Defining a
2-dimensional
array variables
in Java
DEMO:
demo/09-multi-dim-array/02-basics/Define2DimArray.java
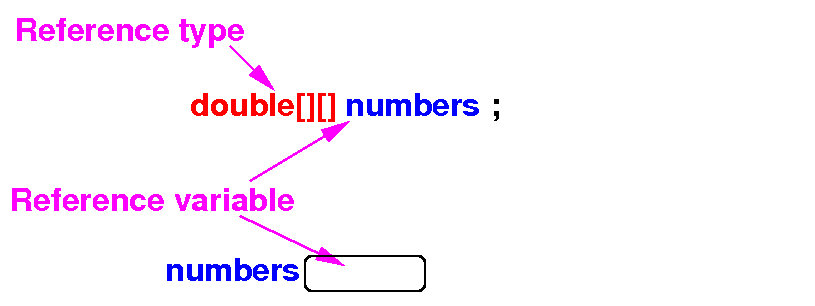
What happens when you
define a
2-dim array in
Java
The effect of the
execution of the
statements are
depicted in
diagrams below:
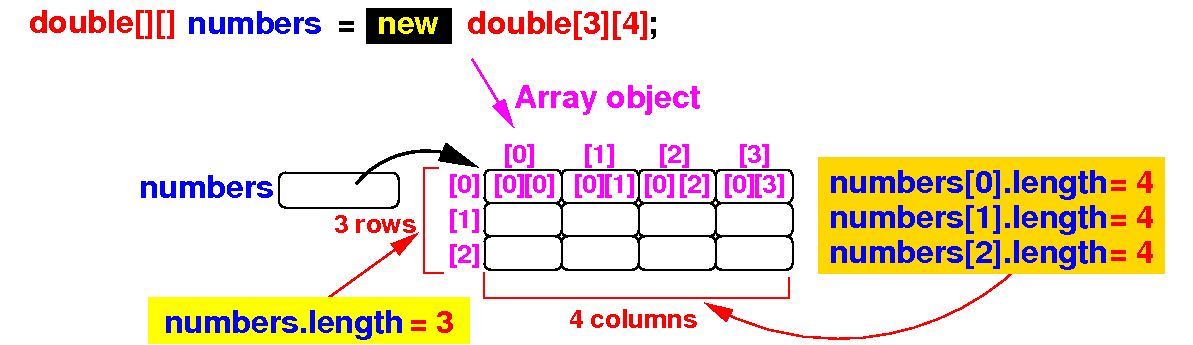
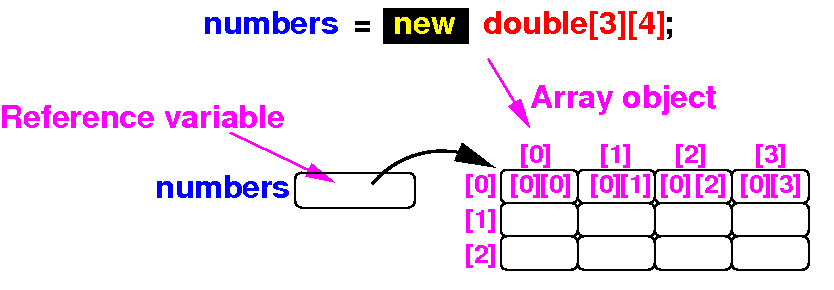
double[][] numbers; Result:
 numbers = new double[3][4];
Result:
numbers = new double[3][4];
Result:
|
Note:
the definition
double[][]
numbers
will define
one variable named
numbers
the type
double[][]
tells the Java compiler
how to
store
data in the
variable
Array variable definition
with
array instantiation
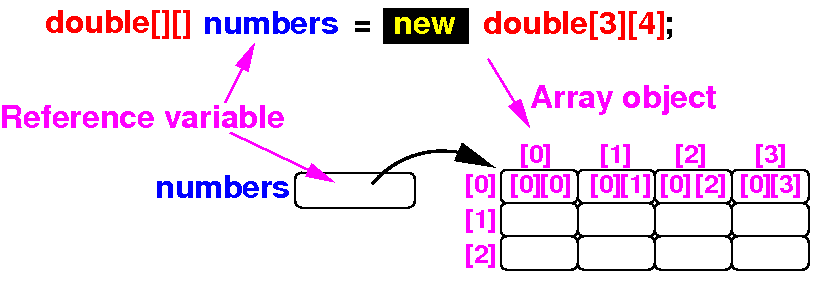
Instead of 2 separate steps:
double[] numbers;
numbers = new double[3][4];
We can also use this one step to define an instantialized array variable:
