|
|
|
|
|
Let's write this sorting algorithm:
public static void mergeSort(double[] a) // Not the actual mergeSort algorithm
{
int middle = a.length/2;
double[] left = new double[a.length/2]; // left half
double[] right = new double[a.length - a.length/2]; // right half
if ( a.length == 1 )
return; // No need to sort an array of 1 element...
// Split: a[0 ..... middle-1] a[middle .... a.length-1]
// left[0 .. middle-1] right[0 ... a.length-1-middle]
for ( int i = 0; i < middle; i++ )
left[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length-middle; i++ )
right[i] = a[i+middle];
// Sort both halves - you can any sort algorithm !
BubbleSort.sort( left );
BubbleSort.sort( right );
/* Merge both sorted arrays
merge( a, left, right ); // We have discussed merge() already...
}
|
Define 2 arrays to store the left half and the right half of the input array:
public static void mergeSort(double[] a) // Not the actual mergeSort algorithm
{
int middle = a.length/2;
double[] left = new double[a.length/2]; // left half
double[] right = new double[a.length - a.length/2]; // right half
// Define variables to split input array into 2 halves
if ( a.length == 1 )
return; // No need to sort an array of 1 element...
// Split: a[0 ..... middle-1] a[middle .... a.length-1]
// left[0 .. middle-1] right[0 ... a.length-1-middle]
for ( int i = 0; i < middle; i++ )
left[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length-middle; i++ )
right[i] = a[i+middle];
// Sort both halves - you can any sort algorithm !
BubbleSort.sort( left );
BubbleSort.sort( right );
/* Merge both sorted arrays
merge( a, left, right ); // We have discussed merge() already...
}
|
If the input array only contains 1 element, we do not need to sort it (because it's already sorted):
public static void mergeSort(double[] a) // Not the actual mergeSort algorithm
{
int middle = a.length/2;
double[] left = new double[a.length/2]; // left half
double[] right = new double[a.length - a.length/2]; // right half
if ( a.length == 1 ) // Base case
return; // No need to sort an array of 1 element...
// Split: a[0 ..... middle-1] a[middle .... a.length-1]
// left[0 .. middle-1] right[0 ... a.length-1-middle]
for ( int i = 0; i < middle; i++ )
left[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length-middle; i++ )
right[i] = a[i+middle];
// Sort both halves - you can any sort algorithm !
BubbleSort.sort( left );
BubbleSort.sort( right );
/* Merge both sorted arrays
merge( a, left, right ); // We have discussed merge() already...
}
|
For arrays with > 1 element, we split the input array into 2 equal halves:
public static void mergeSort(double[] a) // Not the actual mergeSort algorithm
{
int middle = a.length/2;
double[] left = new double[a.length/2]; // left half
double[] right = new double[a.length - a.length/2]; // right half
if ( a.length == 1 ) // Base case
return; // No need to sort an array of 1 element...
// Split: a[0 ..... middle-1] a[middle .... a.length-1]
// as: left[0 .. middle-1] right[0 ... a.length-1-middle]
for ( int i = 0; i < middle; i++ )
left[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length-middle; i++ )
right[i] = a[i+middle];
// Sort both halves - you can any sort algorithm !
BubbleSort.sort( left );
BubbleSort.sort( right );
/* Merge both sorted arrays
merge( a, left, right ); // We have discussed merge() already...
}
|
We sort both halves of the arrays -- we use insertionSort( ), but any sort method can be used:
public static void mergeSort(double[] a) // Not the actual mergeSort algorithm
{
int middle = a.length/2;
double[] left = new double[a.length/2]; // left half
double[] right = new double[a.length - a.length/2]; // right half
if ( a.length == 1 ) // Base case
return; // No need to sort an array of 1 element...
