Review:
how Java
passes arguments to
methods
Recall:
Java
passes the
arguments to a
method by
copying
each
argument to
the
parameter
variable:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x;
x = 4;
System.out.println(x);
increment( x ); // Pass x by copying, just like: a = x
System.out.println(x); // x UNCHANGED ! Explained in more details next
}
public static void increment(int a ) // a and x are different variables !!
{
a = a + 1;
}
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/08-array-param/PassByCopy.java
--
Step in
BlueJ
Methods with
array variables
as
parameters
Array
variables
can be used
as
parameters
in a method:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList1 = {1, 2, 3, 4};
double[] myList2 = {5, 6, 7};
double sum;
sum = arraySum( myList1 ); // Pass array myList1 as argument
sum = arraySum( myList2 ); // Pass array myList2 as argument
}
// Method with an array variable as parameter
// This method returns the sum of the elements in the array x
public static double arraySum( double[] x )
{
double s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ )
s = s + x[i];
return s;
}
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/08-array-param/ArrayParam1.java
There is an
important difference
when we
update an
array argument
-
discussed
next
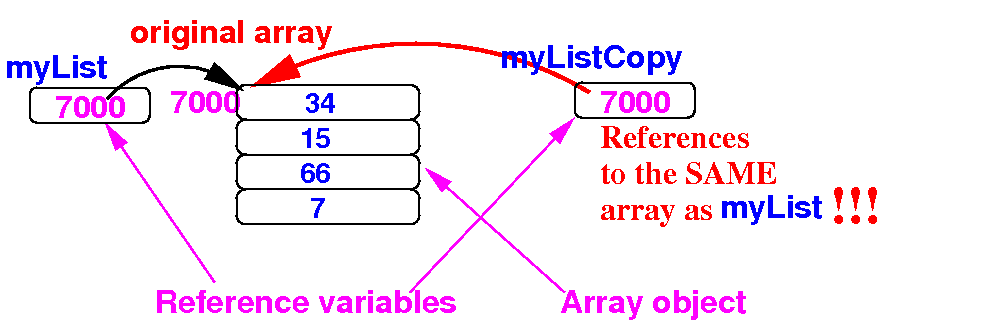
Review:
copying an
array
(reference) variable
will make
an alias !!
- The assignment
myListCopy = myList
copies the
reference
in myList to
myListCopy:
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy;
myListCopy = myList; // Copies the reference
myListCopy[1] = 999; // Will also change myList[1] !!
myList[3] = 999; // Will also change myListCopy[3] !!
|
Schematically:
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/08-array-param/ArrayAlias.java
Passing
array variable arguments
in Java
Effect of
passing array variable arguments
in Java
-
Quiz:
can you tell
what is
printed by
the following
program:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] x = {1, 2, 3};
incrementArray(x); // Pass array reference x
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ )
System.out.print( x[i] + " " ); // Prints: ???
System.out.println();
}
public static void incrementArray( int[] a )
{
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length; i++ )
a[i] = a[i] + 1;
}
|
-
Remember:
the
variable
a is an
alias for the
variable
x
|
Effect of
passing array variable arguments
in Java
- Answer:
2 3 4 !!!
Because
a[i] is
an
alias for
x[i] inside
incrementArray( )
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] x = {1, 2, 3};
incrementArray(x); // Pass array reference x
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ )
System.out.print( x[i] + " " ); // Prints: 2 3 4
System.out.println();
}
public static void incrementArray( int[] a )
{
for ( int i = 0; i < a.length; i++ )
a[i] = a[i] + 1;
}
|
-
Because:
the
variable
a is an
alias for the
variable
x ==>
a[i] is the
same as
x[i]
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/08-array-param/ArrayParam2.java
Contrast:
passing
primitive type
variables
vs
passing
array
variables
- Parameter passing
mechanism in
Java is
always as
follows:
- When you invoke a method
with an argument, the
value of the
argument
is
copied (= assigned)
to the
corresponding
parameter variable.
|
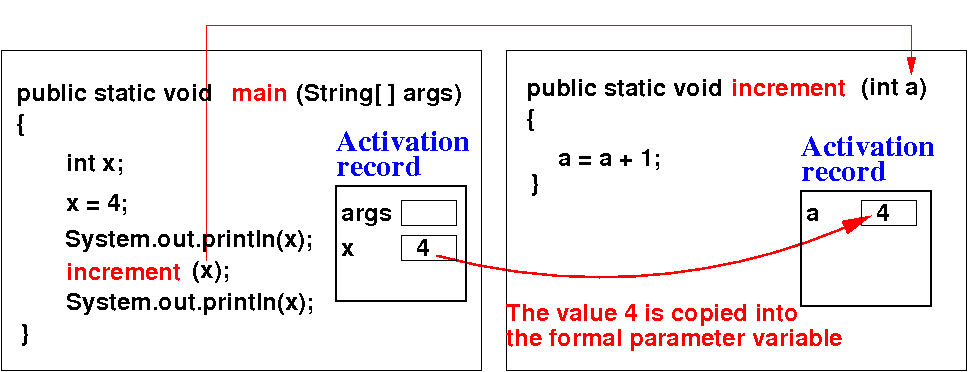
- When passing a
primitive type
variable, the
parameter variable is a
copy
of the argument:
|
Contrast:
passing
primitive type
variables
vs
passing
array
variables
- Parameter passing
mechanism in
Java is
always as
follows:
- When you invoke a method
with an argument, the
value of the
argument
is
copied (= assigned)
to the
corresponding
parameter variable.
