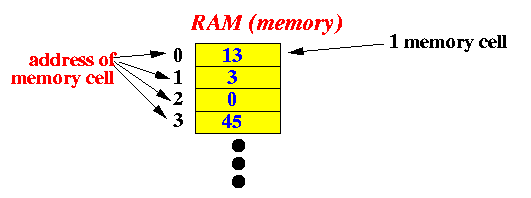
How to
represent
"things" in the
world inside a computer program
-
Fact:
- Computers can
only store
(binary) numbers
|
- There are
things in the
real world that
are
not
numbers,
e.g.:
playing cards:
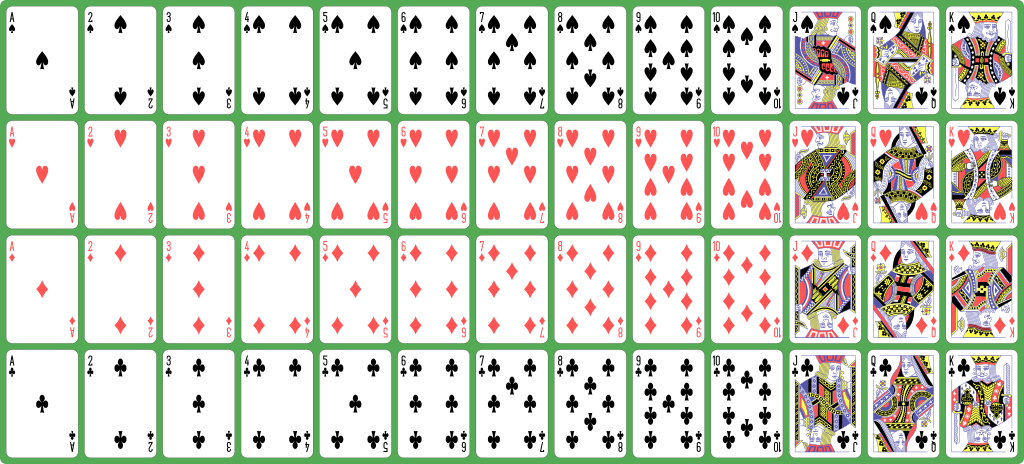
|
Review:
how does the computer store information using
just numbers ?
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- Let's examine a
deck of
playing cards:

4 suites: Spades, Heart, Clubs and Diamonds
Each suite has: Ace, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, Jack, Queen and King
There are 52 number of cards in a deck
|
|
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- We
can
represent the
52 cards in a
deck
with the