// Split: a[0 ..... middle-1] a[middle .... a.length-1]
// as: left[0 .. middle-1] right[0 ... a.length-1-middle]
for ( int i = 0; i < middle; i++ )
left[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length-middle; i++ )
right[i] = a[i+middle];
// Sort both halves - you can use any sort algorithm !
insertionSort( left );
insertionSort( right );
/* Merge both sorted arrays
merge( a, left, right ); // We have discussed merge() already...
}
|
Finally, we use the merge( ) method to merge the 2 sorted array to obtain one sorted output array:
public static void mergeSort(double[] a) // Not the actual mergeSort algorithm
{
int middle = a.length/2;
double[] left = new double[a.length/2]; // left half
double[] right = new double[a.length - a.length/2]; // right half
if ( a.length == 1 ) // Base case
return; // No need to sort an array of 1 element...
// Split: a[0 ..... middle-1] a[middle .... a.length-1]
// as: left[0 .. middle-1] right[0 ... a.length-1-middle]
for ( int i = 0; i < middle; i++ )
left[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length-middle; i++ )
right[i] = a[i+middle];
// Sort both halves - you can use any sort algorithm !
insertionSort( left );
insertionSort( right );
// Merge both sorted arrays
merge( a, left, right ); // We have discussed merge() already...
}
|
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {5.6, 7.8, 2.4, 3.3};
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++)
System.out.print( myList[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
mergeSort( myList );
for (int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++)
System.out.print( myList[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
|
DEMO: demo/08-array/12-sorting/PreMergeSort.java
Note: the merge( ) and insertionSort( ) methods have been discussed previously and must be included in the program
public static void mergeSort(double[] a) // Not the actual mergeSort algorithm
{
int middle = a.length/2;
double[] left = new double[a.length/2]; // left half
double[] right = new double[a.length - a.length/2]; // right half
if ( a.length == 1 ) // Base case
return; // No need to sort an array of 1 element...
// Split: a[0 ..... middle-1] a[middle .... a.length-1]
// as: left[0 .. middle-1] right[0 ... a.length-1-middle]
for ( int i = 0; i < middle; i++ )
left[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length-middle; i++ )
right[i] = a[i+middle];
// Sort both halves - we can use any sort algorithm here:
insertionSort( left ); // I used insertionSort( ) to make it simple
insertionSort( right ); // to explain what we want to achieve
// Merge both sorted arrays
merge( a, left, right ); // We have discussed merge() already...
}
|
public static void mergeSort(double[] a) // The actual mergeSort algorithm
{
int middle = a.length/2;
double[] left = new double[a.length/2]; // left half
double[] right = new double[a.length - a.length/2]; // right half
if ( a.length == 1 ) // Base case
return; // No need to sort an array of 1 element...
// Split: a[0 ..... middle-1] a[middle .... a.length-1]
// as: left[0 .. middle-1] right[0 ... a.length-1-middle]
for ( int i = 0; i < middle; i++ )
left[i] = a[i];
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length-middle; i++ )
right[i] = a[i+middle];
// Sort both halves - the mergeSort algorithm is recursive !
mergeSort( left ); // We use mergeSort itself here !
mergeSort( right ); // We use mergeSort again here !
// Merge both sorted arrays
merge( a, left, right ); // We have discussed merge() already...
