|
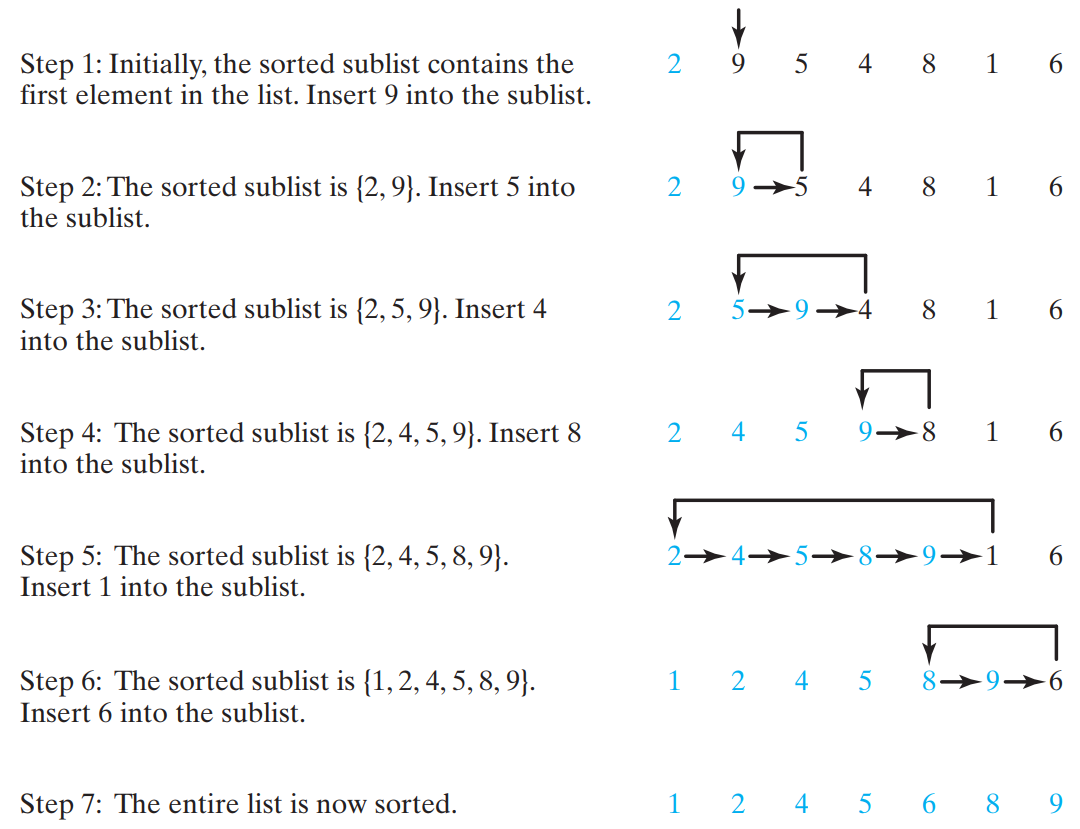
How the insertion sort sort the input: 2 9 5 4 8 1 6:
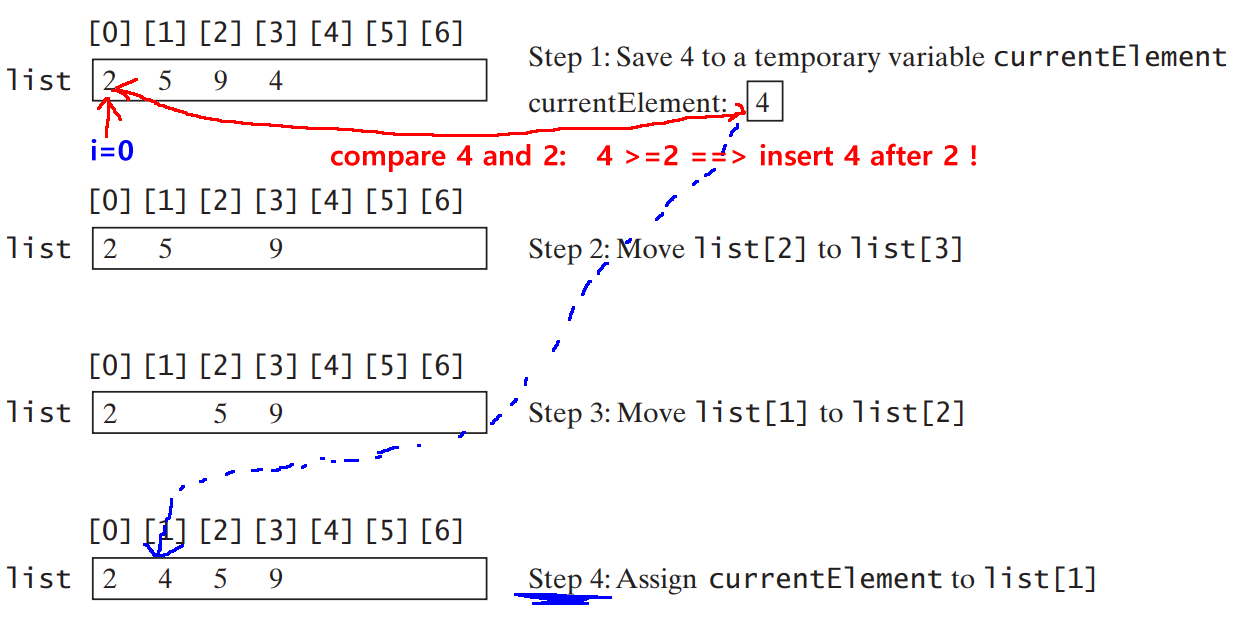
How the insertion sort inserts the next element (4) into a sorted sublist (2 5 9):
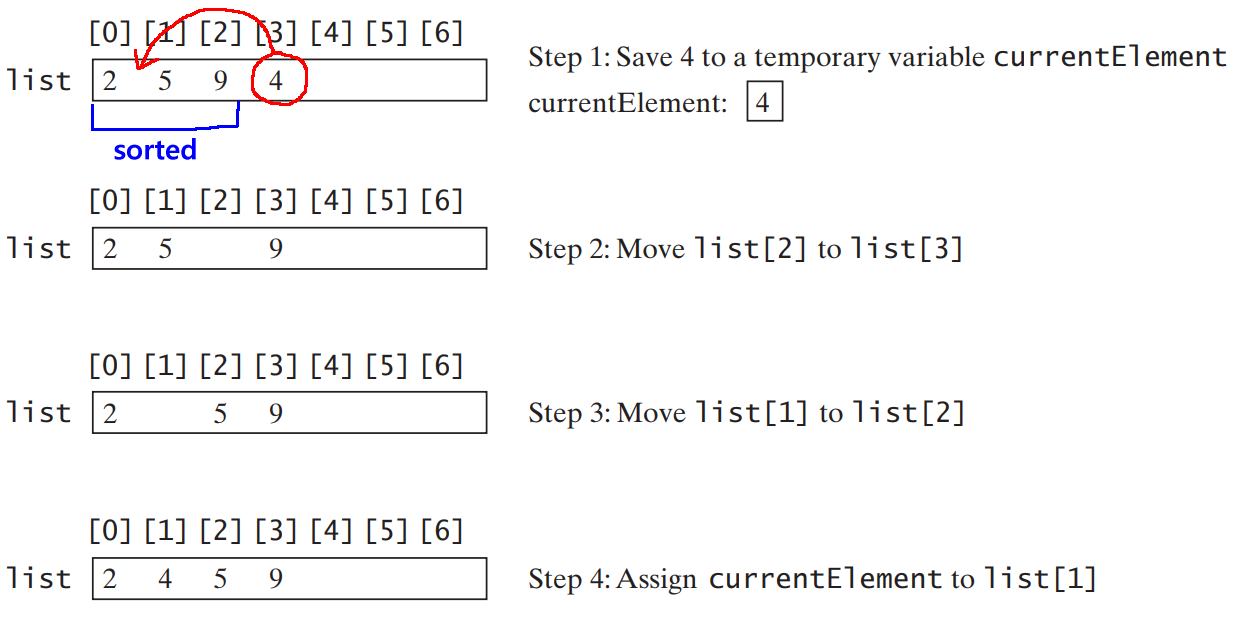
(1) Remove and remember the currentElement:
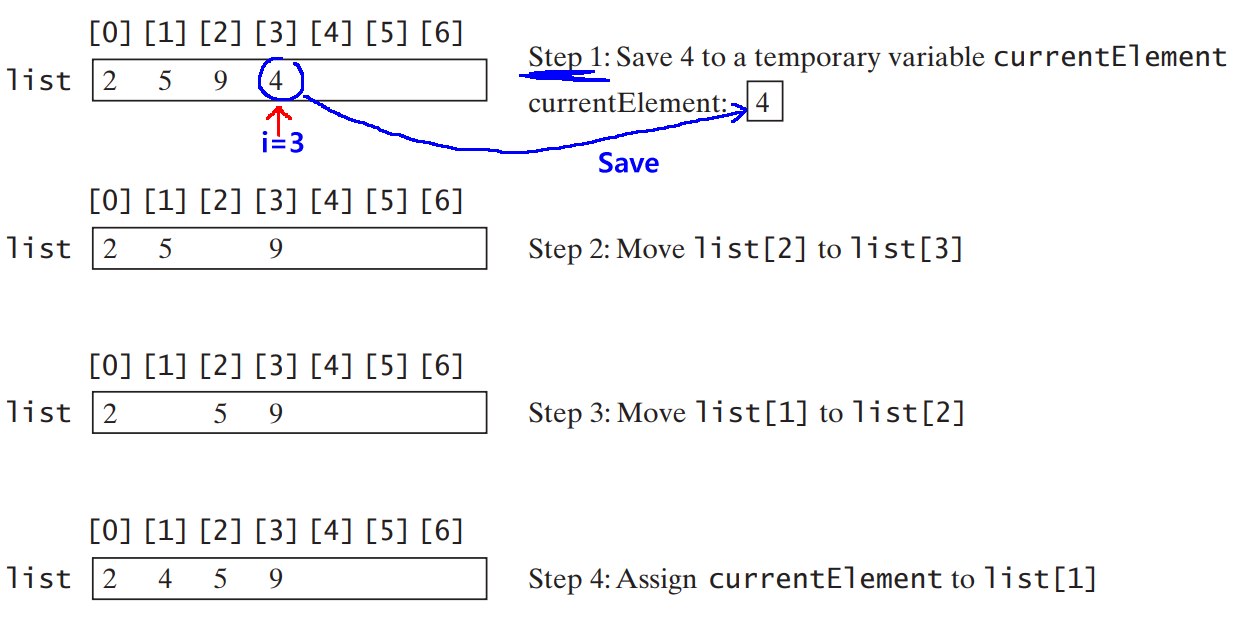
(2) Starting as position i-1 (while position ≥ 0), find the element that preceeds (≤) the currentElement:
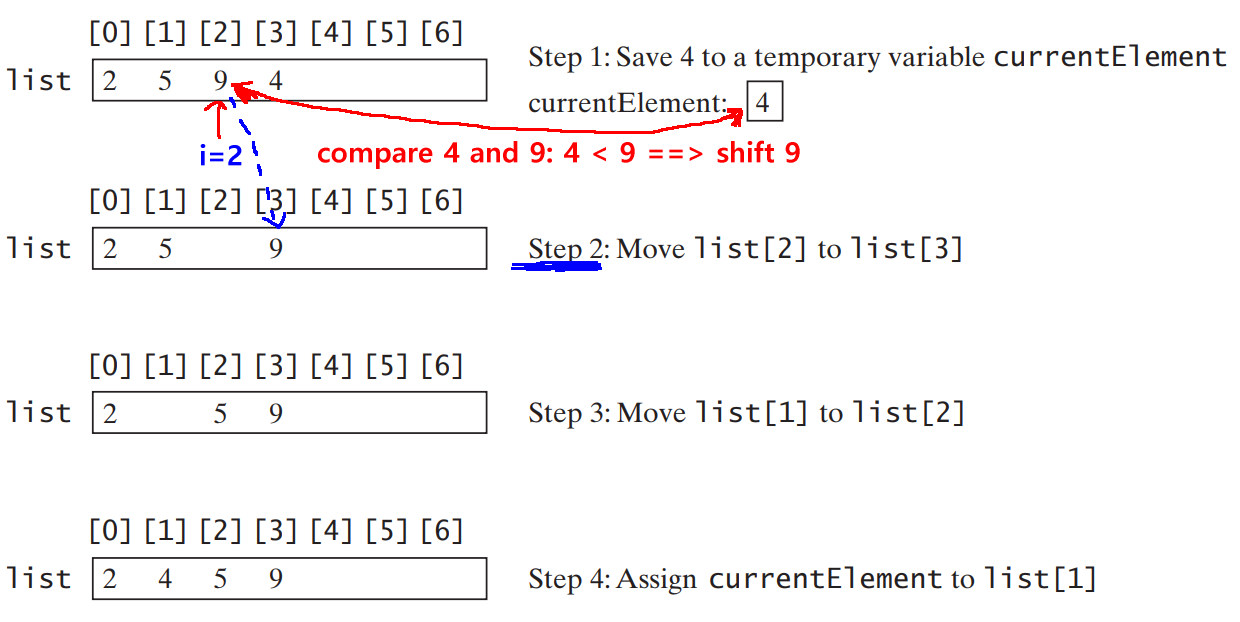
Since 4 < 9, we move 9 up one spot and check the next element
(2) We continue to find the element that preceeds (≤) the currentElement by checking the next element:

Since 4 < 5, we move 5 up one spot and check the next element
(2) We continue to find the element that preceeds (≤) the currentElement by checking the next element:
We have found the element that preceeds (≤) the currentElement: insert the currentElement after this element
We write the Insertion Sort algorithm in Java:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++)
{
/** insert list[i] into a sorted sublist list[0..i-1]
so that: list[0..i] is sorted. */
double currentElement = list[i]; // Remove list[i] and