numbers
0 - 51:

Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
$64,000 question:
how can we
decode
a number to its
corresponding
playing card ?
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- The
spades are
represented with the
numbers
0 - 12:
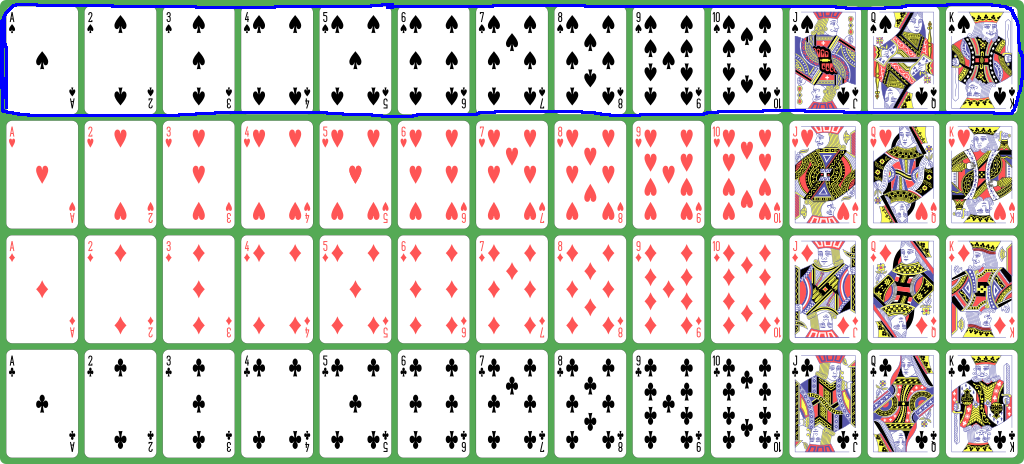
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- The
4 of spades is
represented by
3 =
0×13 + 3:
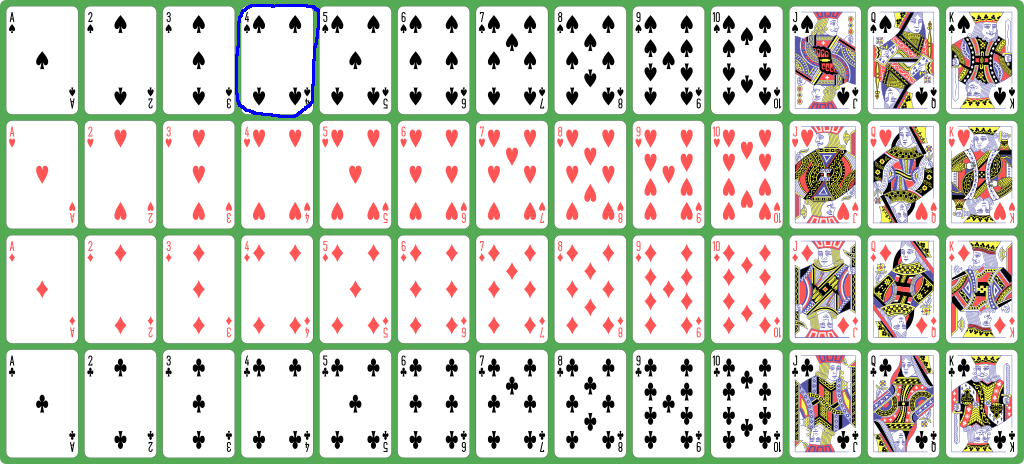
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
Note:
3
/
13 =
0
(the suit)
and
3
%
13 =
3
(the rank)
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
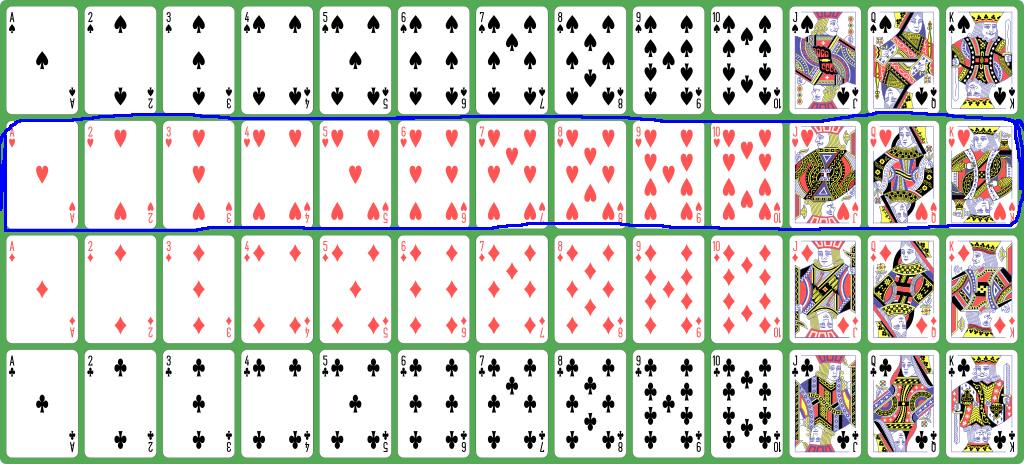
- The
hearts are
represented with the
numbers
13 - 25:
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