}
|
DEMO: demo/08-array/12-sorting/MergeSort.java
Consider the mergeSort( ) algorithm on the following input:

mergeSort(A[0-7]) |
mergeSort( ) first split the input array into 2 halves:
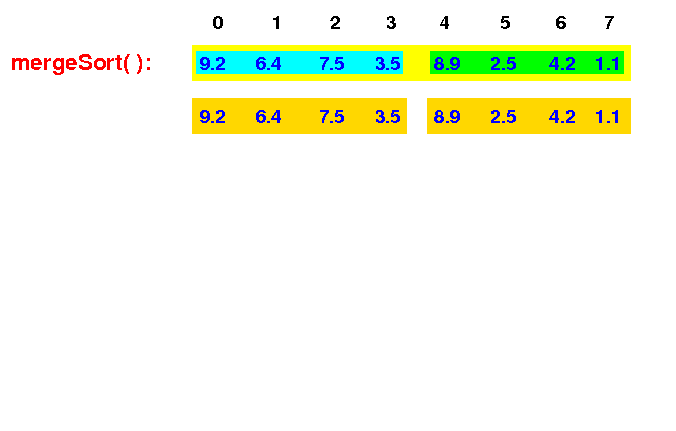
mergeSort(A[0-7]) |
mergeSort( ) then recurses and sort the first half:
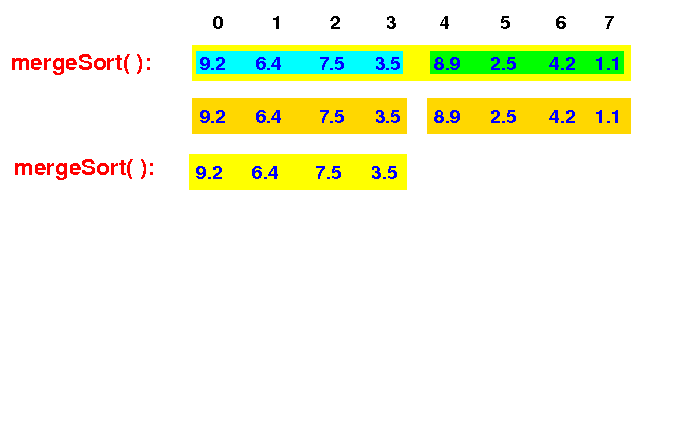
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) |
The new mergeSort( ) first split the input array into 2 halves:
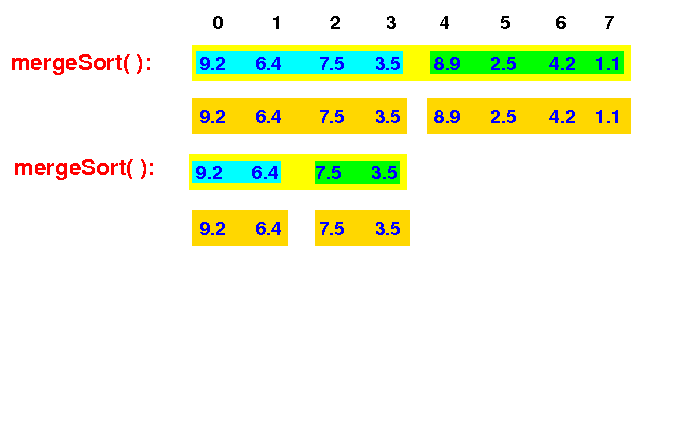
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) |
This mergeSort( ) then recurses and sort the first half:
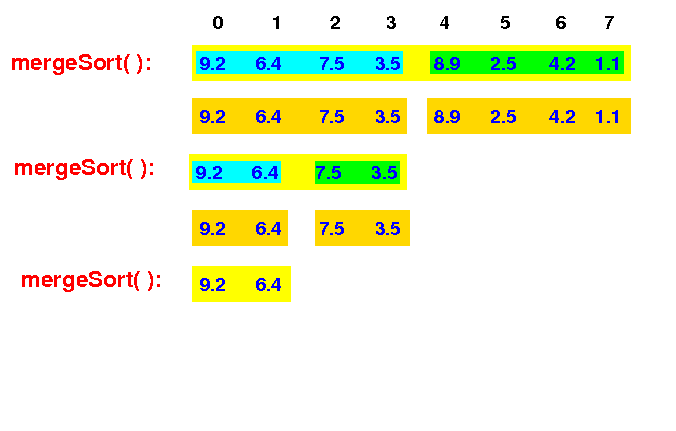
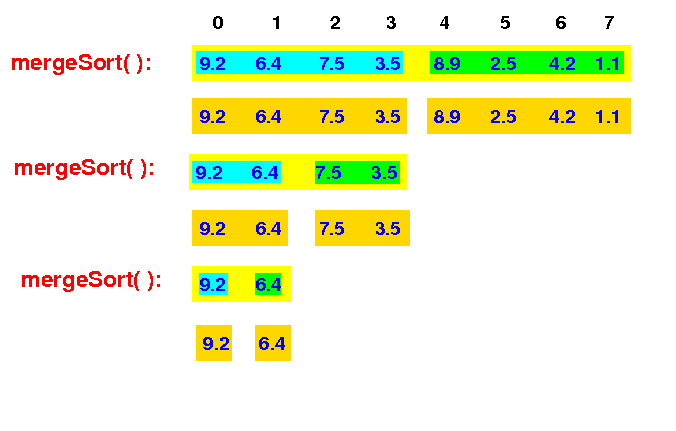
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) --> mergeSort(A[0-1]) |
