Review:
reference
data types and
objects
- Reference
data type:
- All
classes are
reference
data types
|
Example:
Circle is a reference data type
|
- Reference
variables:
- Variables
defined with a
reference
data type
are reference variables.
- Reference variable
(always)
stores an
address of an
object
|
Example:
Circle circle1; // circle1 is a reference variable
// I.e.: circle1 stores an address of a Circle object
|
|
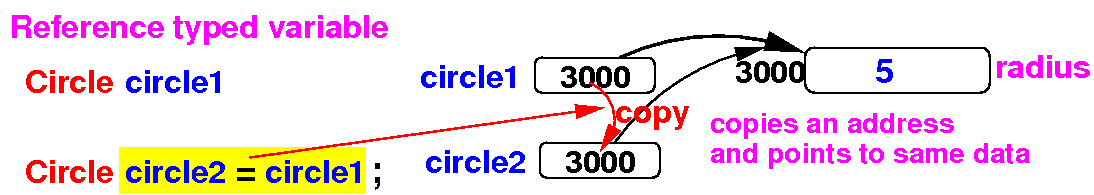
Review:
how
reference
data types and
objects
are stored in memory
Reference variables
and objects are
stored as follows:
Circle is a class or a reference data type
circle1 is a reference variable (stores an address)
circle1 references (points to) a Circle object
|
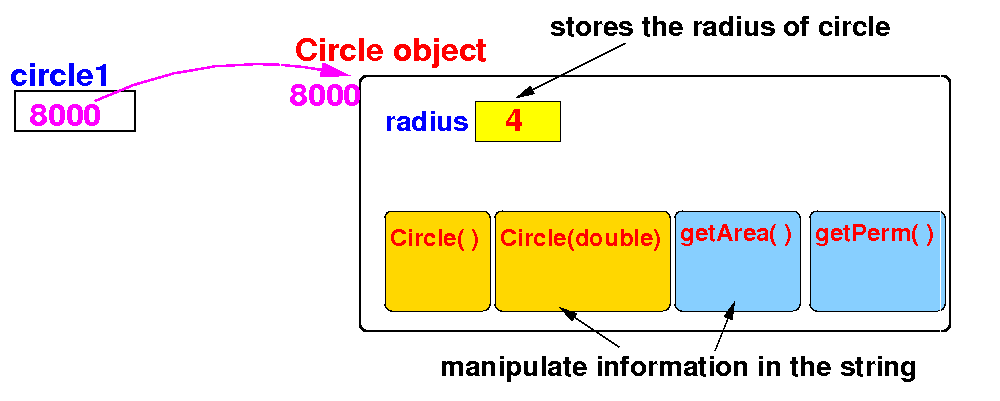
Accesing
members of an object
- the
member access operator
(.)
- An object's
member
can refer to:
- A
data field in
the object
or
- A
method in
the object
|
- After an
object has been
instantiated,
its data fields can be
accessed
and its
methods
can be invoked
using the
dot operator (.):
objectRefVar.dataField accesses a data field in the object
objectRefVar.method(arguments) invokes a method on the object
|
Example:
circle1.radius
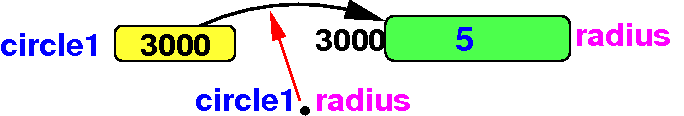
- The
dot (.) operator is
also known as the
object member access
operator
|
Accessing
members of an object
-
Example
public static void main()
{
Circle circle1 = new Circle(); // Create a Circle object circle1
Circle circle2 = new Circle(2); // Create a Circle object circle2
circle1.radius = 10; // Access the radius in circle1 object
circle2.radius = 99; // Access the radius in circle2 object
double area1 = circle1.getArea(); // Invoke getArea() method on circle1
double area2 = circle2.getArea(); // Invoke getArea() method on circle2
}
|
DEMO:
demo/10-classes/06-access-members
Terminology:
instance method
- The method
getArea( )
is invoked
as an operation
on a
specific instance of
Circle objects.
