The
for loop
|
The
for
loop:
a very commonly used syntax
|
The
for
loop:
a very commonly used syntax
example
|
DEMO: demo/05-loops/04-for/Summation.java
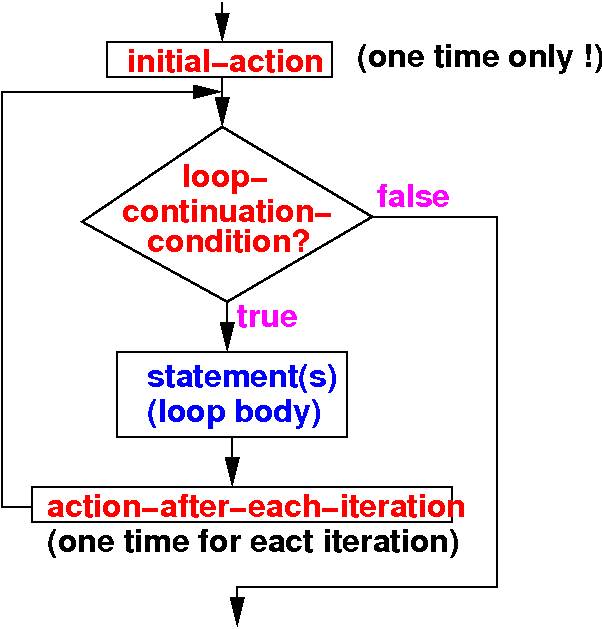
The
for
loop
flow chart
|
Application of the
for loop:
find
all
divisors of
a number
Write a program that reads in a number x and prints out all its divisors:
Plan:
Read in x
We know that: a divisor of x must be < x
Try every number that is < x:
for k = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, ....., x-1:
check if k is a divisor of x
if so: print k
|
Application of the
for loop:
find
all
divisors of
a number
Write a program that reads in a number x and prints out all its divisors:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int x, k;
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
x = input.nextInt();
for ( k = 1; k < x; k++ )
{
if ( x%k == 0 )
System.out.println(k);
}
}
|
DEMO: demo/05-loops/04-for/Divisor.java