Defining
2-dimensional arrays as
arguments to a method
|
Passing
2-dimensional arrays as
arguments to a method
|
DEMO: demo/09-multi-dim-array/04-array-argument/SumArray.java
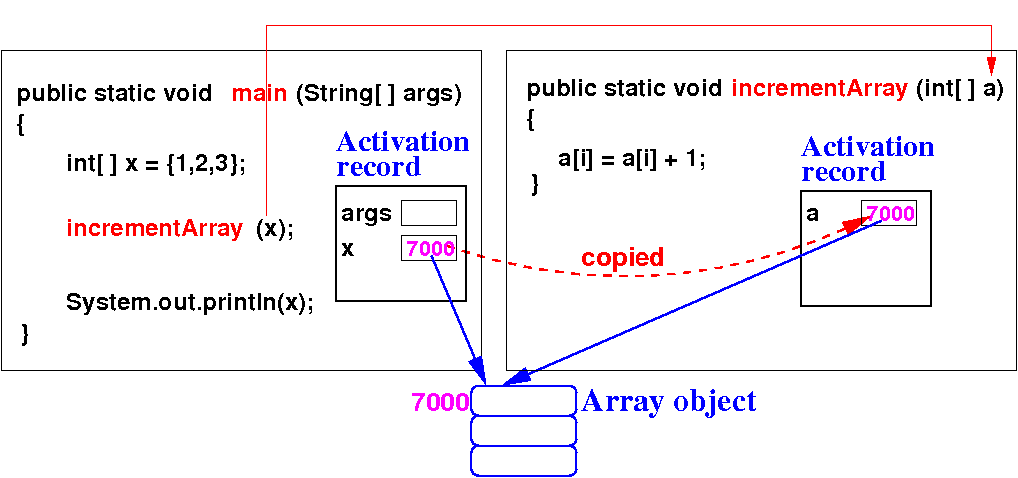
Remember:
Java passes
an array reference to a method
|
Review: In Java, a method can
update the
elements in an
array parameter
In Java, methods can change/update the elements in an array parameter:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] myGrid = { {1,2,3},
{4,5},
{6,7,8,9} };
increment(myGrid); // This method will update elements in myGrid
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(myGrid[0]) ); // [2,3,4] changed !
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(myGrid[1]) ); // [5,6] changed !
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(myGrid[2]) ); // [7,8,9,10] changed !
}
public static void increment(int[][] m)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m[i].length; j++)
m[i][j]++;;
}
|
DEMO: demo/09-multi-dim-array/04-array-argument/UpdateArray.java
Methods that
return a
2-dimensional array