How to
maximize
the sharing of
properties and/or
actions among classes
- We have learned to
use a
class
to
model
objects of the
same type.
Example:
- The Circle class
models
objects that
are round in shape
- The Rectangle class
models
objects that
have 4 sides and
4 right angles
|
-
Different classes
can have
common
properties and/or
behaviors (= actions)
Example:
- Circles and
rectangles can
both have
the
color
property
- Circles and
rectangles can both have
the
getArea()
behavior (= action)
|
- How to
maximize
sharing of
common
properties/behaviors:
- We
"unite"
different
classes into
a
more general
("super") class
|
Discussed next
|
How to
generalize
classes with
common
properties/actions
- Consider a
group of
cats "objects" and
a group of
dogs
"objects":

- $64,000 question:
- How can we
generalize the
cats and
dogs ?
|
|
How to
generalize
classes with
common
properties/actions
- A cat
is a
animal ---
A dog
is a
animal
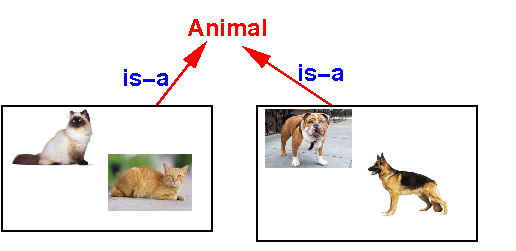
- Answer:
- The
is-a
generalization method will
give us
the
maximum sharing of
properties and
actions
|
|
What do
cats and
dogs and
other animals
have in common ?
-
Properties:
- numOfLegs:
dogs, cats: 4,
chickens: 2,
spider: 8
- numPairOfWings:
dogs, cats: 0,
chickens: 1,
dragenfly: 2.
- And so on
|
-
Actions:
- sound():
dogs: "Woof",
cats: "Maio",
chickens: "Cluck"
- travelSpeed():
dogs: 35 mph,
cats: 30 mph,
cheetah: 60 mph.
- And so on
|
- The
Object Oriented Design
methodology:
- The Object Oriented Design
methodology uses the
is-a
generalization technique
to achive
maximal sharing of
properties (= variables) and
actions (= methods) among
classes
|
|
How to
generalize
classes with
common
properties/actions
- Now consider
circle and
rectangle
objects:
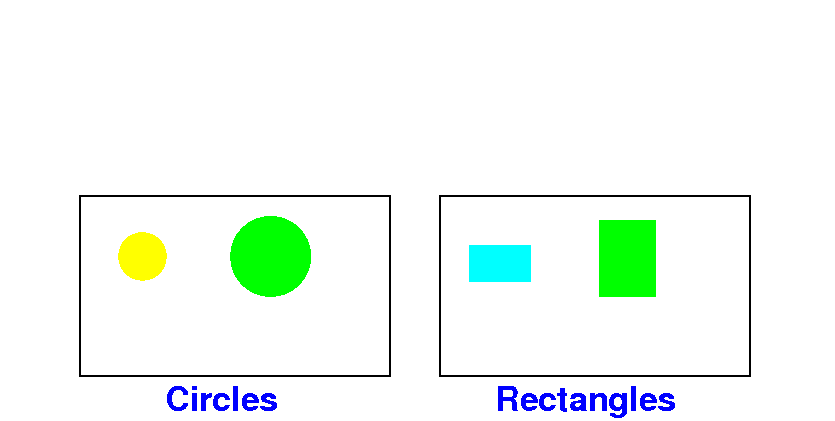
- $64,000 question:
- How can we
generalize
circles and
rectangles ?
