The
ArrayList
class
in the Java library
-
Recall that:
the
size of
an array is
fixed after
it has been created
- One
of the most useful
classes
in the Java library is:
- The
java.util.ArrayList
class
implements
a
variable (= "adjustable") length
array:
|
How to create an
ArrayList
object
- The
official
way to
create an
ArrayList object
is as
follows:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<ObjectType> varName = new ArrayList<ObjectType>();
...
|
- Example:
create an ArrayList of
String
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> varName = new ArrayList<String>();
...
|
|
The short-hand form to create an
ArrayList
object
- The
short-hand
form to
create an
ArrayList object
is as
follows:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<ObjectType> varName = new ArrayList< >(); // empty
...
|
- Example:
shorter form to
create an ArrayList of
String
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class myProg
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> varName = new ArrayList<>(); // Shorter form
...
|
|
DEMO:
demo/11-arrayList/01-intro/Demo.java
What
is inside an
ArrayList object
An
ArrayList
object
contains:
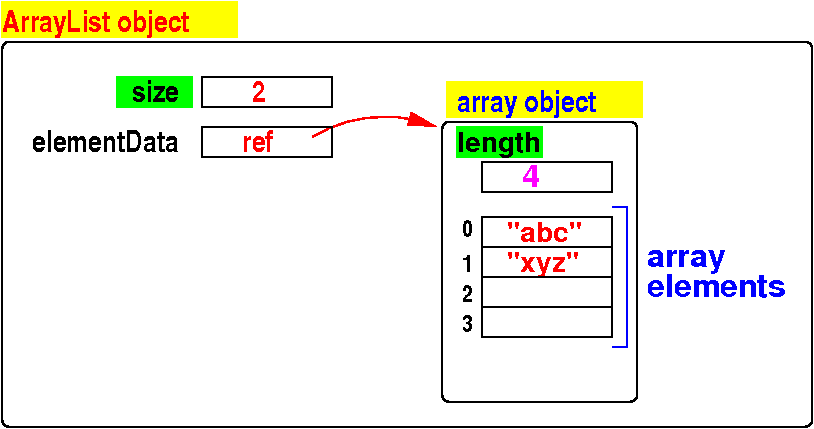
-
size =
number of
elements this is
currently
stored in
the ArrayList object
- elementData that
points to
an
array object that stores
the elements
- The array object
contains
a
length
variable which is the
length of the
array
- The array object
also
contains an
array to
store the data
This array is
not completely
filled
(the number of
slot used is
size)
|
|
DEMO:
demo/11-arrayList/01-intro/Demo2.java
These instance methods of
ArrayList are used to
(1) insert,
(2) look up,
(3) update and
(4) remove
elements in an ArrayList
object:
Note: E can be any reference type (i.e.: not a primitive data type)
add(E e):
Appends the element e to the end of this ArrayList.
add(int index, E e)
Inserts the element e at position index in this ArrayList.
get(int index):
Returns the element e at the position index in this list.
set(int index, int newValue):
Replace the element at position index in this ArrayList with newValue
Returns the old element e
remove(int index):
Removes the element at the position index from this list.
remove(E e):
Removes the first occurrence of the element e from this list.
|
These instance methods of
ArrayList are used to
search for
a specific
element
e
in an ArrayList
object:
Note: E can be any reference type (i.e.: not a primitive data type)
contains(E e):
Returns true if e is found in this list
Returns false otherwise
indexOf(E e):
Returns the index of the first occurrence of element e in this list
Returns -1 when not found
lastIndexOf(E e):
Returns the index of the last occurrence of element e in this list
Returns -1 when not found
|
These instance methods of
ArrayList are used to
(1) find information and
(2) reset
an
ArrayList
object:
size():
Returns the number of elements in this list.
isEmpty():
Returns true if this list contains no elements.
Otherwise return false
clear():
Removes all of the elements from this list.
(I.e.: the ArrayList will be empty)
|
In the next couple of
slides, we will study
examples that
show you
how to
use
these (instance) methods
❮
❯