The new mergeSort( ) first split the input array into 2 halves:
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) --> mergeSort(A[0-1]) |
This mergeSort( ) then recurses and sort the first half:
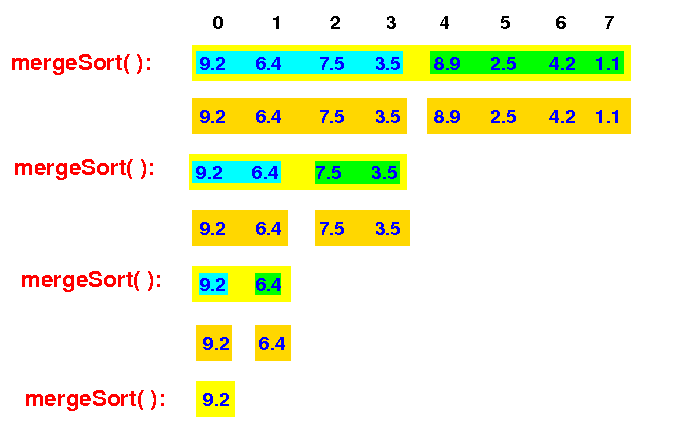
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) --> mergeSort(A[0-1]) --> mergeSort(A[0-0])
|
The input array consists of 1 element (= base case) and mergeSort( ) returns
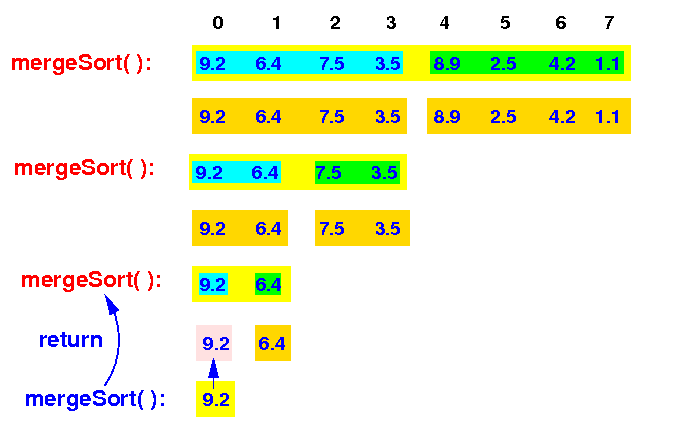
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) --> mergeSort(A[0-1]) <== |
The mergeSort( ) then recurses and sort the 2nd half:
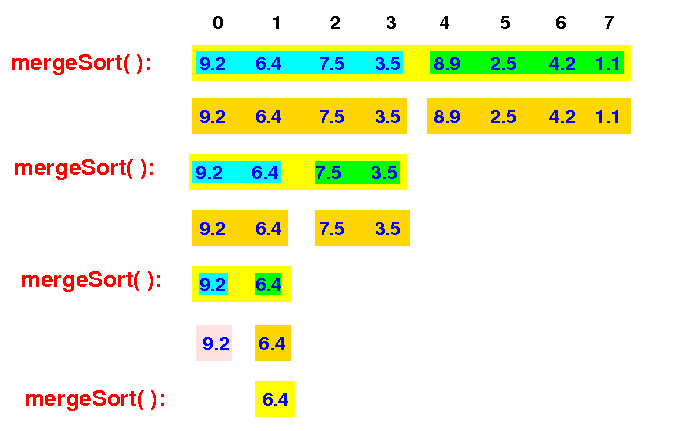
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) --> mergeSort(A[0-1]) --> mergeSort(A[1-1])
|
The input array consists of 1 element (= base case) and mergeSort( ) returns
