We want to change the size of the array object that is referenced by the array variable myList:
|
Background information:
|
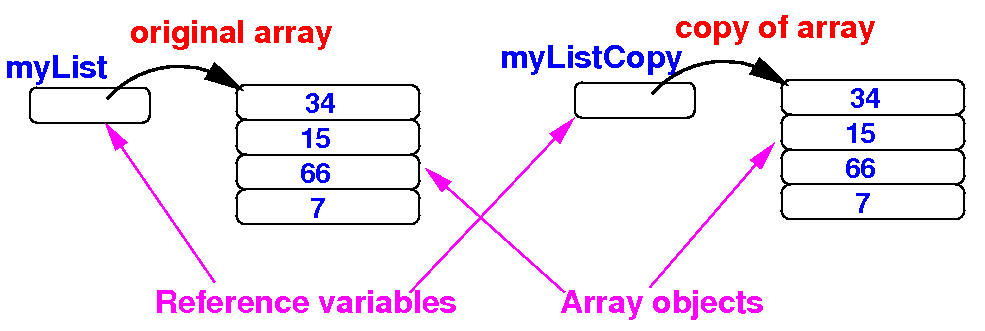
In Java, we can make a copy of an array object by copying all its elements:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ myList.length ];
/* ------------------------------------------------
Copy all the elements
from myList to myListCopy
------------------------------------------------ */
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
}
|
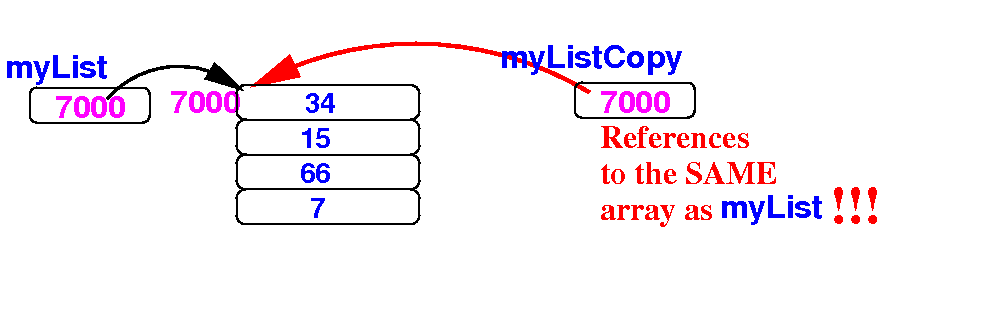
In Java, assigning an array references will create an alias:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy;
myListCopy = myList; // Copies the reference
}
|
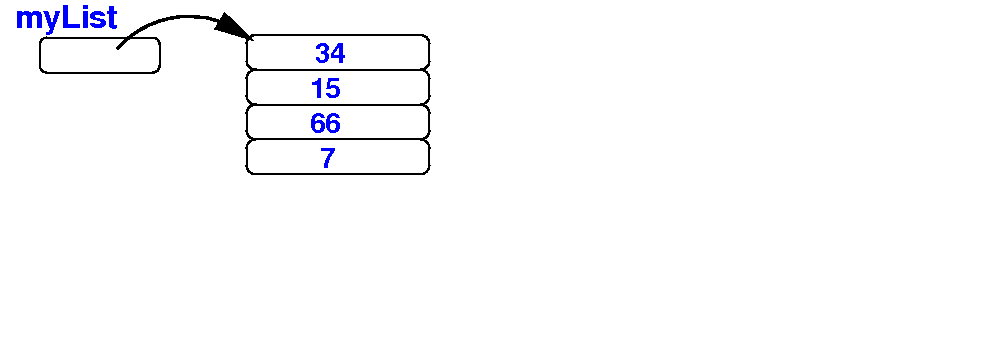
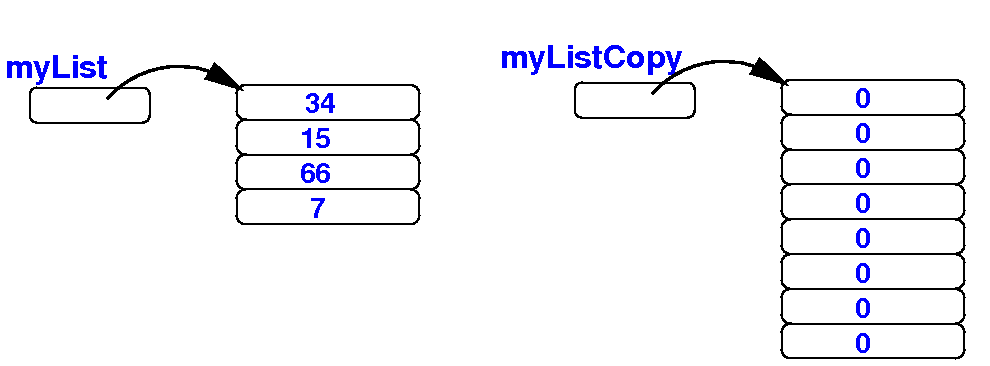
Initially, we have the array myList:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ 2*myList.length ];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
myList = myListCopy;
}
Schematically:
|
(1) we first create a larger array:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ 2*myList.length ];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
myList = myListCopy;
}
Schematically:
|
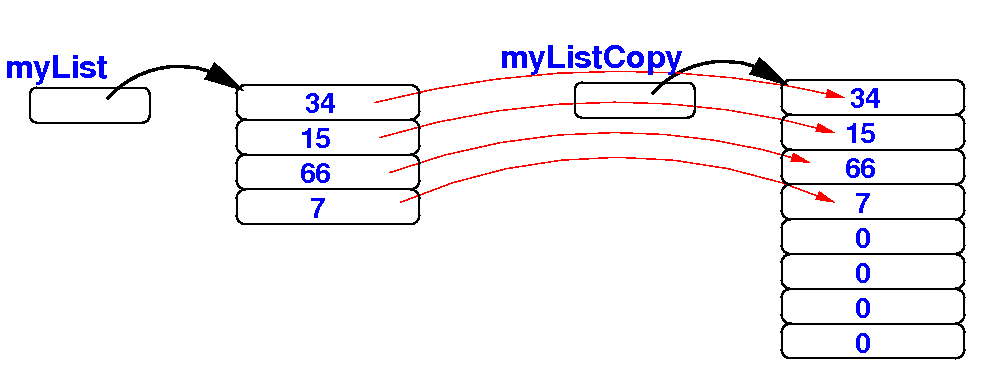
