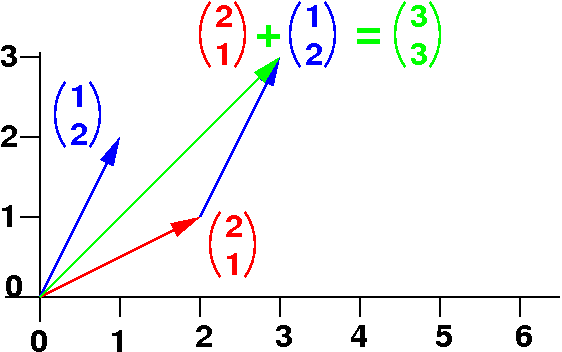
|
|
|
|
|
Vector operations are commonly provided as methods (because they are useful operations):
public static double[] vectorAdd( double[] vector1, double[] vector2)
{
double[] vector3 = new double[vector1.length];
for ( int i = 0; i < vector1.length; i++ )
vector3[i] = vector1[i] + vector2[i];
return vector3;
}
|
Let's write a vectorAdd( ) method that adds the input vectors and return the result
(1) create an output vector to store the result:
public static double[] vectorAdd( double[] vector1, double[] vector2)
{
double[] vector3 = new double[vector1.length];
for ( int i = 0; i < vector1.length; i++ )
vector3[i] = vector1[i] + vector2[i];
return vector3;
}
|
(2) add the input vectors and store the result in vector3:
public static double[] vectorAdd( double[] vector1, double[] vector2)
{
double[] vector3 = new double[vector1.length];
for ( int i = 0; i < vector1.length; i++ )
vector3[i] = vector1[i] + vector2[i];
return vector3;
}
|
(3) return the result vector vector3:
public static double[] vectorAdd( double[] vector1, double[] vector2)
{
double[] vector3 = new double[vector1.length];
for ( int i = 0; i < vector1.length; i++ )
vector3[i] = vector1[i] + vector2[i];
return vector3;
}
|
Demo program on next slide
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] v1 = {1,2,3};
double[] v2 = {1,1,1};
double[] v3;
v3 = vectorAdd(v1,v2);
System.out.println( Arrays.toString(v1) + " + " +
Arrays.toString(v2) + " = " +
Arrays.toString(v3) );
}
public static double[] vectorAdd( double[] vector1, double[] vector2)
{
double[] vector3 = new double[vector1.length];
for ( int i = 0; i < vector1.length; i++ )
vector3[i] = vector1[i] + vector2[i];
return vector3;
}
|
DEMO: demo/08-array/16-vectors/VectorAdd.java