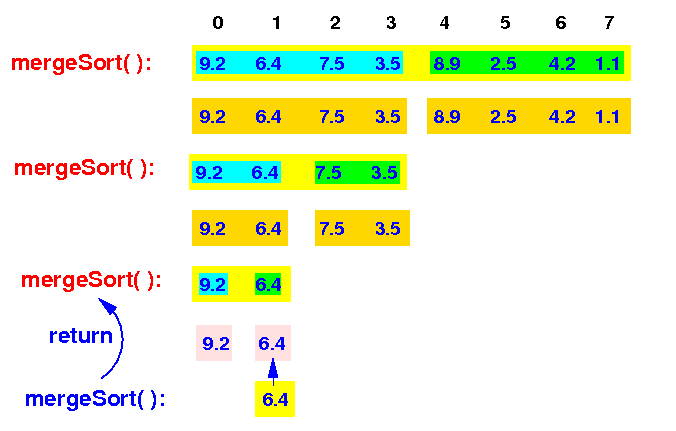
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) --> mergeSort(A[0-1]) <== |
Merge sort will finally merge the 2 sorted arrays and return to the previous mergeSort( ):
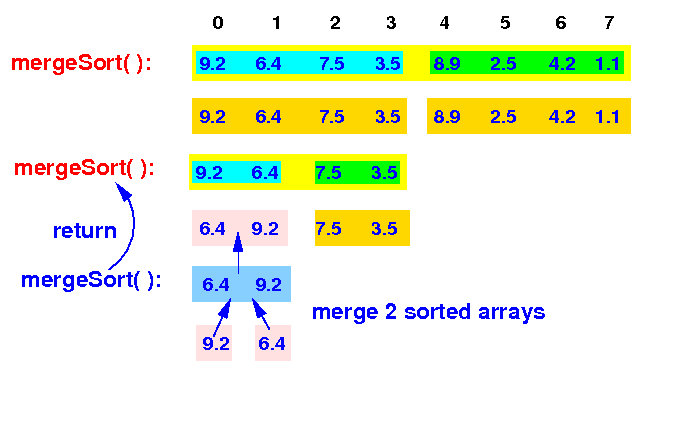
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) <== |
This mergeSort( ) then recurses and sort the 2nd half:
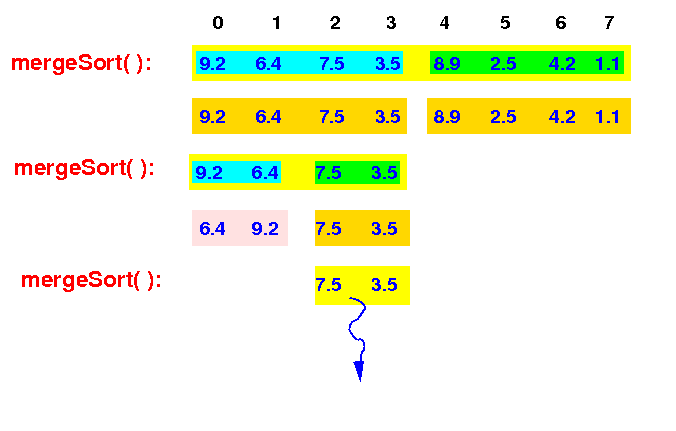
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) --> mergeSort(A[2-3]) |
The new mergeSort( ) will repeat the previously shown steps (omitted) - the result is sorting the input array:
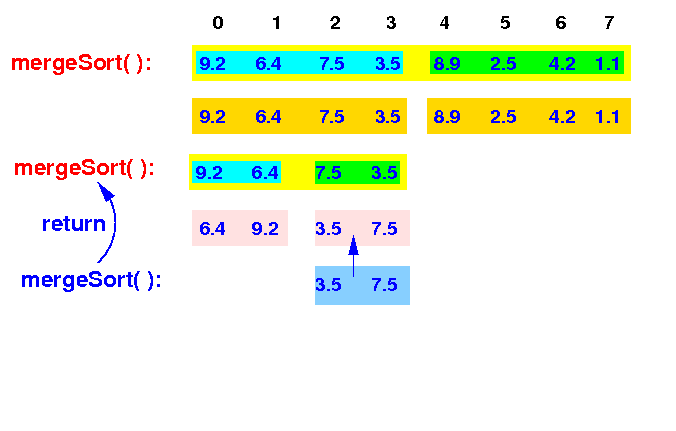
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]) <== |
The 2nd level mergeSort( ) will merge the 2 sorted arrays and ...
