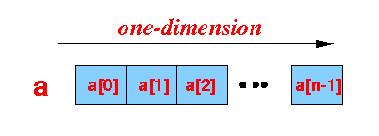
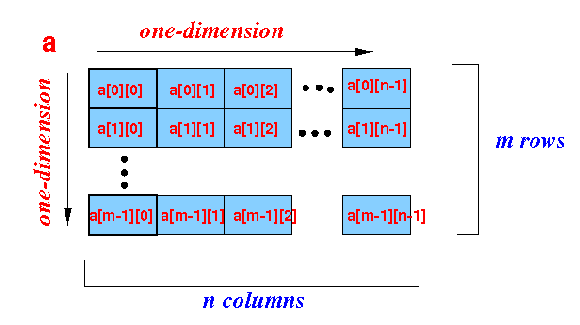
What is a
2-dimensional array ?
|
Using
multi-dimensional
arrays to
store data
|
Using
multi-dimensional
arrays to store data
|
Accessing
elements in a
multi-dimensional arrays
|
Using multi-dimensional arrays to store data
|
DEMO: demo/09-multi-dim-array/01-intro/Demo.java