|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
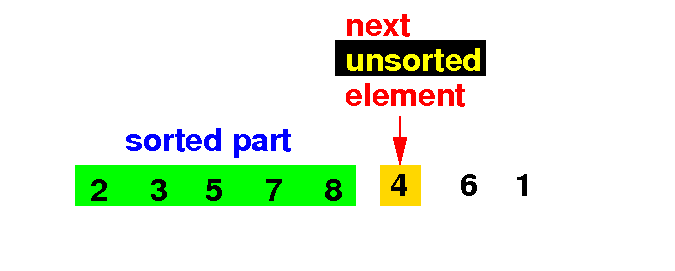
We now write the Insertion Sort algorithm in Java:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
|
We start the for-loop with i = 1 because: a list with one element (list[0]) is always sorted:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++) // Go through all unsorted elements
{
// A list with 1 element is always sorted
// So: list[0] is sorted
// Therefore: the first unsorted element is list[ 1 ]
Task to be performed by the loop-body:
insert list[i] into the sorted sublist list[0..i-1]
Result: list[0..i] will become sorted.
|
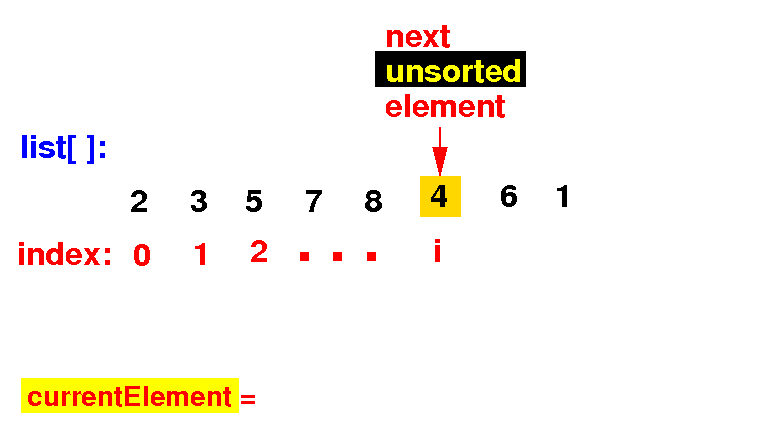
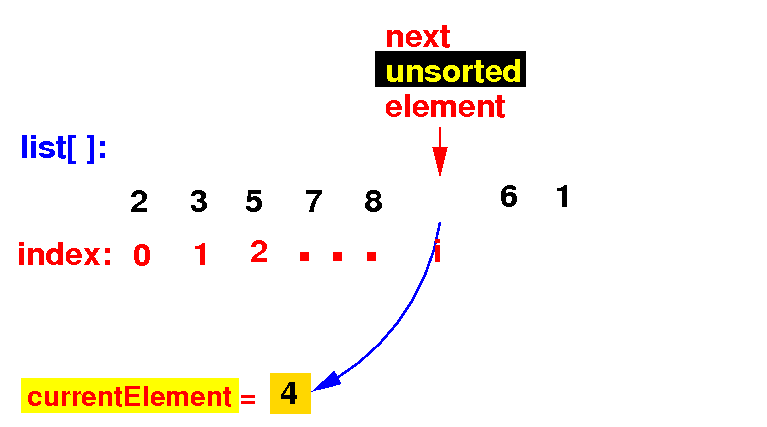
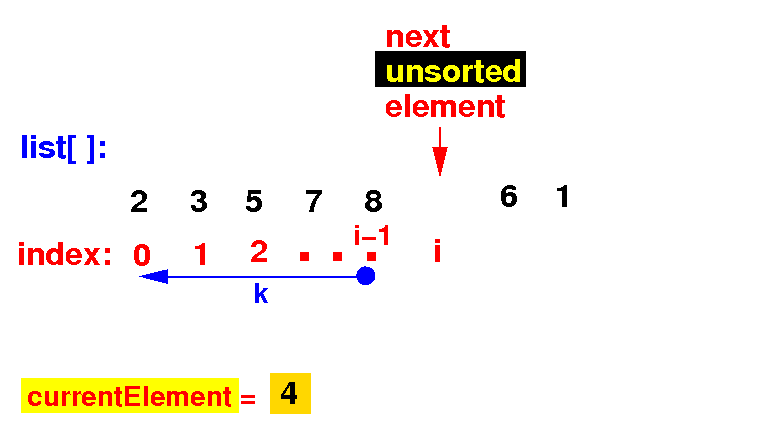
(1) Save the next unsorted element list[i] in currentElement (and position i in the array is open):