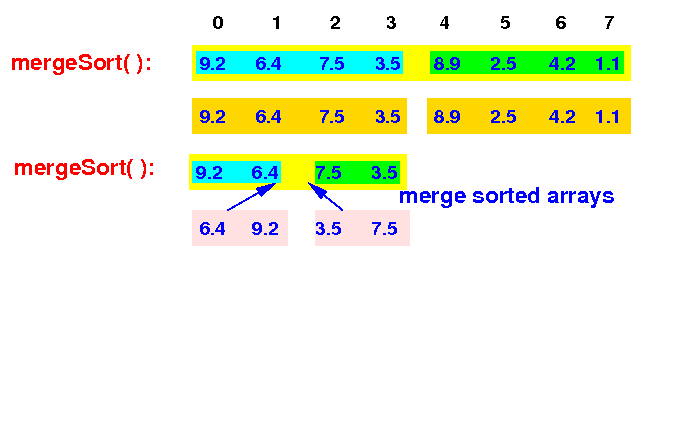
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[0-3]): merge(A[0-1], A[2-3]) |
The 2nd level mergeSort( ) will merge the 2 sorted arrays and return to the top level mergeSort( ):
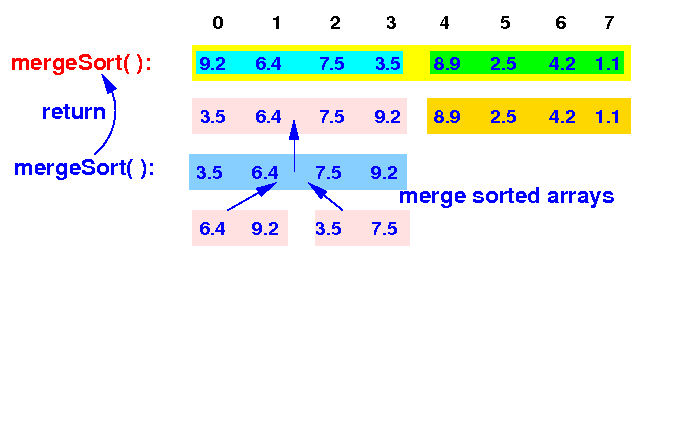
mergeSort(A[0-7]) <== |
The top level mergeSort( ) then recurses and sort the 2nd half:
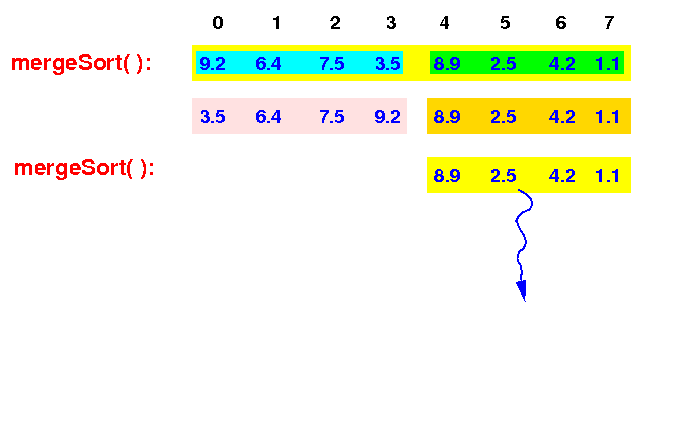
mergeSort(A[0-7]) --> mergeSort(A[4-7]) |