|
|
How to
generalize
classes with
common
properties/actions
- A circle
is-a
geometric shape ---
A rectangle
is-a
geometric shape
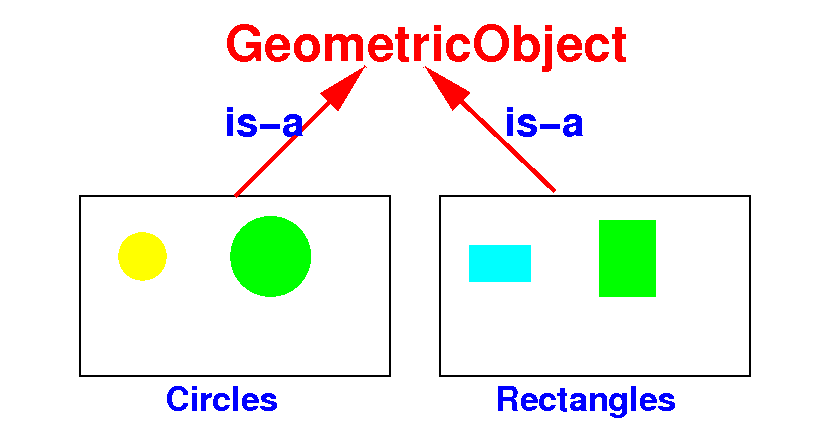
- Answer:
-
Geometric shapes
are closed figures
created using points,
line segments,
circles, and
curves.
|
|
What do
circles and
rectangles and
other geometric shapes
share ?

- Properties:
- color:
each shape can have its own color
- numOfSides:
circle, oval: 0,
triangle: 3,
rectangle: 4.
- And so on
|
- Actions:
- getArea():
returns the area of the
geometric shape
- getPerimeter():
returns the perimeter of the
geometric shape
- And so on
|
|
How to
design the
class hierarchy
using the
is-a generalization
technique
- First,
determine
all the
program classes that you will
need to
solve the
problem:

- Determine the
properties and
actions that are
needed in
each class
|
How to
design the
class hierarchy
using the
is-a generalization
technique
- Then,
generalize
similar
program classes
using the
is-a
generalization:

- Use the
properties and
actions in
each class
to
find the
"more general" classes
|
How to
design the
class hierarchy
using the
is-a generalization
technique
- If possible,
generalize
further:
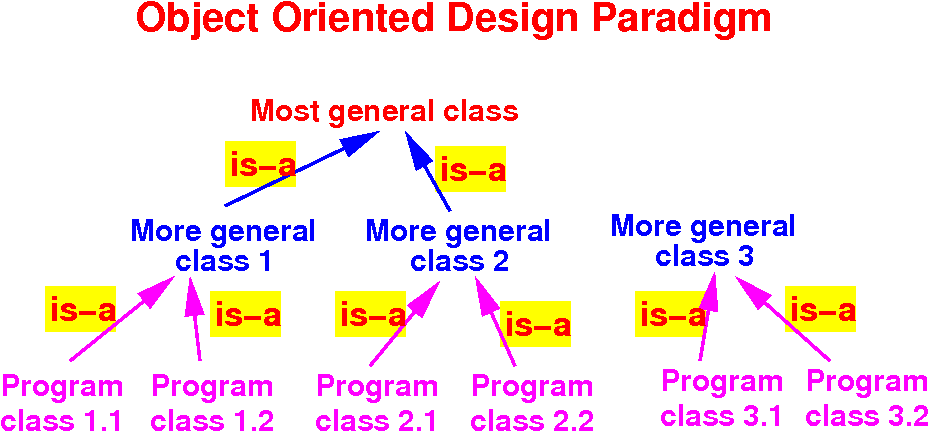
- Use the
final hierarchy to
determine the
properties and
actions of
each class
|
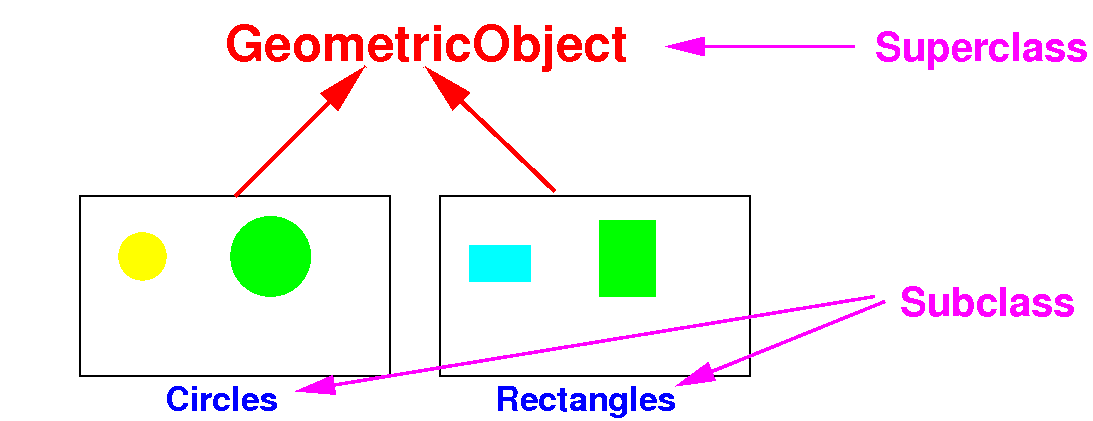
