Processing data stored in
arrays
-
background information
- The computer hardware
only provides
instructions that
process
primitive
data types:
byte short/char int long float double boolean
|
- Data stored
in arrays
must
be
processed
one
array element
at a time:
- We
must use
a
loop-statement
to
iterate over
all the
elements in an
array to
process the data
stored in an
array
|
-
Recall that:
arrayVarName.length = the length (= # elements) in the array
|
- The
typical
program code to
process data
stored in
an array arrayVarName is
like this:
for ( int i = 0; i < arrayVarName.length; i++ )
"process data stored in arrayVarName[i]"
|
|
Processing arrays 1:
initialization and printing
- Exercise:
- Write code that
define an
array myList of
10 double variables
and initialize
myList[i] with
i*i
-
Print the
array out.
|
Answer:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = new double[10];
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
myList[i] = i*i;
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.println("myList[" + i + "] = " + myList[i]);
}
|
|
Processing arrays 1:
initialization and printing
Processing arrays 1:
initialization and printing
Processing arrays 1:
initialization and printing
Processing arrays 1:
initialization and printing
DEMO:
demo/08-array/03-array-processing/PrintArray.java
Processing arrays 2:
sum all elements in an array
Processing arrays 2:
sum all elements in an array
Processing arrays 2:
sum all elements in an array
Processing arrays 2:
sum all elements in an array
DEMO:
demo/08-array/03-array-processing/SumArray.java
Processing arrays 3:
find the largest value
and its index in an array
Processing arrays 3:
find the largest value
and its index in an array
Processing arrays 3:
find the largest value
and its index in an array
Processing arrays 3:
find the largest value
and its index in an array
DEMO:
demo/08-array/03-array-processing/SumArray.java
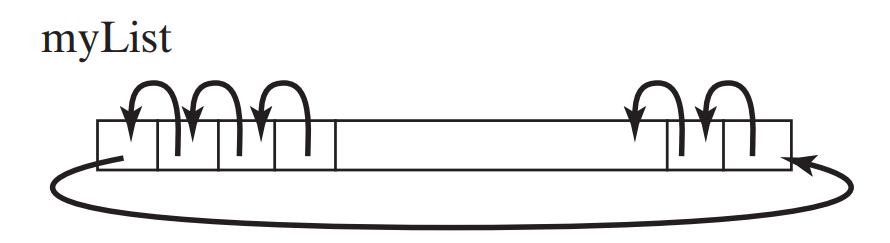
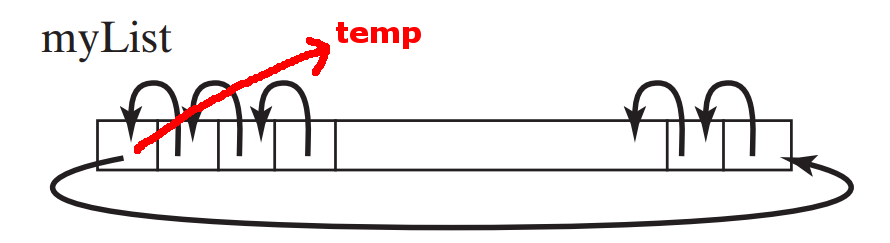
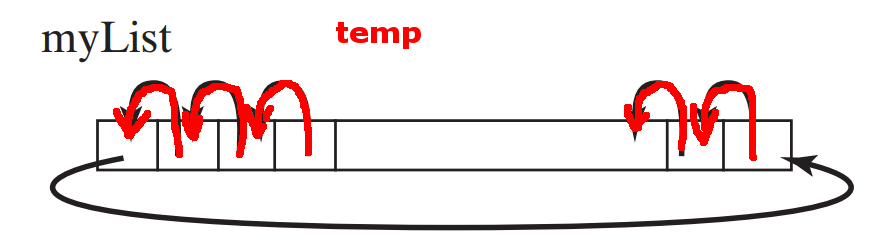
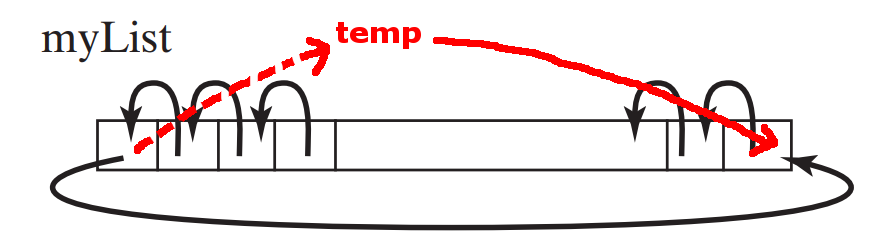
Processing arrays 4:
shift the elements in an array one place to the left
Processing arrays 4:
shift the elements in an array one place to the left
Processing arrays 4:
shift the elements in an array one place to the left
Processing arrays 4:
shift the elements in an array one place to the left
DEMO:
demo/08-array/03-array-processing/ShiftArray.java
Processing arrays 5:
random shuffle
- In many
computer applications, you need to
randomly re-order the
elements
in an array.