- The method
getArea( )
is referred to
as an
instance method,
because you invoke it only
on a
specific instance.
|
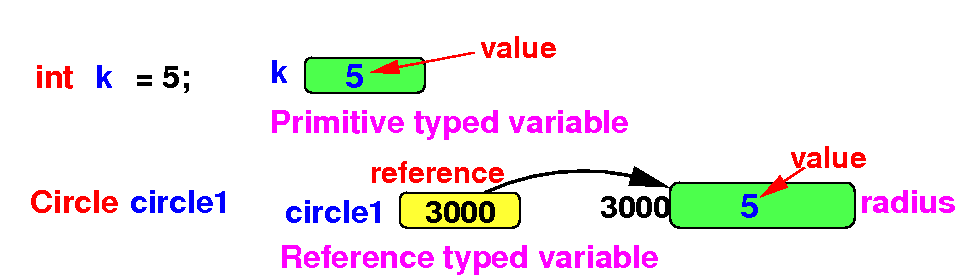
Reference type
variables and
primitive type
variables
are stored
differently
- All variables consist
of memory cells that
store a
value (binary number)
- However:
how the
number is
used can
be different !
|
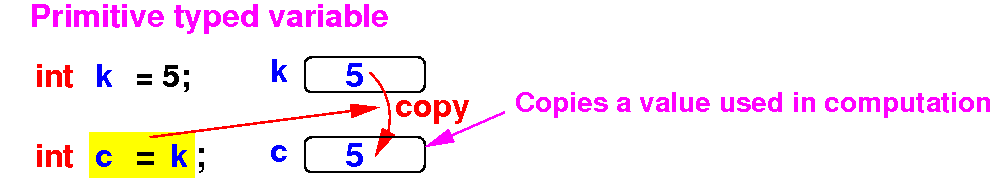
- A variable of
a
primitive type
stores the
value itself
- I.e.: the
number in
used in
computations
|
- A variable of
a
reference type
stores a
reference (= memory address)
of the location of
the
object
(= properties of the
object)
- I.e.: the number
is
used to
locate (= access) an
object (its properties)
|
Schematically:
|
An
important consequence
of the
difference ways of storing variables
DEMO:
demo/10-classes/07-aliasing/Demo.java
An
important consequence
of the
difference ways
of storing variables
DEMO:
demo/10-classes/07-aliasing/Demo.java
Why Java have
reference typed variables and
primitive typed variables
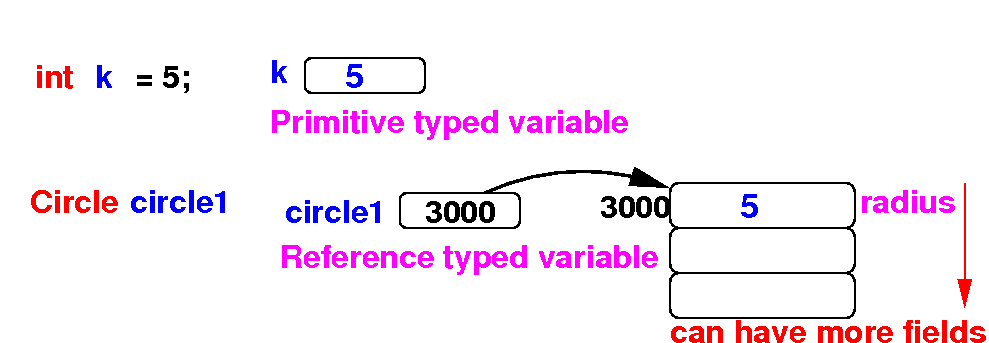
-
Variables
of a primitive data type can
only store
1 value but can
be accessed
quickly
- Such variables are
mainly used in
computations
|
-
Objects can have
many
data fields
and can allow the
programmer to
represent
complex things in the
real world
- Objects are
mainly used for
data representation
- Accessing to
data in an
object is
slower
(need 2 memory accesses)
|
|
❮
❯