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++) // Go through all unsorted elements
{
double currentElement = list[i]; // Save list[i] in currentElement
|
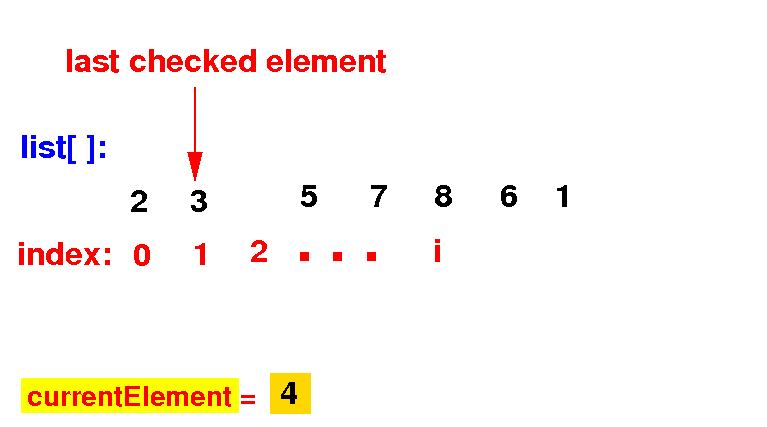
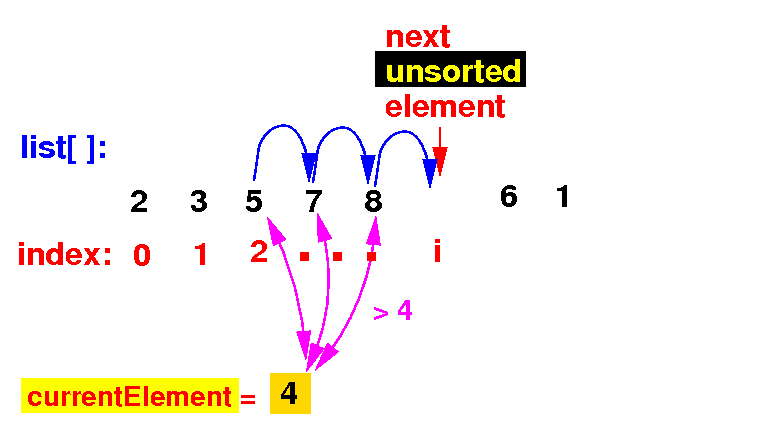
(2a) Find the correct position of currentElement by examining all element to its left:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++) // Go through all unsorted elements
{
double currentElement = list[i]; // Save list[i] in currentElement
// Find the correct position of currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
|
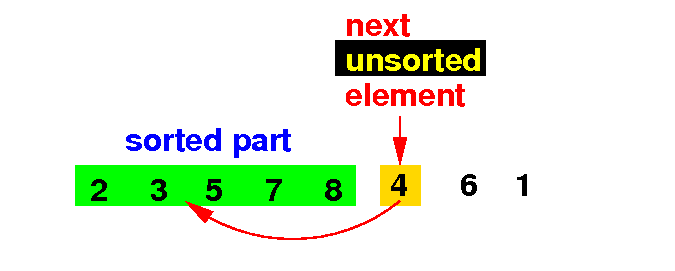
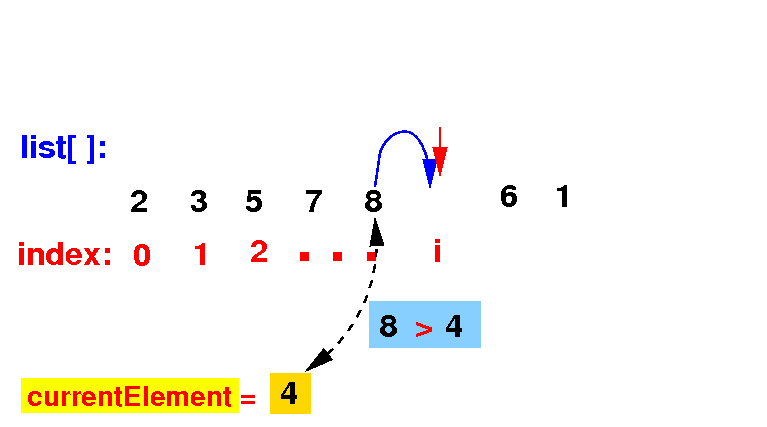
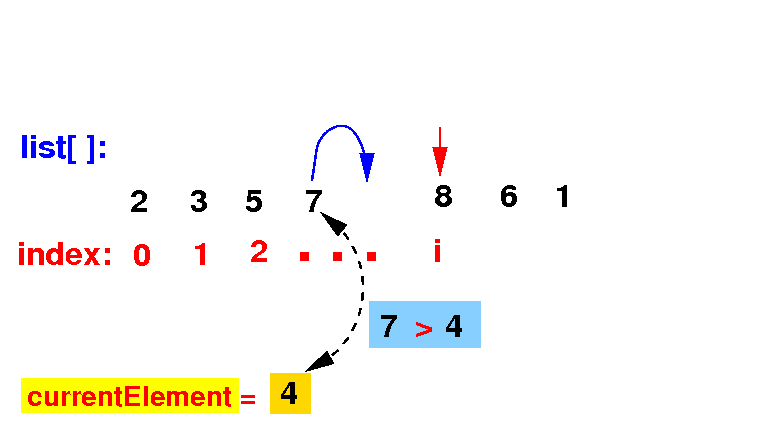
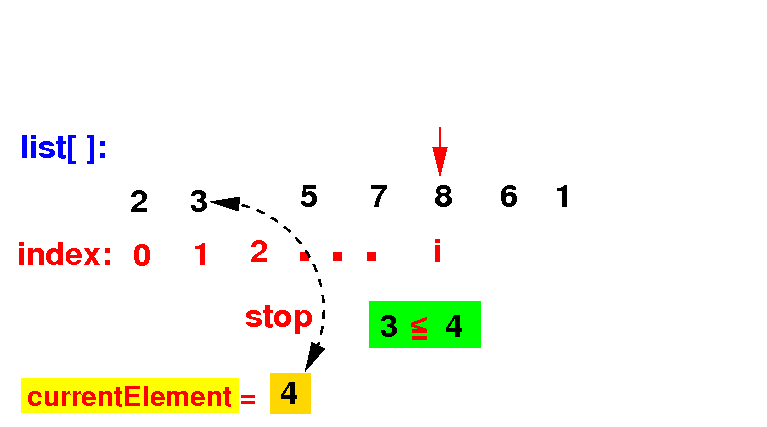
(2b) If the list[k] > currentElement, we move that element to the right:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++) // Go through all unsorted elements