|
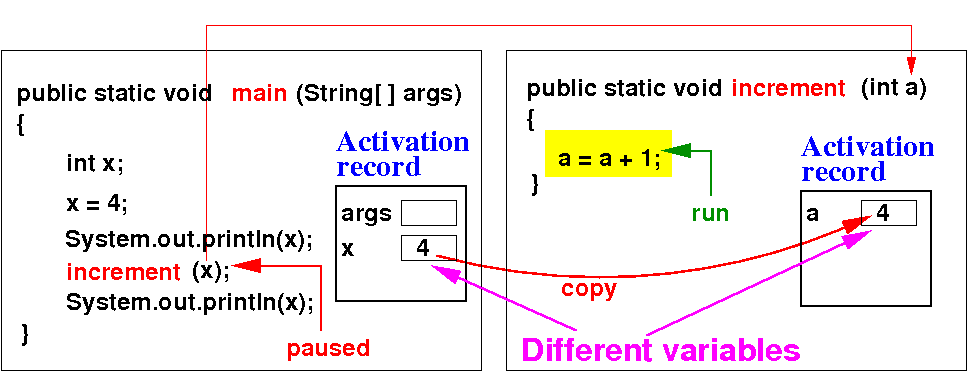
- The method will
work with an
independent
copy of the
argument variable:
|
Contrast:
passing
primitive type
variables
vs
passing
array
variables
- Parameter passing
mechanism in
Java is
always as
follows:
- When you invoke a method
with an argument, the
value of the
argument
is
copied (= assigned)
to the
corresponding
parameter variable.
|
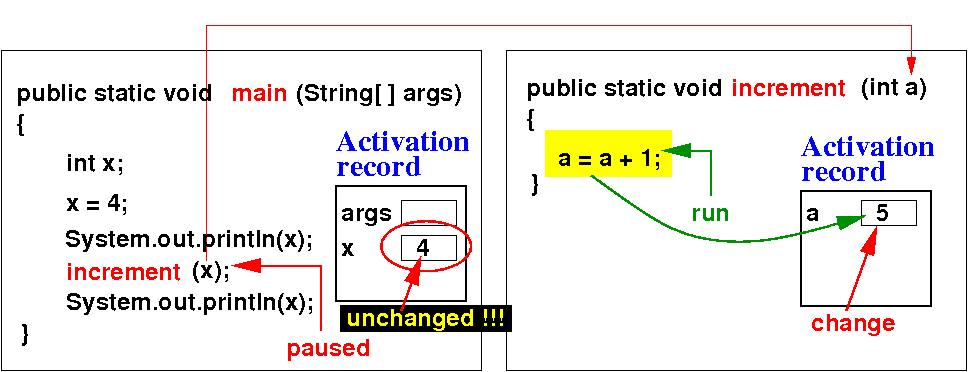
- The method
will not change
the value in the
argument variable:
|
Contrast:
passing
primitive type
variables
vs
passing
array
variables
- Parameter passing
mechanism in
Java is
always as
follows:
- When you invoke a method
with an argument, the
value of the
argument
is
copied (= assigned)
to the
corresponding
parameter variable.
