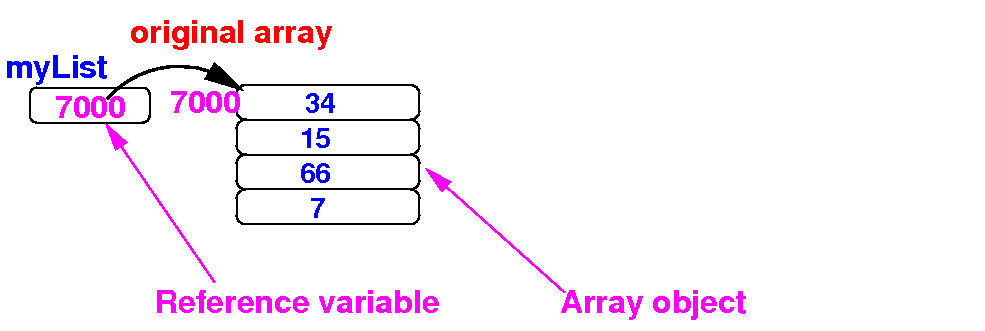
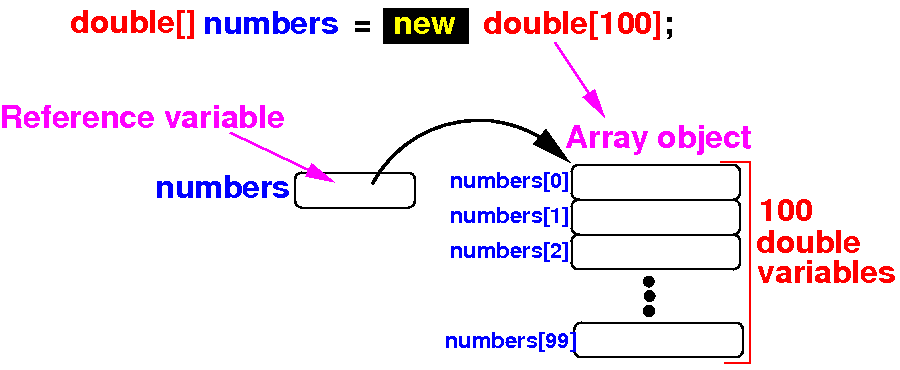
Review:
arrays in Java
- An
array in
Java
consists of
2 parts:
- An
array reference variable
(which is not an
array, but a
variable that
references to
an array object)
- The
array object
which consists of
N
consecutive
variables
|
- Schematically:
|
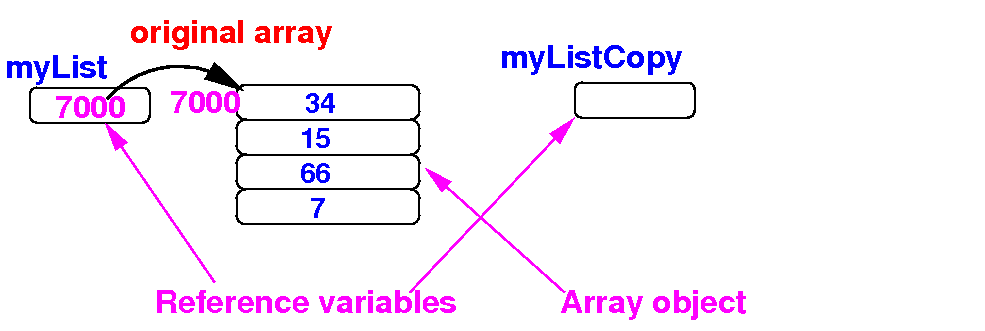
What does it
mean to
copy a
variable ?
What does it
mean to
copy an
array ?