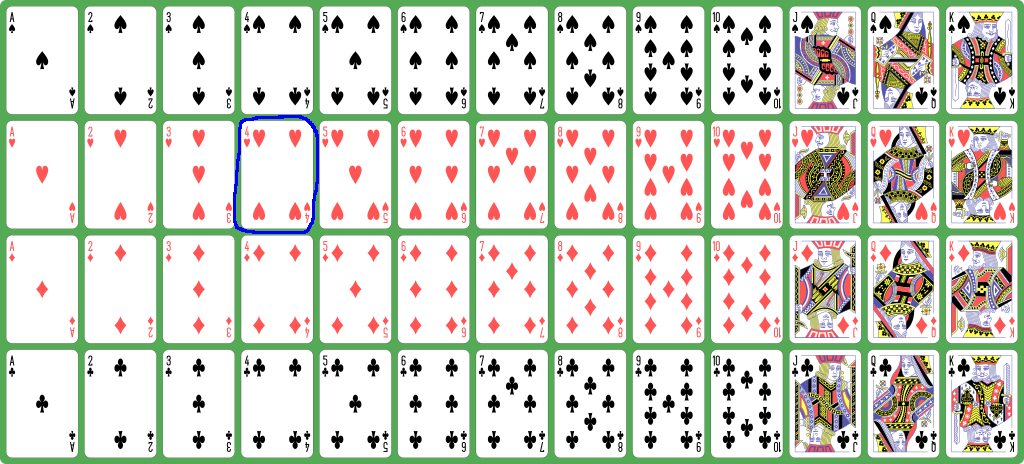
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- The
4 of hearts is
represented by
16 =
1×13 + 3:
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
Note:
16
/
13 =
1
(the suit)
and
16
%
13 =
3
(the rank)
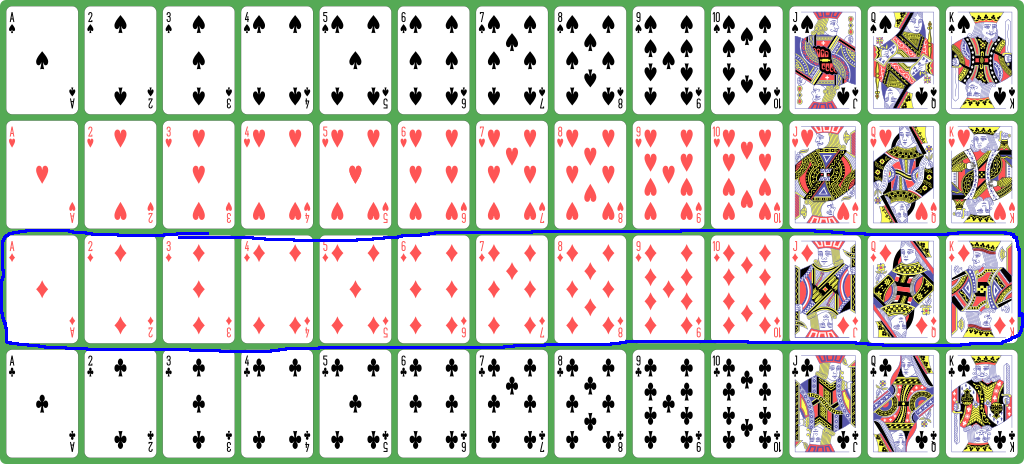
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- The
diamonds are
represented with the
numbers
26 - 38:
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
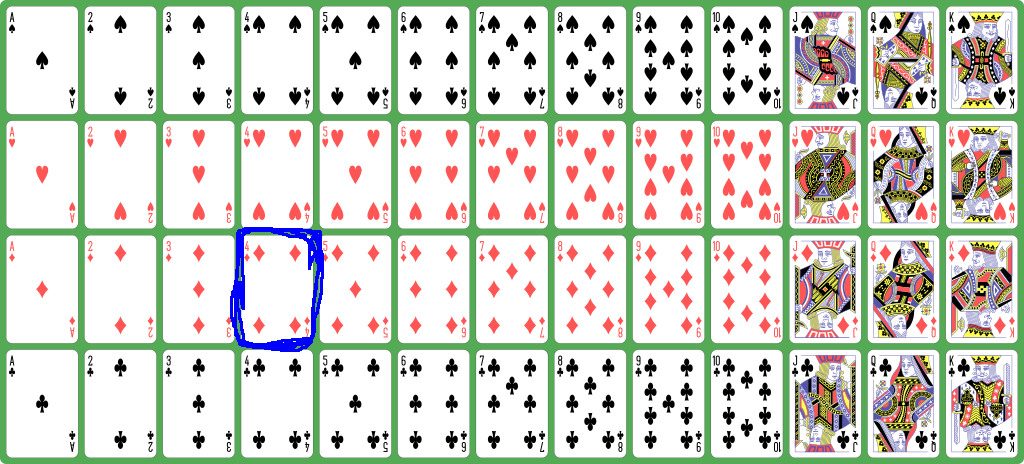
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- The
4 of diamonds is
represented by
29 =
2×13 + 3:
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
Note:
29
/
13 =
2
(the suit)
and
29
%
13 =
3
(the rank)
