Review:
caveat when using
ArrayList
- The ArrayList
must
be used with
an
class (= reference type)
I.e.:
- An ArrayList
cannot be used to
store data of
a
primitive
data type
(such as
int,
double, etc)
|
- This program will
generate a
compile error:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<int> myList = new ArrayList<>(); // Compile error
}
}
|
- We can solve this
problem
with classes that
contain a variable
of a primitive type
(a.k.a.: a
"wrapper" class)
|
Making
a
int
primitive data type variable
into an
object
- We can
"package"
an
int
primitive
data types
variable
into an
object
as follows:
public class IntegerObj // A "wrapper" class
{
public int value; // contains a variable of some primitive type
// Constructor
public IntegerObj(int x)
{
value = x;
}
}
|
- Now we can
create
int
objects:
IntegerObj a = new IntegerObj(4);
System.out.println( a.value );
|
|
DEMO:
demo/12-wrapper/01-intro/Demo1.java
+
IntegerObj.java
ArrayList with
"packaged"
primitive data types
- We can
use the
IntegerObj
class
to create an
ArrayList of
"integers":
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Demo2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<IntegerObj> myList = new ArrayList<>();
myList.add( new IntegerObj(7) );
myList.add( new IntegerObj(4) );
myList.add( new IntegerObj(9) );
System.out.println( myList );
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/12-wrapper/01-intro/Demo2.java
+
IntegerObj.java
Wrapper classes
- Because
Java has
many
library classes that
only
works with
reference types
(and
do not
work with
primitive
data types):
- The
Wrapper classes
in Java are:
Primitive Data Type Corresponding Wrapper Class
============================================
byte Byte
short Short
int Integer
long Long
float Float
double Double
boolean Boolean
char Character
|
|
Example using a
Wrapper class
Integer
- The
wrapper class for
the primitive type
int
is:
- We can
create an
ArrayList object that
store
int values
using the
wrapper class
Integer:
public class IntegerWrapper
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<Integer> myList = new ArrayList<>();
myList.add( new Integer(7) );
myList.add( new Integer(4) );
myList.add( new Integer(9) );
System.out.println( myList );
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/12-wrapper/01-intro/IntegerWrapper.java
Another
example
using a Wrapper class
Double
- If you want to
store
double typed
values
in an
ArrayList object, then
you can use the
Double
wrapper class:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<Double> myList = new ArrayList<>();
myList.add( new Double(7.0) );
myList.add( new Double(4.0) );
myList.add( new Double(9.0) );
System.out.println( myList );
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/12-wrapper/01-intro/DoubleWrapper.java
Other
things
defined inside
wrapper classes
- In addition to the
primitive type
variable,
wrapper classes
also contain:
-
Maximum
and
Minimum
range
constants
- These constants denote
the largest and the
smallest value that
a variable of this
primitive type can
store
|
-
Constructors
- Used to initialize the
primitive type
variable
|
-
Accessor
methods
- These methods will
return the
value of the
primitive
variable
in the wrapper class
object
|
-
Conversion
methods
- These methods
convert
a
number string
to
the primitive type
representation and
vice versa
|
|
|
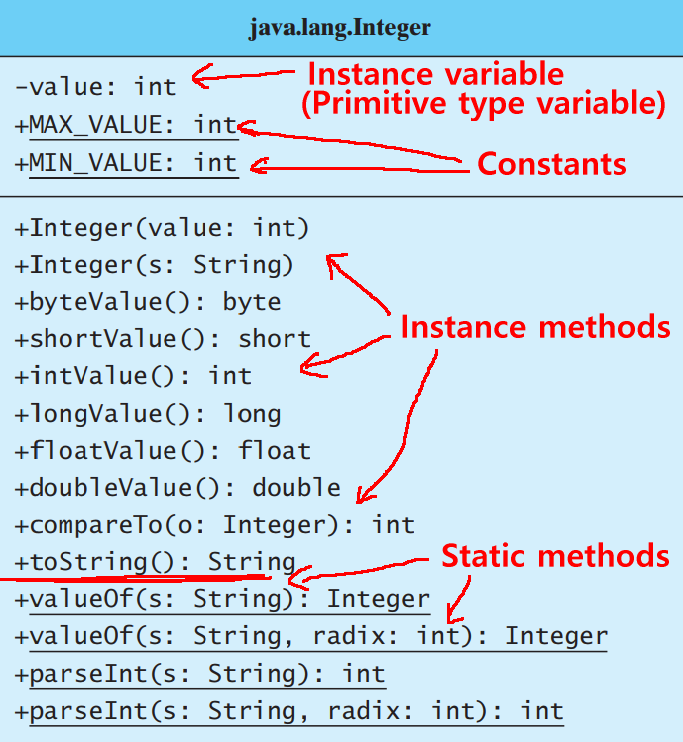
Other
things
defined inside
wrapper classes:
Integer
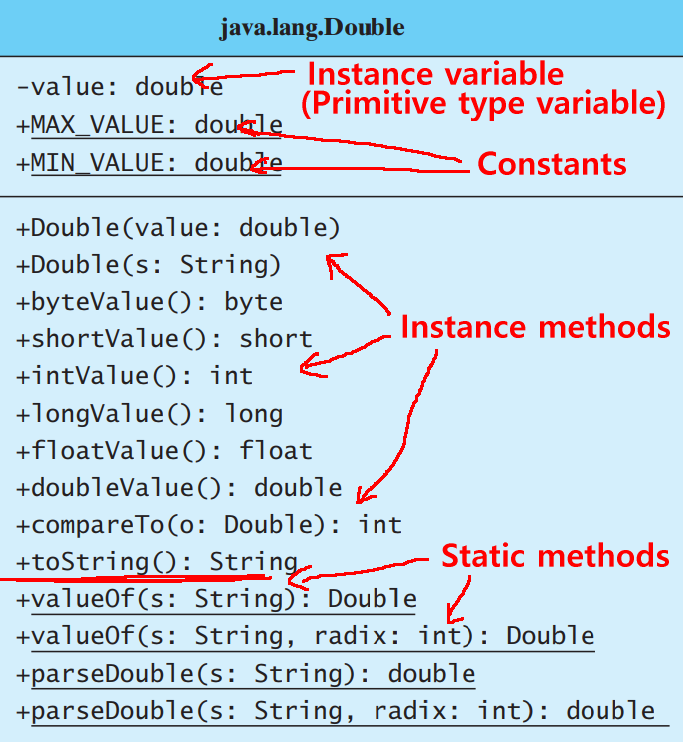
Other
things
defined inside
wrapper classes:
Double
The
MAX_VALUE
and
MIN_VALUE
range constants
in a wrapper class
DEMO:
demo/12-wrapper/01-intro/RangeConstants.java
The
constructors
in wrapper classes
DEMO:
demo/12-wrapper/01-intro/Constructors.java
The
accessor method
in wrapper classes
DEMO:
demo/12-wrapper/01-intro/Accessor.java
The
String
conversion method
in wrapper classes
Important fact:
wrapper class objects are
immutable
-
Wrapper class
objects are
immutable
Because:
a wrapper class does
not
contain any
mutator methods:
The
instance variable (value)
is private,
therefore, it
cannot be
updated !!!
|
❮
❯