- This operation
is called
shuffling.
|
- Example:
- We will soon
use
an
array to
represent
a
deck of playing cards
- The
shuffle
operation will
simulate the
shuffling of
a deck of cards
|
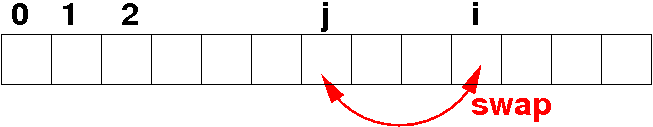
- How to
randomly re-order
elements in
an array:
for
every
index
i
of an array do:
- randomly generate
an index j
between 0 and
myList.length-1
- swap
myList[i]
with myList[j], as follows:
|
|
Processing arrays 5:
random shuffle
- Write code that
perform a
random shuffle on the
elements in
array
myList:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = { 1, 4, 9, 3, 7, 5, 6};
// Random suffle on array myList
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; ++ )
{
int j = (int)(Math.random() * myList.length);
// swap myList[i] and myList[j]
double temp = myList[i];
myList[i] = myList[j];
myList[j] = temp;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.print(myList[i] + " ");
}
|
|
Processing arrays 5:
random shuffle
- Perform the
random swap
operation
for
each
element in the
array:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = { 1, 4, 9, 3, 7, 5, 6};
// Random suffle on array myList
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
{
int j = (int)(Math.random() * myList.length);
// swap myList[i] and myList[j]
double temp = myList[i];
myList[i] = myList[j];
myList[j] = temp;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.print(myList[i] + " ");
}
|
|
Processing arrays 5:
random shuffle
- Pick a
random
integer from
range
[0 ..
myList.length]
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = { 1, 4, 9, 3, 7, 5, 6};
// Random suffle on array myList
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
{
int j = (int)(Math.random() * myList.length);
// swap myList[i] and myList[j]
double temp = myList[i];
myList[i] = myList[j];
myList[j] = temp;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.print(myList[i] + " ");
}
|
|
Processing arrays 5:
random shuffle
- Swap the
elements
myList[i] with the
randomly selected
myList[j]:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = { 1, 4, 9, 3, 7, 5, 6};
// Random suffle on array myList
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
{
int j = (int)(Math.random() * myList.length);
// swap myList[i] and myList[j]
double temp = myList[i];
myList[i] = myList[j];
myList[j] = temp;
}
for ( int i = 0; i < myList.length; i++ )
System.out.print(myList[i] + " ");
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/03-array-processing/RandomShuffle.java
Use array to organize information
array used as an information lookup
structure
- Previously, we
wrote a
method
getMonthName(month)
that translate
a month number to
a month name:
public static String getMonthName(int month)
{
String monthName = "";
switch (month)
{
case 1: monthName = "January"; break;
case 2: monthName = "February"; break;
case 3: monthName = "March"; break;
case 4: monthName = "April"; break;
case 5: monthName = "May"; break;
case 6: monthName = "June"; break;
case 7: monthName = "July"; break;
case 8: monthName = "August"; break;
case 9: monthName = "September"; break;
case 10: monthName = "October"; break;
case 11: monthName = "November"; break;
case 12: monthName = "December"; break;
}
return monthName;
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/03-array-processing/ArrayInfoStruct.java
Use array to organize information
array used as an information lookup
structure
- If we store
the month names in
an array as
follows:
public static String getMonthName(int month)
{
String[] months = {"January", "February", "March",
"April", "May", "June",
"July", "August", "September",
"October", "Novenber", "December"};
// Notice that: month[0] = "January"
month[1] = "February"
and so on
}
|
|
Use array to organize information
array used as an information lookup
structure
- We can write the
method
getMonthName(month)
as a
simple
lookup in the
months array:
public static String getMonthName(int month)
{
String[] months = {"January", "February", "March",
"April", "May", "June",
"July", "August", "September",
"October", "Novenber", "December"};
return months[month−1];
// We do not need to use a switch statement
// This is much faster
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/03-array-processing/ArrayInfoStruct.java
❮
❯