double[] numbers = new double[3][4];
Result:
|
Using a
2-dimensional
array
Using a
2-dimensional
array
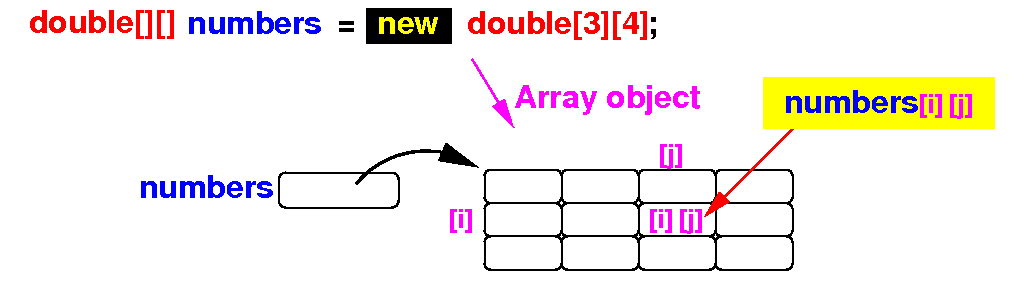
- An element in
a 2-dimensional array is
identified by
2 indexes
- The "row"
(= first) index
- The "column"
(= second) index
|
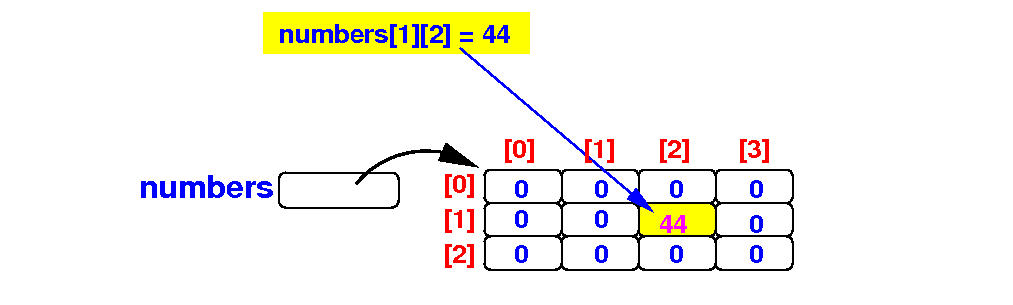
- To access the
element in
the
row i
and
column j,
use:
Schematically:
|
Using a
2-dimensional
array
example
DEMO:
demo/09-multi-dim-array/02-basics/Use2DimArray.java
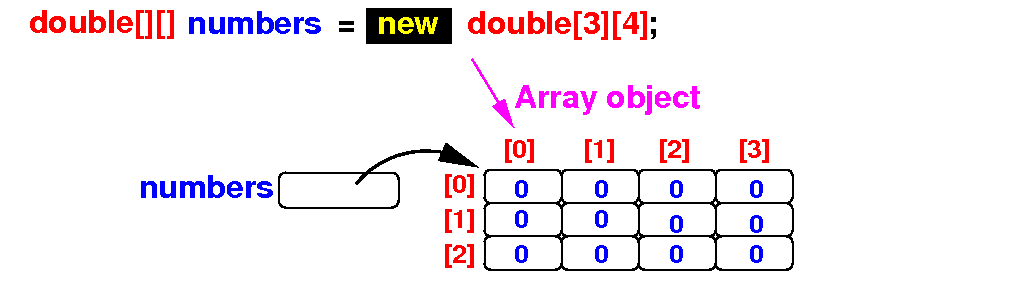
Default
initial values
and
array initializers
-
Default values:
- A array
created with the
new operator
are
initialized with
the
default value 0
or false
|
- Java
provides
array initializers to
defined an
initialized
2-dimensional array:
dataType[][] arrayRefVar = { {value00, value01, ..., value0M},