- Copy an
array means:
- Make a duplicate of
an array where
the duplicate contains
the same data as
the original
- Updating array elements
in the duplicate
must
not
affect
the data in the original array
|
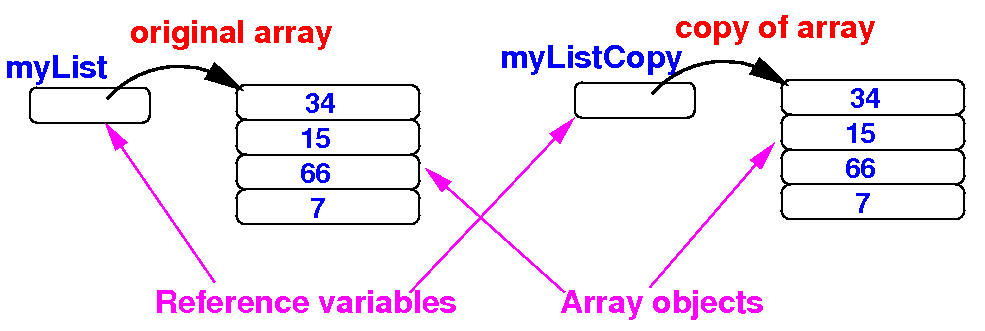
- Schematically:
before
making a copy of the
array myList
|
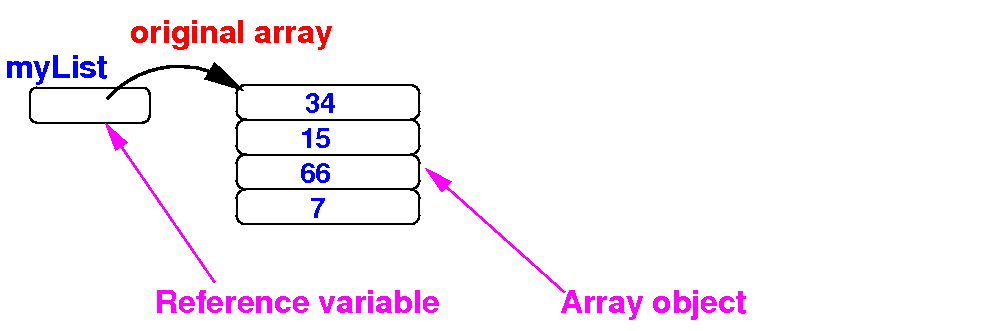
What does it
mean to
copy an array
- Copy an
array means:
- Make a duplicate of
an array where
the duplicate contains
the same data as
the original
- Updating array elements
in the duplicate
must not affect
the data in the original array
|
- Schematically:
after
making a copy of the
array myList
|
How to
copy an array in
Java
step-by-step instructions
- Initial state:

public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ myList.length ];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
}
|
|
How to
copy an array in
Java
step-by-step instructions
- Step 1:
create an
array to
store the
copy
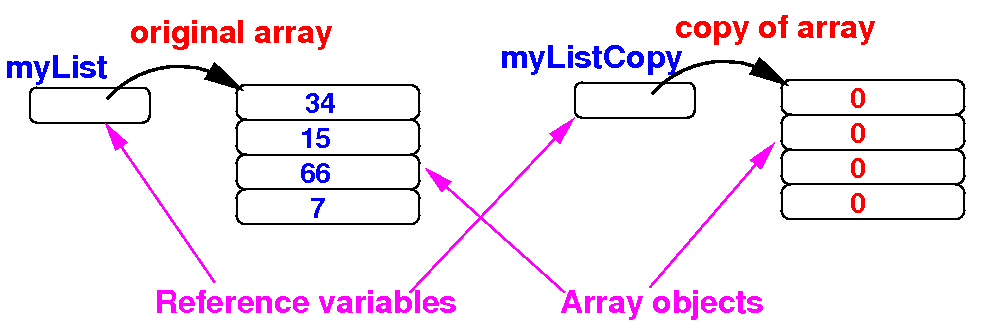
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ myList.length ];
// Note: all entries of array are 0 (zero) !
}
|
|
How to
copy an array in
Java
step-by-step instructions
- Step 2:
copy the
array elements to
the
copy array
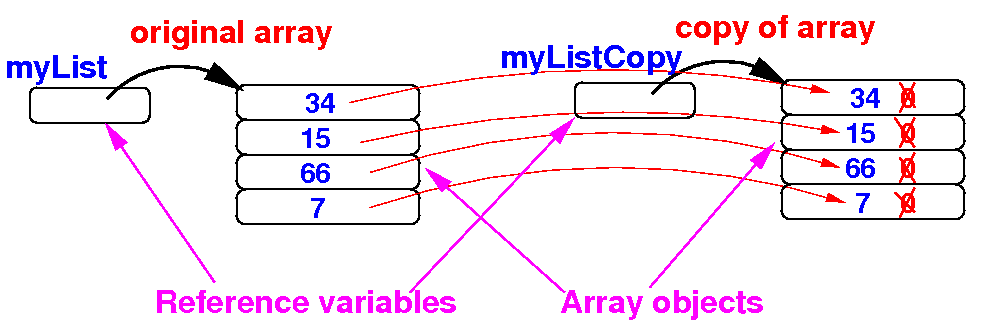
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy = new double[ myList.length ];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myListCopy[i] = myList[i];
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/06-copy-array/CopyArray.java
Demo in
BleuJ
A
common
error
in array copy
The effect of
assignment
using a
reference variable
The effect of
assignment
using a
reference variable
The effect of
assignment
using a
reference variable
- The assignment
myListCopy = myList
copies the
reference
in myList to
myListCopy:
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy;
myListCopy = myList; // Copies the reference
|
Schematically:
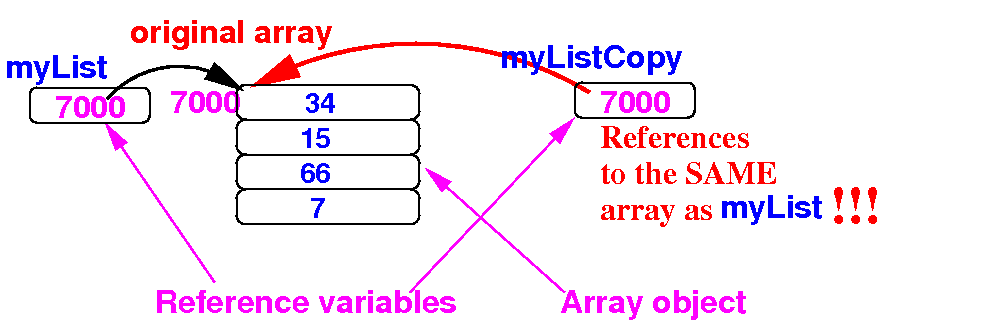
|
The effect of
assignment
using a
reference variable
- Because
myListCopy
and myList
reference
the
same
array object,
updates made to
myListCopy[i]
will
also
affect
myList[i] and
vice verse:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy;
myListCopy = myList; // Does not copy an array object
myListCopy[1] = 999; // Will also change myList[1] !!
myList[3] = 999; // Will also change myListCopy[3] !!
