Review:
Reference data types and variables
-
Review:
reference
data type:
- All
Java classes are
reference
data types
- We can
define
(reference) variables with:
ClassName refVarName ;
Example:
String s ;
|
|
-
Review:
reference
variables:
- Variables
defined with a
class
is known
as a
reference variable.
-
Reference variable can
store a
reference (= address) of an
object of the
corresponding class
|
|
Reference
data types and variables
Illustrated
|
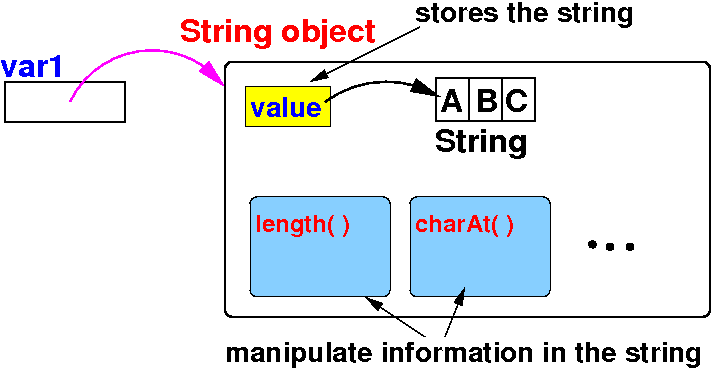
Reference variable stores an
address of an object
|
Reference variable points to an object
|
|
|
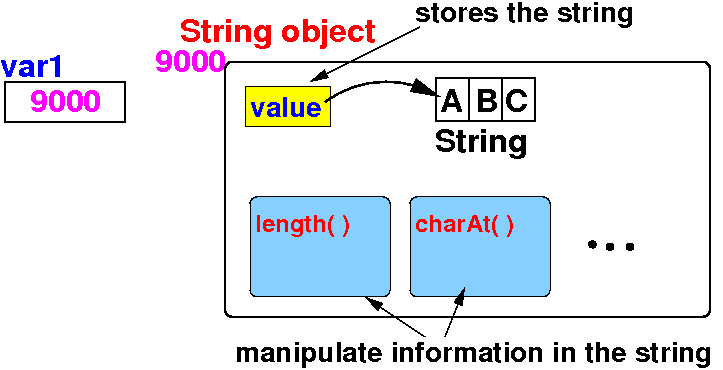
String is a class, a.k.a. a reference data type
var1 is a reference variable
"ABC" is a (String typed) object
var1 references (points to) the "ABC" String object
|
Array in
Java is
also a
reference
data type
Defining array variables
in Java
DEMO:
demo/08-array/02-basics/ArrayObject.java
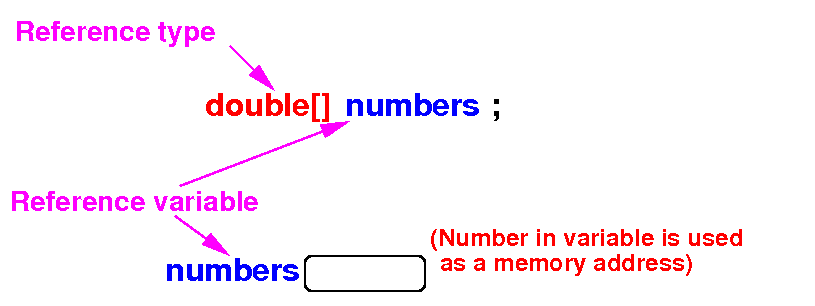
What happens inside the
computer when you define and
array
double[] numbers; What happens inside the computer
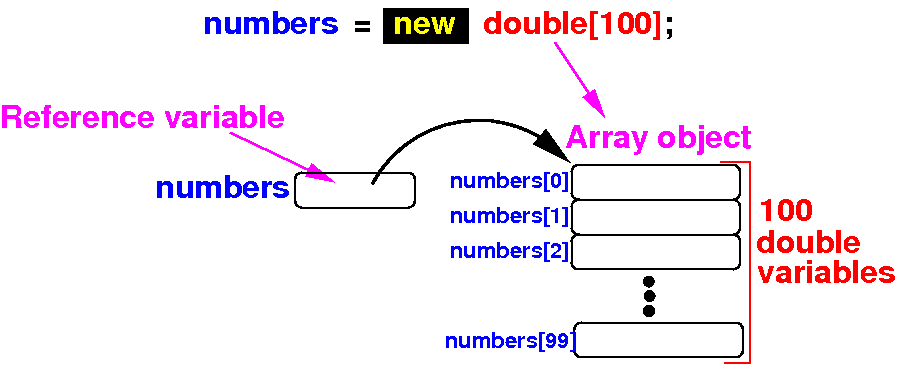
 numbers = new double[100];
What happens inside the computer
numbers = new double[100];
What happens inside the computer
|
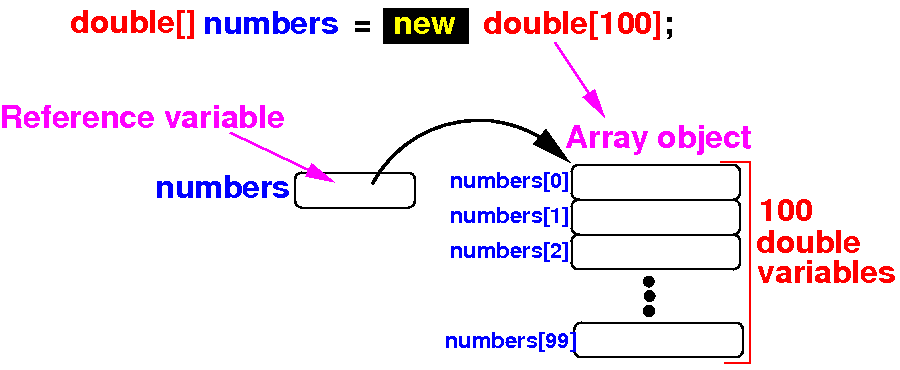
Combining the
(1) array variable definition
and (2)
array creation steps
Instead of 2 steps:
double[] numbers; // Step 1
numbers = new double[100]; // Step 2
We can combine the steps to define an initialized array variable:
double[] numbers = new double[100]; // Combine steps 1 and 2
Result:
|
Using an array
- The
length
(= number of elements)