{
double currentElement = list[i]; // Save list[i] in currentElement
// Find the correct position of currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] one spot to the right
else
break; // Found the insert location
|
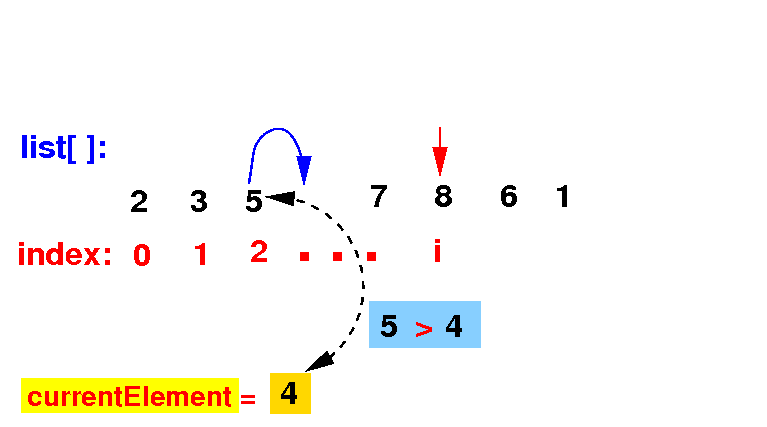
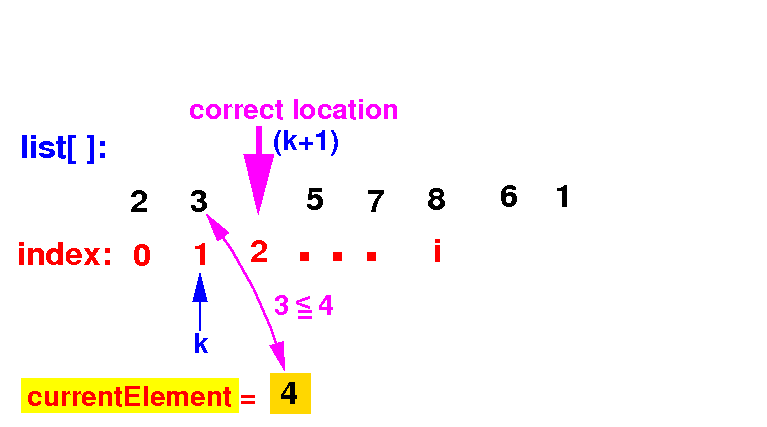
(2c) If the list[k] ≤ currentElement, we stop the search: we have found the correct position
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++) // Go through all unsorted elements
{
double currentElement = list[i]; // Save list[i] in currentElement
// Find the correct position of currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] one spot to the right
else
break; // Stop, the correct location = k+1
|
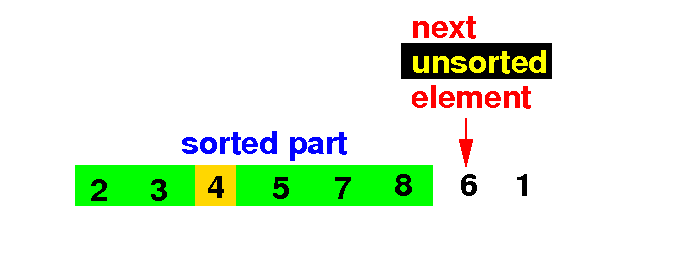
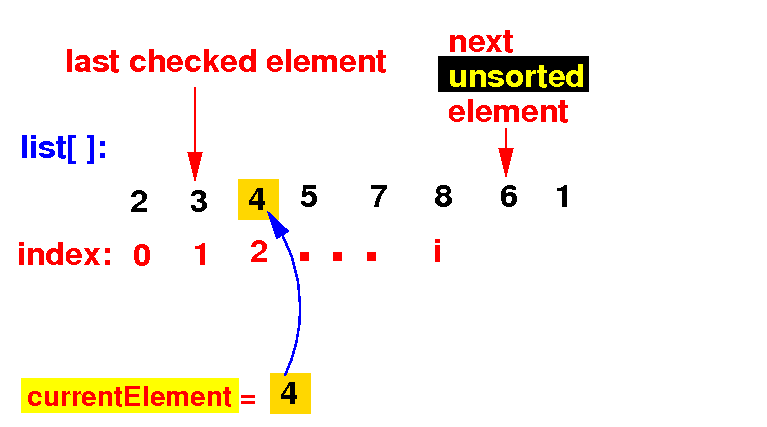
(3) Put currentElement in its correct position:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++) // Go through all unsorted elements
{
double currentElement = list[i]; // Save list[i] in currentElement
// Find the correct position of currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] one spot to the right
else
break; // Stop, the correct location = k+1
list[k+1] = currentElement; //Put currentElement in its correct location
|
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {6, 5 , 3 , 1, 8 , 7, 2, 4};
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.println(myList[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
insertionSort(myList);
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.println(myList[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
|
DEMO: demo/08-array/12-sorting/InsertionSort.java
 }
}
}
}  }
}
}
}  }
}
}
}