(2) Next, we copy the elements from myList to the larger array:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ 2*myList.length ];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
myList = myListCopy;
}
Schematically:
|
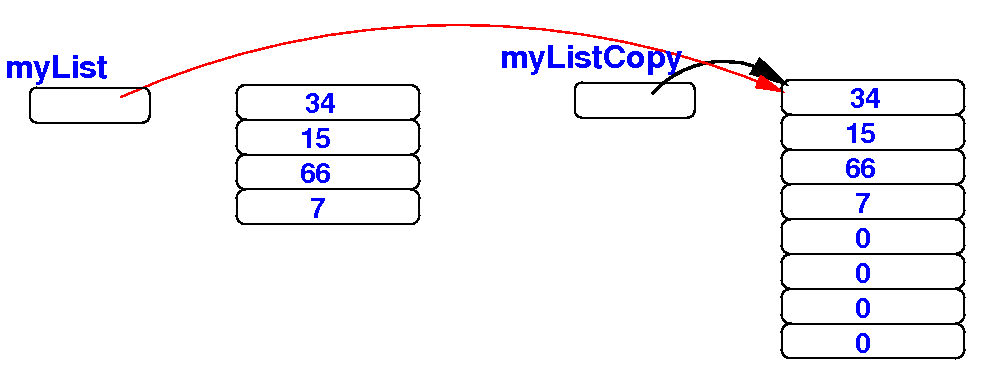
(3) Finally, we reference the larger array with the array variable myList:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ 2*myList.length ];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
myList = myListCopy;
}
Schematically:
|
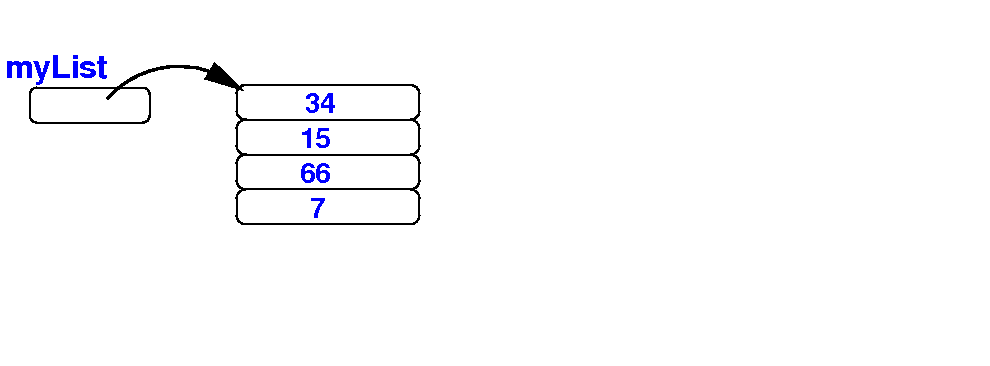
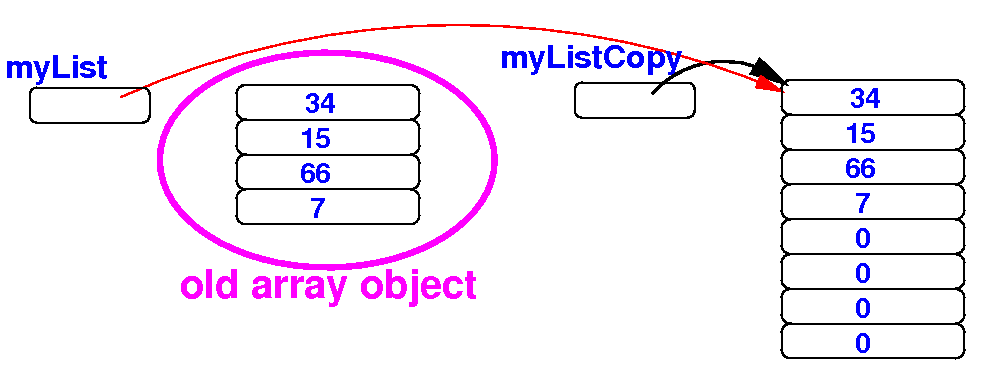
When we remove the extraneous variables, you can clearly see that myList points to a larger array:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ 2*myList.length ];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
myList = myListCopy;
}
Schematically:
|
Demo program:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ ) // Print before changing size
System.out.print(myList[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
double[] myListCopy = new double[ 2*myList.length ];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
myList = myListCopy;
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ ) // Print after changing size
System.out.print(myList[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
|
DEMO: demo/08-array/07-change-array-size/Demo1.java
|