of an array:
- Each array
has a variable called
length that
contains the
length (= # elements)
of that array:
ArrayType arrayVarName = new ArrayType[N];
arrayVar.length contains N (= # elements in the array)
|
|
- Each element is
uniquely identified by
an
index
- The first element
of the array
has
index 0
- The last element has
index
arrayName.length−1
|
- To
access the
ith element in
the array arrayName, use:
|
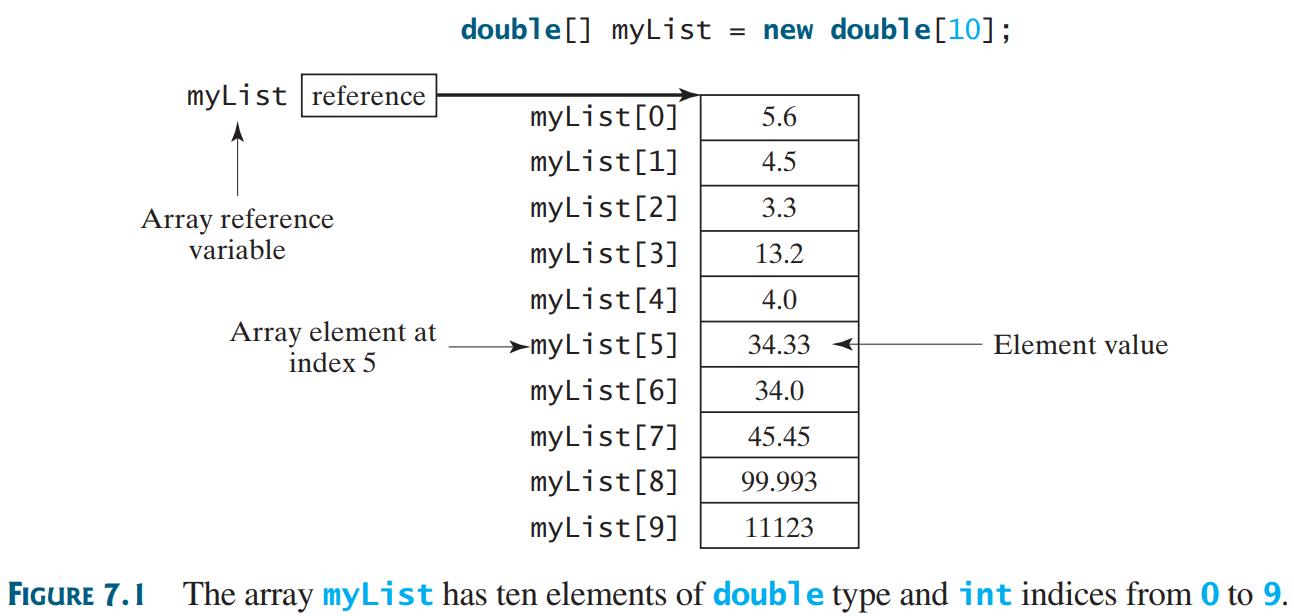
Example:
defining and using array
double[] myList = new double[10];
myList[0] = 5.6; myList[1] = 4.5;
myList[2] = 3.3; myList[3] = 13.2;
myList[4] = 4.0; myList[5] = 34.33;
myList[6] = 34.0; myList[7] = 45.45;
myList[8] = 99.993; myList[9] = 11123;
Result: (show in BlueJ - double click on object)
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/02-basics/UseArray.java
Show
array object in
BlueJ
The default
initial values in arrays and
array initializers
DEMO:
demo/08-array/02-basics/ArrayInitializer.java
Important facts
about arrays
- Once an
array is
created
(with new or
an initializer),
its
size
is
fixed:
double[] myList = new double[10]; // array of 10 elements
|
- The index used
tp
access
an array element
must be
between
0 and
arrayName.length−1
- If you use an
index
outside the
range
of
0 and
arrayName.length−1,
you will get a
ArrayIndexOutOfBound
error
|
Example:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] myList = {1.9, 2.9, 3.4, 3.5}; ; // 4 elements in array
double x;
x = myList[3]; // OK
x = myList[4]; // Error
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/08-array/02-basics/IndexError.java
❮
❯


 numbers =
numbers = 