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/06-copy-array/ArrayAlias.java
Demo in
BlueJ
Alias
- We saw in the
last example that:
myListCopy
and
myList
were
different names that
refer to
same
the
array object:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {34, 15, 66, 7};
double[] myListCopy;
myListCopy = myList; // Does not copy an array object
myListCopy[1] = 999; // Will also change myList[1] !!
myList[3] = 999; // Will also change myListCopy[3] !!
}
|
-
Alias:
- When
different
variable names
refer to the
same
object, they are
called
aliases
in Computer Science
|
|
Quiz:
what
is printed by the following Java program
What is
printed by
this program:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] b = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5};
int[] x;
x = a; // x is now an alias for a
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints ???
System.out.println();
x = b; // x is now an alias for b
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints ???
System.out.println();
}
|
Quiz:
what is printed by the following Java program
Answer:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] a = {1, 2, 3, 4};
int[] b = {9, 8, 7, 6, 5};
int[] x;
x = a; // x is now an alias for a
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints 1 2 3 4
System.out.println();
x = b; // x is now an alias for b
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints 9 8 7 6 5
System.out.println();
}
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/06-copy-array/QuizAlias.java
Review:
assigning references and
alias
The reason
why the
first for-loop
prints the
elements in
array a
is because
x
is an alias of
a:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
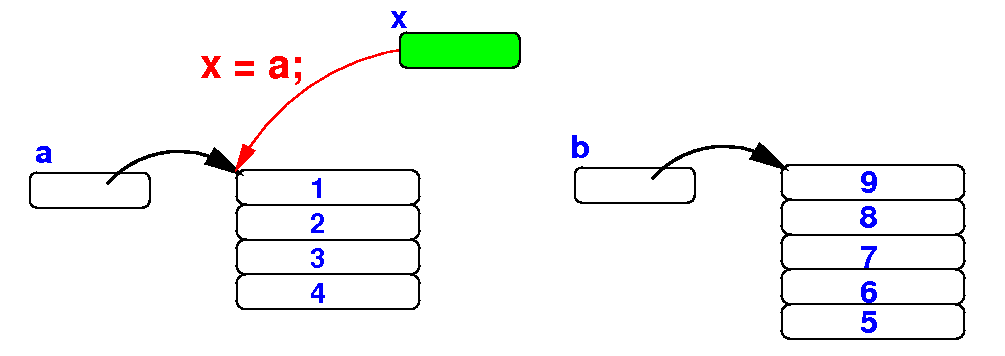 x = a; // x is now an alias for a
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints a[ ]
System.out.println();
x = b; // x is now an alias for b
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints b[ ]
System.out.println();
}
x = a; // x is now an alias for a
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints a[ ]
System.out.println();
x = b; // x is now an alias for b
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints b[ ]
System.out.println();
}
|
Review:
assigning references and
alias
The reason
why the
second for-loop
prints the
elements in
array b
is because
x
is an alias of
b:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
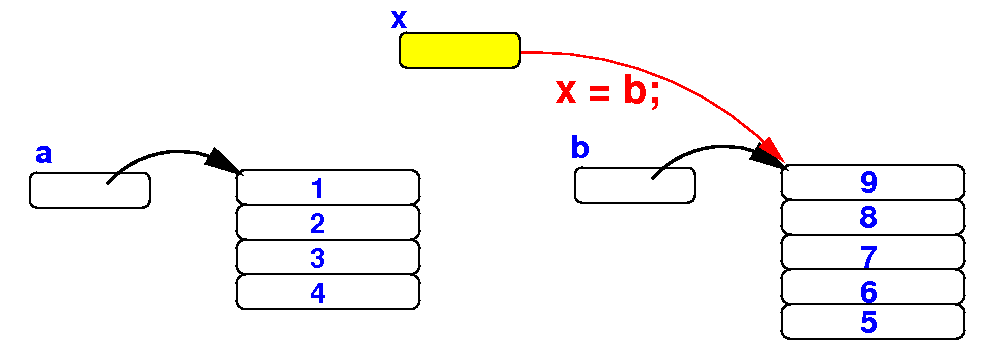 x = a; // x is now an alias for a
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints a[ ]
System.out.println();
x = b; // x is now an alias for b
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints b[ ]
System.out.println();
}
x = a; // x is now an alias for a
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints a[ ]
System.out.println();
x = b; // x is now an alias for b
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++)
System.out.print(x[i] + " "); // Prints b[ ]
System.out.println();
}
|
❮
❯