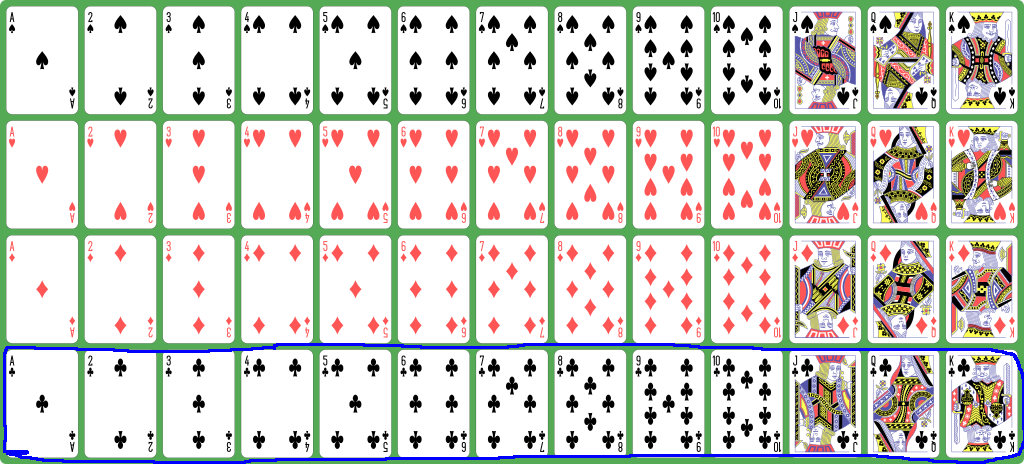
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- The
clubs are
represented with the
numbers
39 - 51:
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
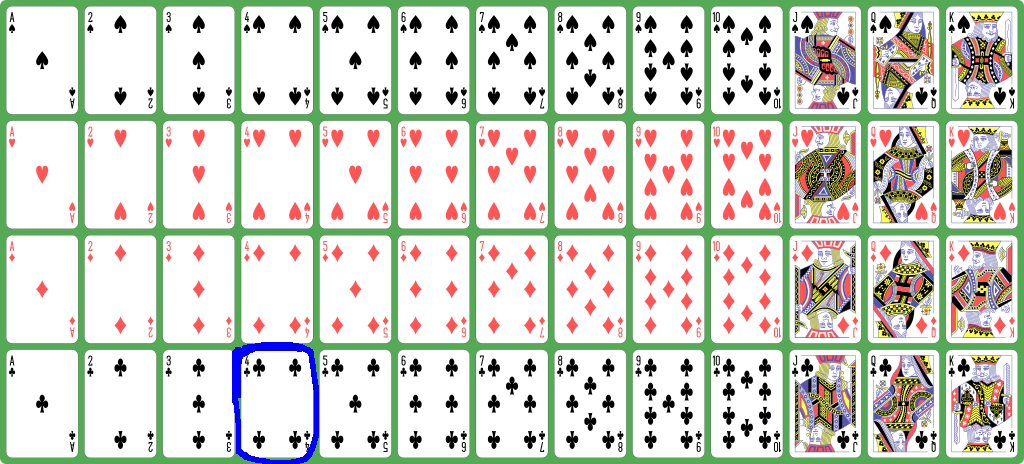
How to represent a
deck of playing cards
inside a computer program
- The
4 of clubs is
represented by
42 =
3×13 + 3:
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
Note:
42
/
13 =
3
(the suit)
and
42
%
13 =
3
(the rank)
Quiz:
which card is represented by
the number
7 ?
- Suppose you are
dealt the
card with
the number
7 -
what's the card ???

Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
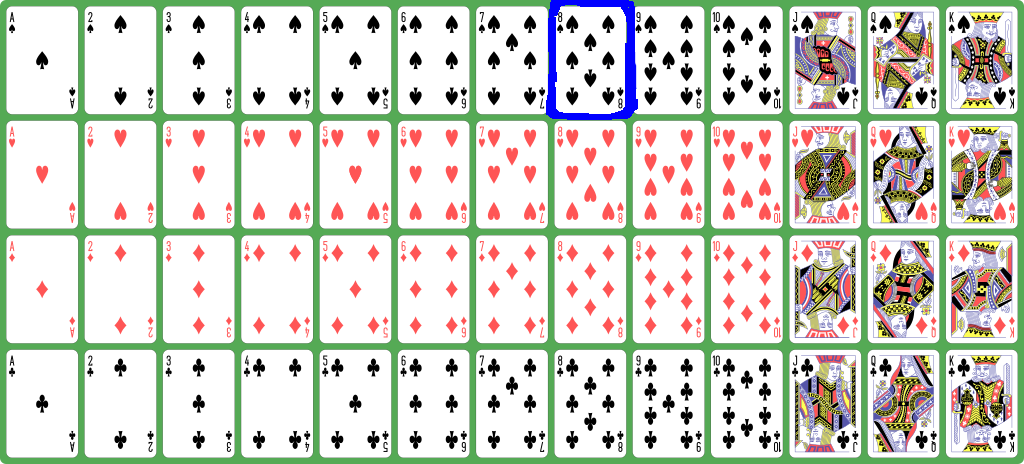
Quiz:
which card is represented by
the number
7 ?