The new mergeSort( ) will repeat the previously shown steps ( omitted) - the result is sorting the input array:
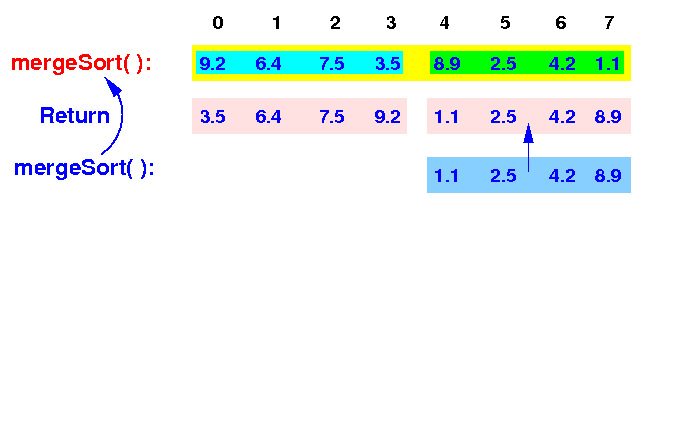
mergeSort(A[0-7]) <== |
Finally, the top level mergeSort( ) will merge the sorted arrays:
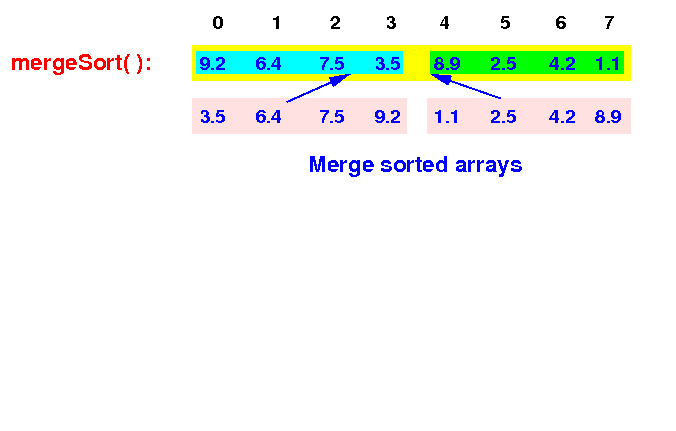
mergeSort(A[0-7]): merge(A[0-3], A[4-7]) |
Final result:
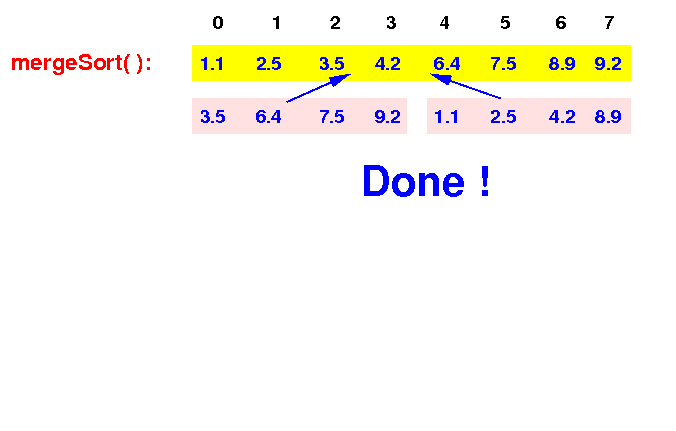
mergeSort(A[0-7]): return (array is sorted !) |