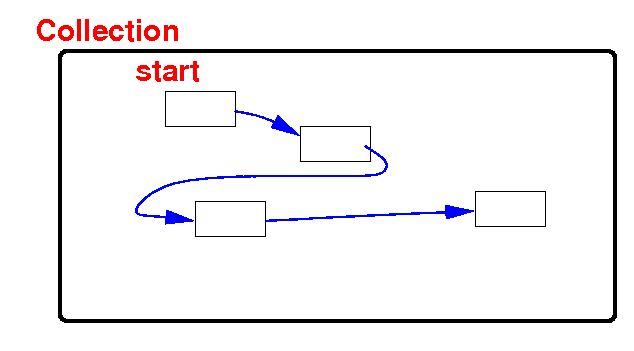
Collections
|
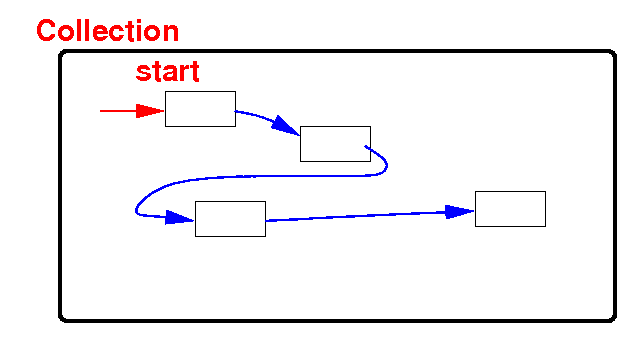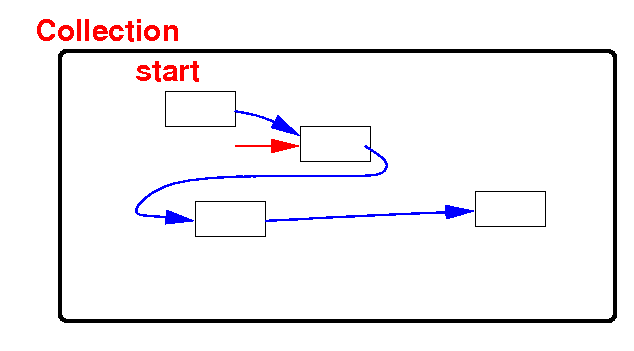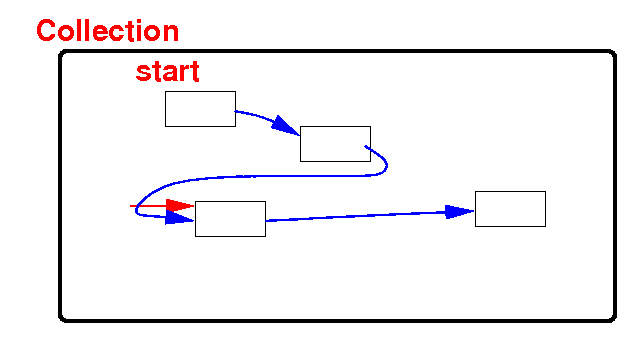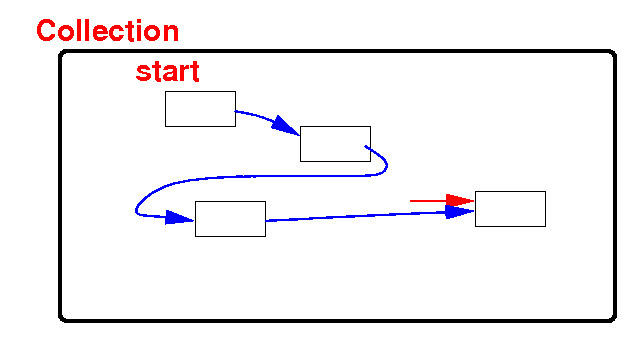
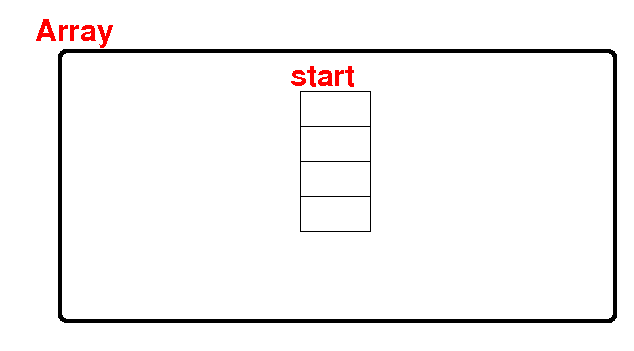
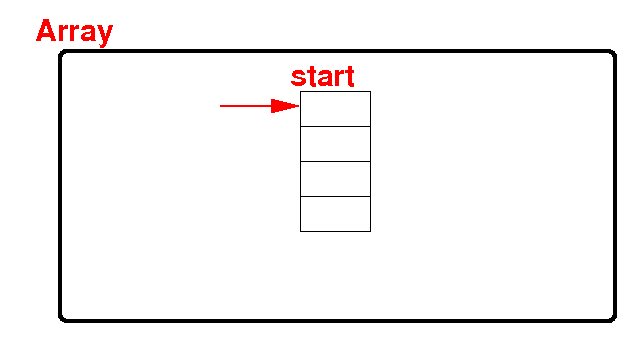