{value10, value11, ....... ., value1N},
... };
|
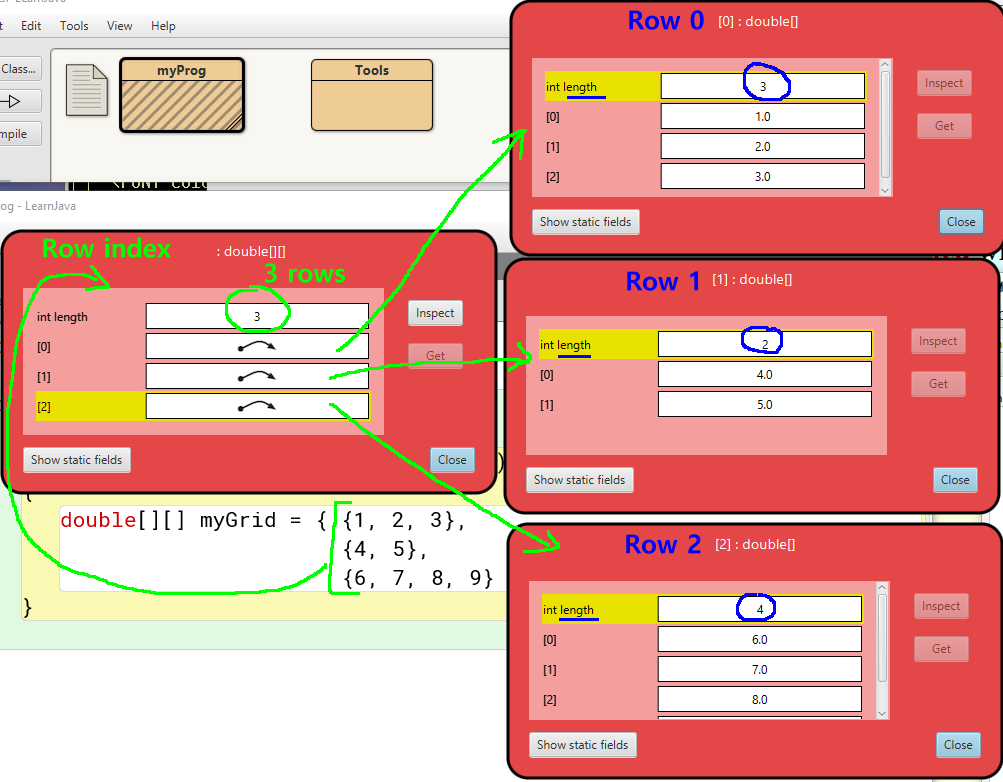
- Example: defining an
initialized
array
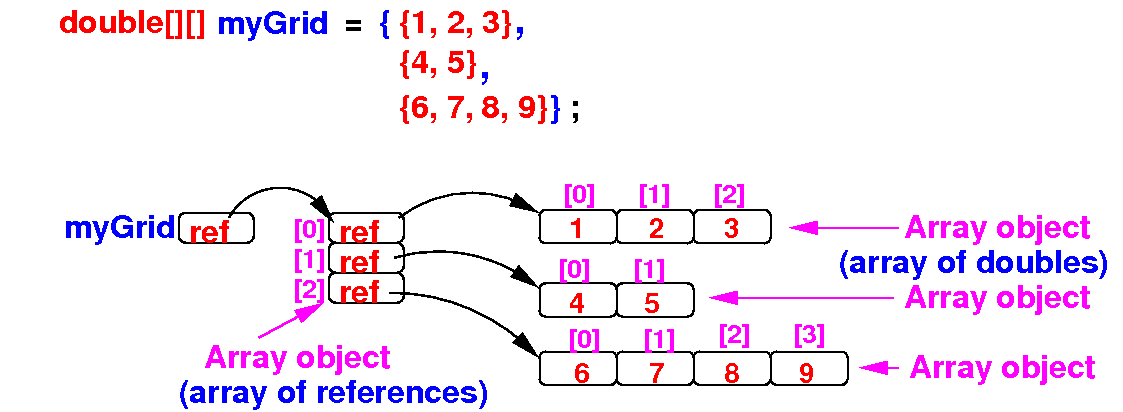
double[][] myGrid = { {1, 2, 3}, // Row 1 has 3 elements
{4, 5}, // Row 2 has 2 elements
{6, 7, 8, 9} }; // Row 3 has 4 elements
|
|
DEMO:
demo/09-multi-dim-array/02-basics/ArrayInit.java
Show with
Inspect
How Java stores
a 2-dimensional array
snapshot from BlueJ
How Java stores
a 2-dimensional array
- A 2-dimensional array in
Java is
stored as
follows:
- Java
2-dimensional arrays
have the following
properties:
- Each
row of
a 2-dimensional array is
an
independent
array
|
-
Therefore:
different rows in a
2-dimensional array can have
different lengths
- Arrays of
this kind
is known as a
ragged
array
(Most
programming languages have
rectangular
arrays)
|
❮
❯

 numbers =
numbers =