- 7 /
13 =
0 ≡
spades
and
7 %
13 =
7 ≡
rank 8
-
Answer: 8 of spades
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
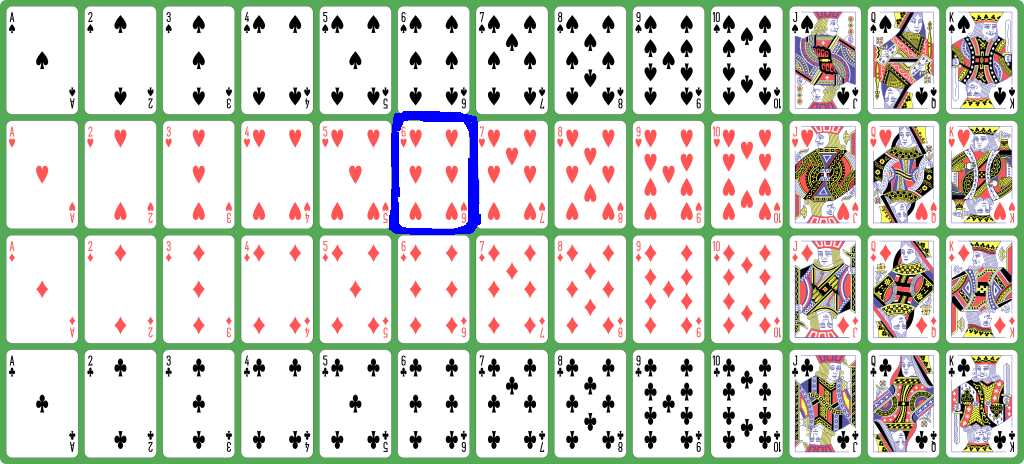
Quiz:
which card is represented by
the number
18 ?
- Suppose you are
dealt the
card with
the number
18 -
what's the card ???

Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
Quiz:
which card is represented by
the number
18 ?
- 18 /
13 =
1 ≡
hearts
and
18 %
13 =
5 ≡
rank 6
-
Answer: 6 of hearts
Ace 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K
Spades: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Hearts: 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Diamonds: 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
Clubs: 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51
|
|
Method to
interprete a
card number in Java
- The following
method will
translate a
card number to
English:
public static String num2Card( int n )
{
/* --------------------------------------------------
Help arrays to translate the card code (0 - 51)
to their English names
-------------------------------------------------- */
String[] suits = {"Spades", "Hearts", "Diamonds", "Clubs"};
String[] ranks = {"Ace", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7",
"8", "9", "10", "Jack", "Queen", "King"};
int cardSuit = n / 13; // 0 => Spades, 1 => Hearts, etc
int cardRank = n % 13; // 0 => Ace, 1 => 2, 2 => 3, etc
return ranks[cardRank] + " of " + suits[cardSuit];
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/05-deck-of-card/Num2Card.java
How a computer program can
simulate a card game
- To
represent
a
deck of cards, we
use an
array of
52 elements
containing the
number codes
0, 1, ..., 51 which
represent
all the
cards
in a deck:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] deck = new int[52]; // Represents a deck of cards
for ( int i = 0; i < deck.length; i++ )
deck[i] = i; // Card codes: 0, 1, 2, ...., 51
// Shuffle the deck of cards
for (int i = 0; i < deck.length; i++)
{ // Generate an index randomly
int j = (int)(Math.random() * deck.length);
int temp = deck[i];
deck[i] = deck[j];
deck[j] = temp;
}
// Deal 4 cards
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
System.out.println( num2Card(deck[i]) );
}
|
|
How a computer program can
simulate a card game
- To
simulate
the
shuffling of the deck
we use the
random shuffle
code that
we have
studied before:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] deck = new int[52]; // Represents a deck of cards
for ( int i = 0; i < deck.length; i++ )
deck[i] = i; // Card codes: 0, 1, 2, ...., 51
// Randomly shuffle the deck of cards
for (int i = 0; i < deck.length; i++)
{ // Generate an index randomly
int j = (int)(Math.random() * deck.length);
int temp = deck[i]; // Swap
deck[i] = deck[j];
deck[j] = temp;
}
// Deal 4 cards
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
System.out.println( num2Card(deck[i]) );
}
|
|
How a computer program can
simulate a card game
- These
are the
first
4 cards
of the
shuffled
deck:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[] deck = new int[52];
for ( int i = 0; i < deck.length; i++ )
deck[i] = i; // 0, 1, 2, ...., 51
// Randomly shuffle the deck of cards
for (int i = 0; i < deck.length; i++)
{ // Generate an index randomly
int j = (int)(Math.random() * deck.length);
int temp = deck[i]; // Swap
deck[i] = deck[j];
deck[j] = temp;
}
// "Deal" 4 cards
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
System.out.println( num2Card(deck[i]) );
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/05-deck-of-card/DealCard.java
❮
❯