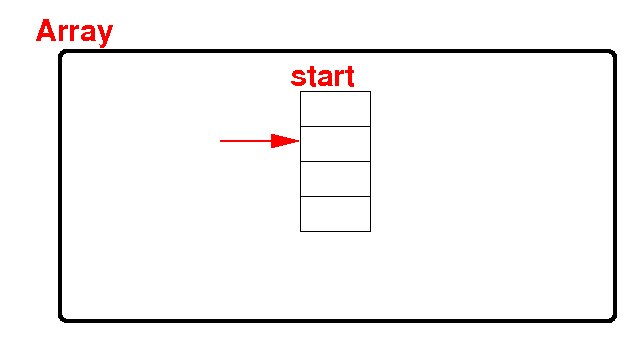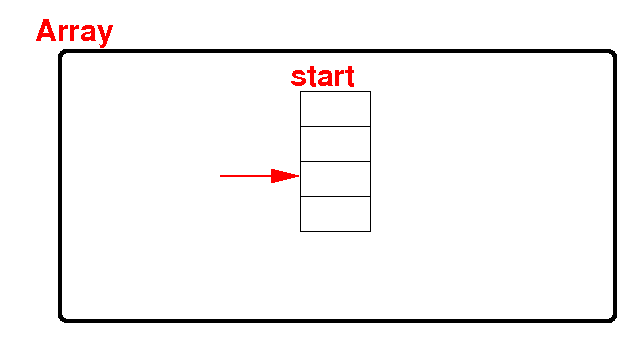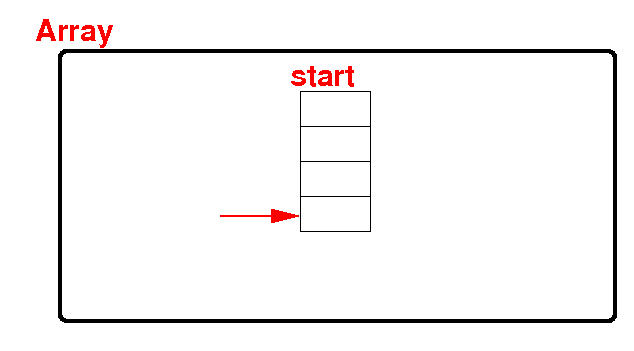
An array is
a collection
|
Iterators and the
for-each
loop
|
DEMO: demo/08-array/04-for-each-loop/Demo1.java
Example
for-each
loop
sum all values in array
|
DEMO: demo/08-array/04-for-each-loop/SumArray.java