|
- When passing an
array
variable, the
parameter variable is an
alias
of the argument:
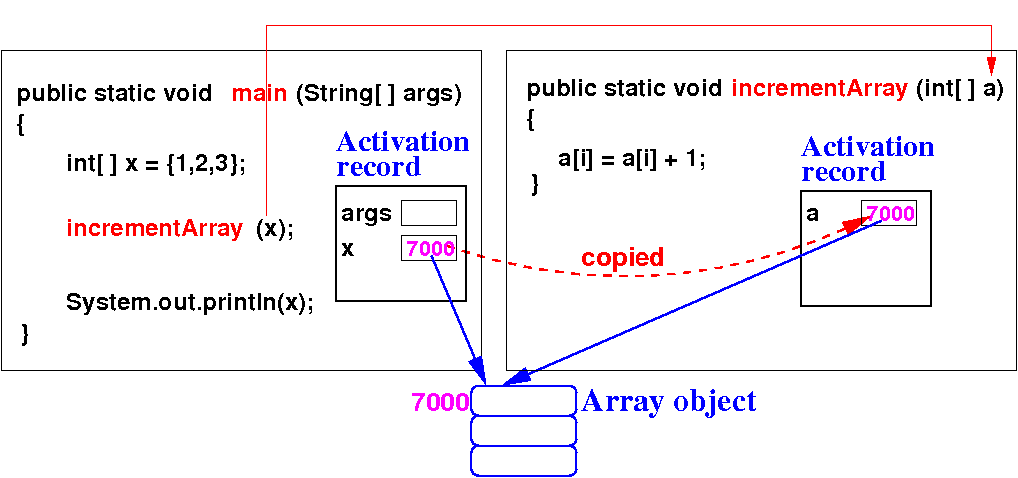
|
Contrast:
passing
primitive type
variables
vs
passing
array
variables
- Parameter passing
mechanism in
Java is
always as
follows:
- When you invoke a method
with an argument, the
value of the
argument
is
copied (= assigned)
to the
corresponding
parameter variable.
|
-
Therefore:
a[k] and
x[k] are
the
same
array element:
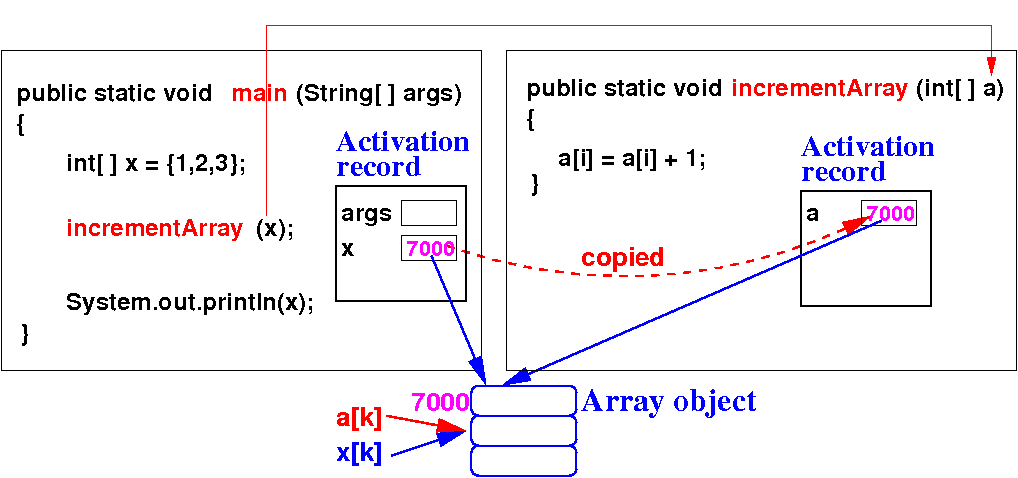
|
Contrast:
passing
primitive type
variables
vs
passing
array
variables
- Parameter passing
mechanism in
Java is
always as
follows:
- When you invoke a method
with an argument, the
value of the
argument
is
copied (= assigned)
to the
corresponding
parameter variable.
|
- The method
can change
the value in the
argument array variable
using
x[k]:
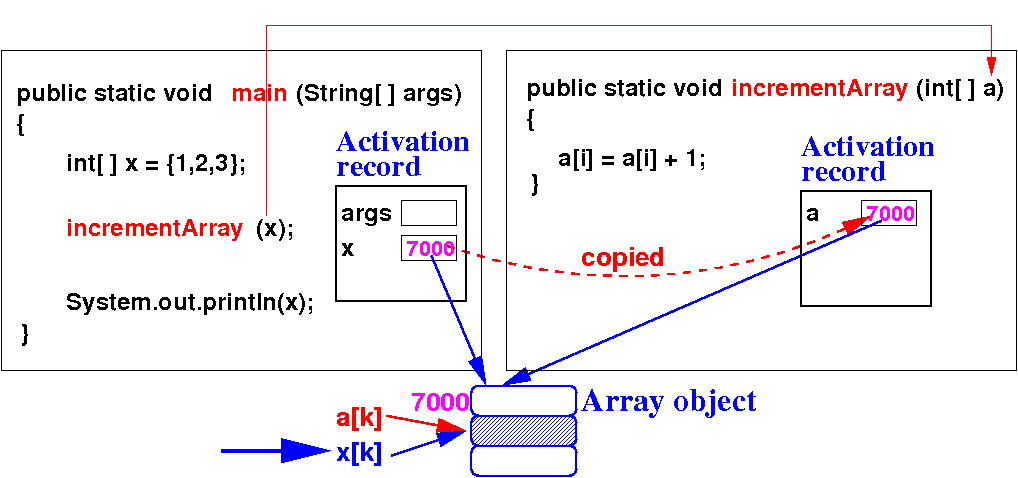
|
❮
❯






