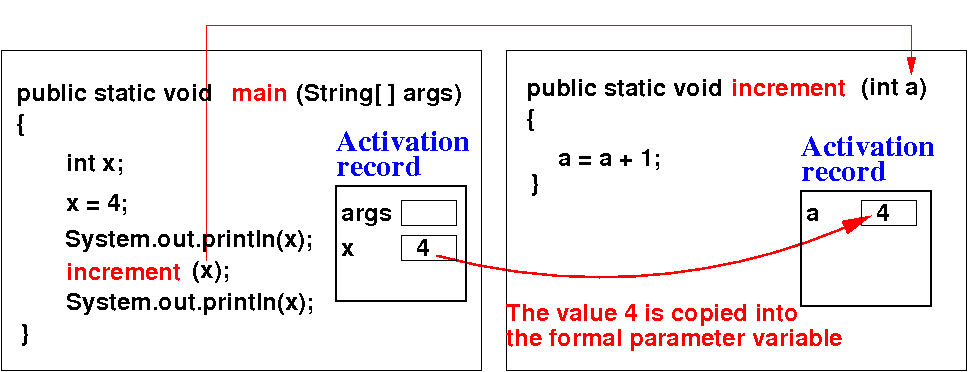
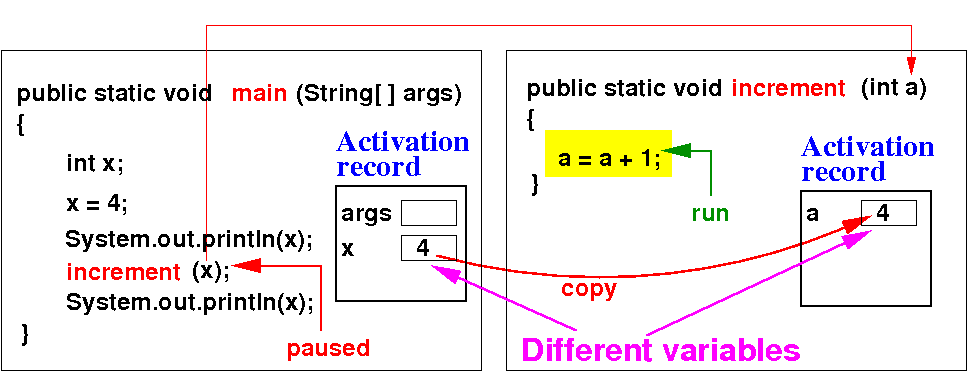
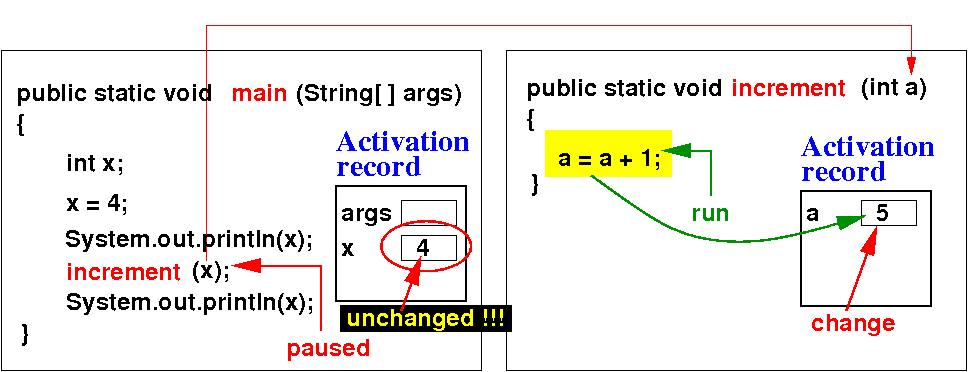
Consider a method increment( ) that updates the parameter variable:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x;
x = 4;
System.out.println(x);
increment( x ); // Pass x
System.out.println(x); // What value will be printed ?
}
public static void increment(int a )
{
a = a + 1; // Changes the parameter variable
}
|
DEMO: demo/06-methods/03-pass-by-value/Demo.java -- Run in BlueJ
Program that shows the effect of copying a variable:
public class Copy
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, x;
x = 4; // CHANGES the value in x to 4
a = x; // CHANGES the value in a in x (i.e.: copy)
a = a + 1; // CHANGES the value in a to a+1
}
}
|
DEMO: demo/06-methods/03-pass-by-value/Copy.java -- Step in BlueJ
The statement a = x makes a copy of the variable x in the variable a
public class Copy
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a, x;
x = 4; // CHANGES the value in x to 4
a = x; // Makes a copy of x in a
a = a + 1; // CHANGES the value in a to a+1
}
}
|
Important:
a copy and its
original are
independent
when the copy
in variable a is
changed by
a =
a + 1, the
value
in variable x is
not changed
DEMO: demo/06-methods/03-pass-by-value/Copy.java -- Step in BlueJ
Java passes the arguments to method invocations by copying each argument to the parameter variable:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x;
x = 4;
System.out.println(x);
increment( x ); // Pass x by copying, just like: a = x
System.out.println(x); // x UNCHANGED ! Explained in more details next
}
public static void increment(int a ) // a and x are different variables !!
{
a = a + 1;
}
|
DEMO: demo/06-methods/03-pass-by-value/PassByCopy.java -- Step in BlueJ
|
|
|
Each method can name their own variables independently from other methods:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x ;
x = 4;
System.out.println(x);
increment( x ); // Pass main's x by copying
System.out.println(x);
}
public static void increment(int x )
{
x = x + 1; // Uses increment's x in operation
}
|
Variables defined in different methods are independent (different) variables
DEMO: demo/06-methods/03-pass-by-value/Copy.java
Demo with BlueJ: show the different value in variable x in the activation records when stopped after x++