
public int x;
public SomeClass()
{
x = 99;
}
public void method1( )
{
System.out.println("I am SomeClass.method1(). x = " + x);
}
public void method2( )
{
System.out.println("I am SomeClass.method2(). x = " + x);
}
}
|
|