|
The Circle class has no constructors defined:
public class Circle
{
double radius = 1; /** The radius of this circle */
// Circle has no constructors defined....
// The Java compiler will insert the default constructor !
}
|
The Circle class has no constructors, so the Java compiler will insert the default constructor
A subclass object always contains a superclass object:
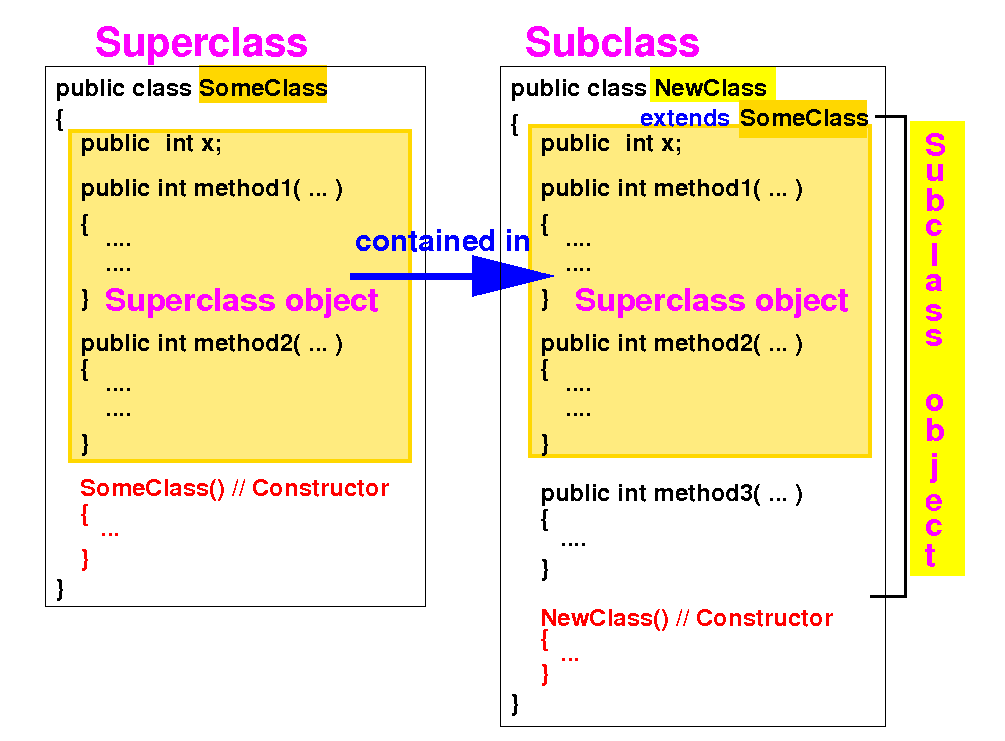
And objects are initialized using a constructor...
Therefore: a constructor in the subclass must invoke some constructor in its superclass as its first statement:
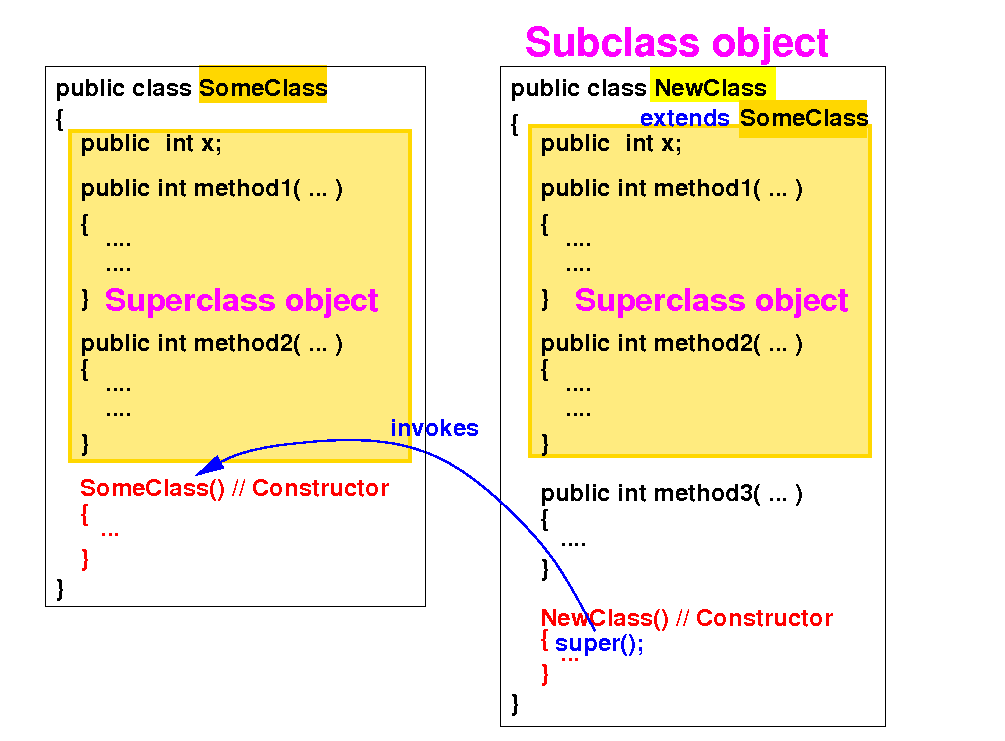
The keyword super( ... ) is used to invoke a constructor in its superclass
If a constructor in the subclass does NOT invoke any constructor in its superclass as its first statement:
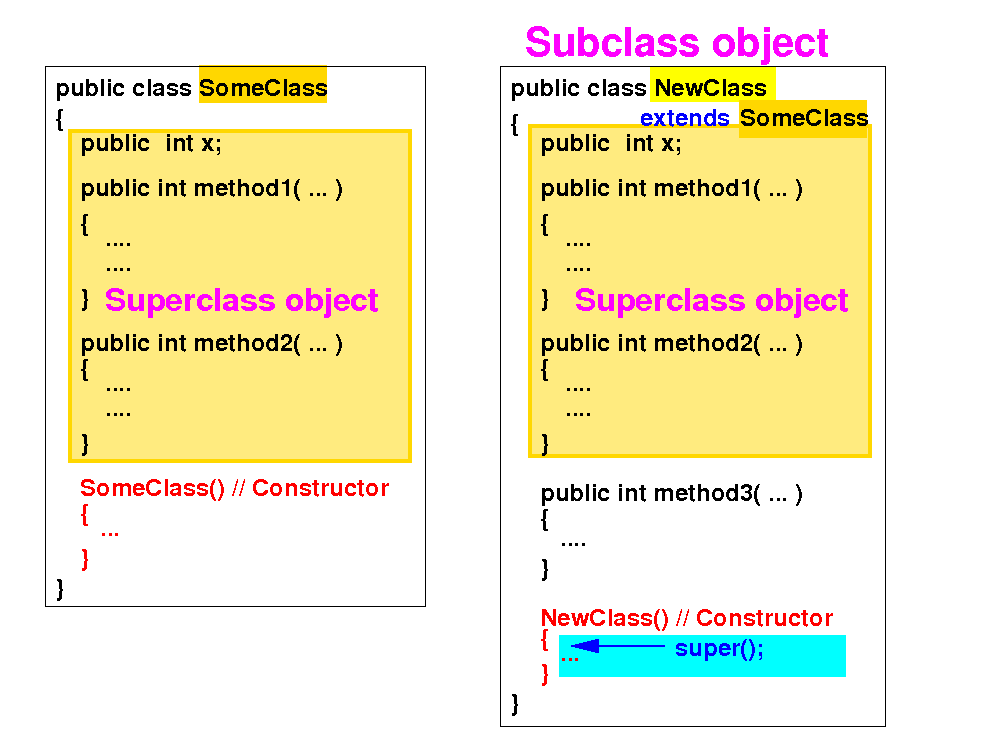
Then: the Java compiler will automatically insert the call super( ) as the first statement
|
|
|
Example that shows that the GeometricObject class inherited the toString() method from the Object class
public class GeometricObject
{
private String color;
GeometricObject( String col )
{
color = col;
}
public String getColor()
{
return color;
}
public double getArea() // Dummy method
{
return 0; // Some default value
}
// No "toString()" method defined !
}
|
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GeometricObject a =
new GeometricObject("red");
// We can call the toString() method
// using a GeometricObject object
System.out.println( a.toString( ) );
}
}
|
Example that shows that the Circle class also inherited the toString() method from the Object class
public class Circle extends GeometricObject { private double radius; Circle(String col, double r) { super(col); radius = r; } public double getRadius() { return radius; } public double getArea() { return 3.14159*radius*radius; } // No "toString()" method defined ! } |
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Circle a = new Circle("red", 2.0);
// We can call the toString() method
// using a Circle object
System.out.println( a.toString( ) );
}
}
|
We can override the inherited toString() method to print out an object in a more suitable format:
public class Circle extends GeometricObject { private double radius; Circle(String col, double r) { super(col); radius = r; } ... // Override the "toString()" method public String toString() { return "Color = " + getColor() + " : " + "radius = " + radius; } } |
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Circle a = new Circle("red", 2.0);
// We can call the toString() method
// using a Circle object
System.out.println( a.toString( ) );
}
}
|
|