Terminology:
superclass and
subclass
-
Superclass
= the
more general
class in the
is-a relationship
(a.k.a.:
parent class)
-
Subclass = the
more specific
class in the
is-a relationship
(a.k.a.:
child class)
Example:
|
Relationship
between a
superclass and its
subclasses
How to define
a subclass
using a
superclass in
Java
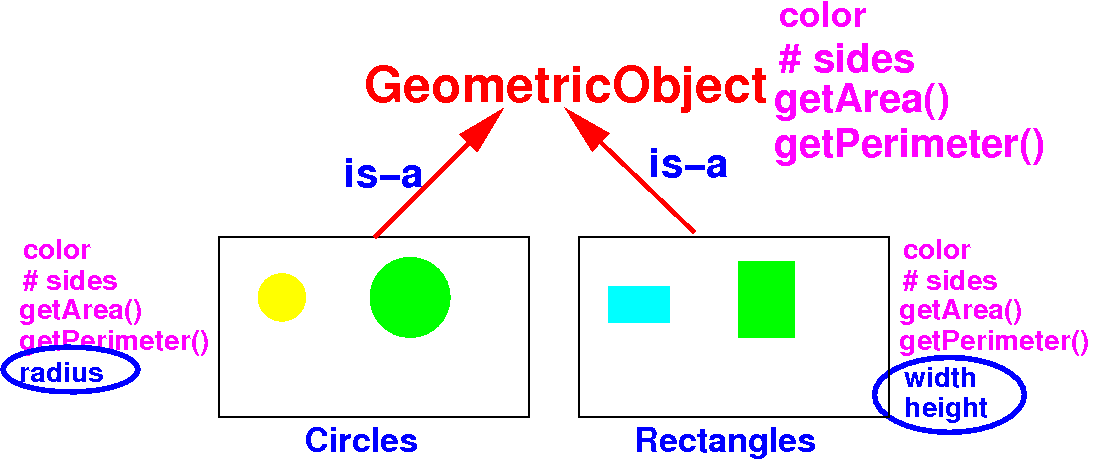 public class GeometricObject
{
private String color;
private int numSides;
public double getArea() { .... }
public double getPerimeter() { .... }
}
public class Circle extends GeometricObject // (1) inherits all variables and normal methods
{
private double radius; // (2) Add more properties if needed
public double getRadius() { ... } // (3) Add new methods if needed
public double getArea() { ... } // (4) Override some inherited method if needed
}
public class GeometricObject
{
private String color;
private int numSides;
public double getArea() { .... }
public double getPerimeter() { .... }
}
public class Circle extends GeometricObject // (1) inherits all variables and normal methods
{
private double radius; // (2) Add more properties if needed
public double getRadius() { ... } // (3) Add new methods if needed
public double getArea() { ... } // (4) Override some inherited method if needed
}
|
We will study an
example on
how to design
a superclass and
subclass
next
❮
❯

