Methods that
return an
array reference
|
Methods that
return an
array reference
example
Write a reverse( ) method that (1) reverses the elements in its input list[] and (2) returns the result array:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] myList = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] out; // Output of algorithm
out = reverse(myList);
for ( int i = 0; i < out.length; i++)
System.out.print(out[i] + " ");
}
public static int[] reverse(int[] list)
{
}
|
Methods that
return an
array reference
example
(1) Create an array to store the result
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] myList = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] out; // Output of algorithm
out = reverse(myList);
for ( int i = 0; i < out.length; i++)
System.out.print(out[i] + " ");
}
public static int[] reverse(int[] list)
{
int[] result = new int[list.length];
}
|
Methods that
return an
array reference
example
(2) To reverse the elements in the input array, we copy the elements to the result array in reverse order:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] myList = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] out; // Output of algorithm
out = reverse(myList);
for ( int i = 0; i < out.length; i++)
System.out.print(out[i] + " ");
}
public static int[] reverse(int[] list)
{
int[] result = new int[list.length];
|
Methods that
return an
array reference
example
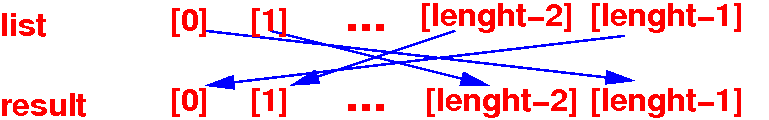
(2) This for-loop will copy the elements in the list array in the reverse order to result array:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] myList = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] out; // Output of algorithm
out = reverse(myList);
for ( int i = 0; i < out.length; i++)
System.out.print(out[i] + " ");
}
public static int[] reverse(int[] list)
{
int[] result = new int[list.length];
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++)
result[(list.length-1) - i] = list[i];
}
|
Methods that
return an
array reference
example
(3) Return the result
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] myList = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] out; // Output of algorithm
out = reverse(myList);
for ( int i = 0; i < out.length; i++)
System.out.print(out[i] + " ");
}
public static int[] reverse(int[] list)
{
int[] result = new int[list.length];
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++)
result[(list.length-1) - i] = list[i];
return result;
}
|
DEMO: demo/08-array/10-return-array/ReturnArray.java
 }
}