// save in currentElement
// Look for element list[k] that preceeds (≤) currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] up one spot
else
break; // Found the insert location
// Insert the currentElement after list[k]
list[k + 1] = currentElement;
}
}
|
(1) Save list[i] in currentElement (and position i in the array is open):
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++)
{
/** insert list[i] into a sorted sublist list[0..i-1]
so that: list[0..i] is sorted. */
double currentElement = list[i]; // Remove list[i] and
// save in currentElement
// Look for element list[k] that preceeds (≤) currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] up one spot
else
break; // Found the insert location
// Insert the currentElement after list[k]
list[k + 1] = currentElement;
}
}
|
(2) Find the element list[k] that preceeds (≤) the currentElement:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++)
{
/** insert list[i] into a sorted sublist list[0..i-1]
so that: list[0..i] is sorted. */
double currentElement = list[i]; // Remove list[i] and
// save in currentElement
// Look for element list[k] that preceeds (≤) currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] up one spot
else
break; // Found the insert location
// Insert the currentElement after list[k]
list[k + 1] = currentElement;
}
}
|
We compare element list[k] with currentElement
(3a) If element list[k] comes after (>) the currentElement, we shift it up 1 spot:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++)
{
/** insert list[i] into a sorted sublist list[0..i-1]
so that: list[0..i] is sorted. */
double currentElement = list[i]; // Remove list[i] and
// save in currentElement
// Look for element list[k] that preceeds (≤) currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] up one spot
else
break; // Found the insert location
// Insert the currentElement after list[k]
list[k + 1] = currentElement;
}
}
|
(3a) If element list[k] comes before (≤) the currentElement, we exit the loop (found the insert position):
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++)
{
/** insert list[i] into a sorted sublist list[0..i-1]
so that: list[0..i] is sorted. */
double currentElement = list[i]; // Remove list[i] and
// save in currentElement
// Look for element list[k] that preceeds (≤) currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] up one spot
else
break; // Found the insert position
// Insert the currentElement after list[k]
list[k + 1] = currentElement;
}
}
|
(4) Insert currentElement after list[k]:
public static void insertionSort(double[] list)
{
for (int i = 1 ; i < list.length; i++)
{
/** insert list[i] into a sorted sublist list[0..i-1]
so that: list[0..i] is sorted. */
double currentElement = list[i]; // Remove list[i] and
// save in currentElement
// Look for element list[k] that preceeds (≤) currentElement
int k;
for (k = i - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if ( list[k] > currentElement )
list[k + 1] = list[k]; // Move list[k] up one spot
else
break; // Found the insert position
// Insert currentElement after list[k]
list[k + 1] = currentElement;
}
}
|
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {6, 5 , 3 , 1, 8 , 7, 2, 4};
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.println(myList[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
insertionSort(myList);
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.println(myList[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
|