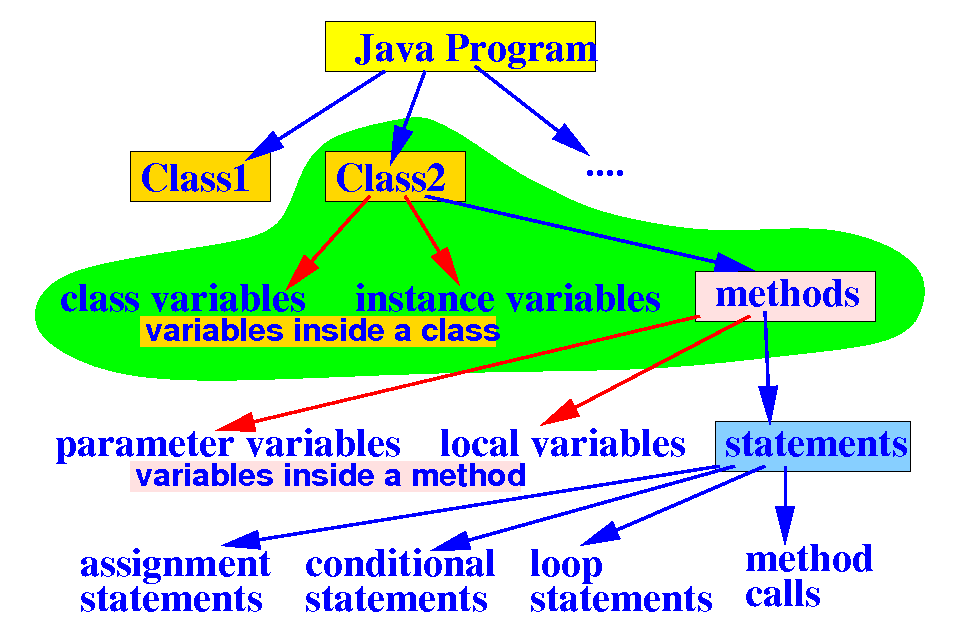
Review:
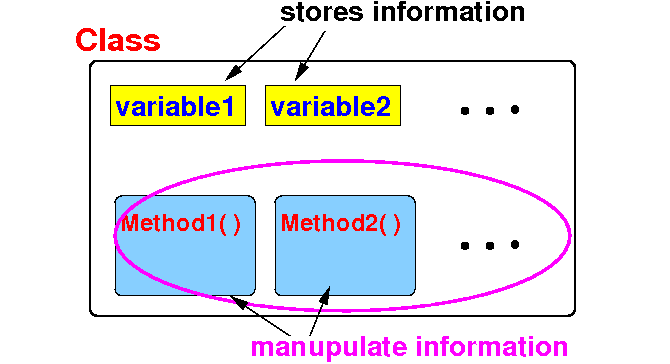
Java
class
- Review:
- A
class in
Java is used
to:
- Group
related
variables
and
methods together
|
|
|
Review:
Java
class
- Review:
- A
class in
Java is used
to:
- Group
related
variables
and
methods together
|
|
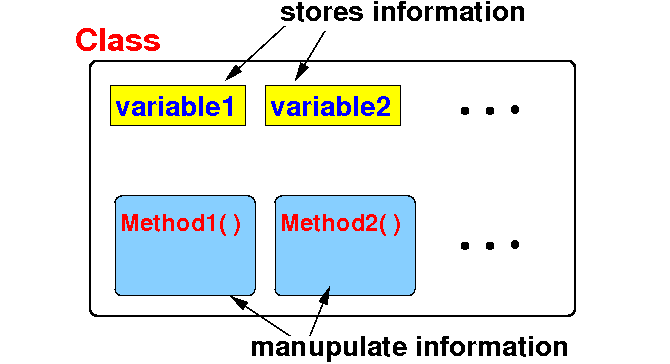
- Schematic
representation of
a class:
|
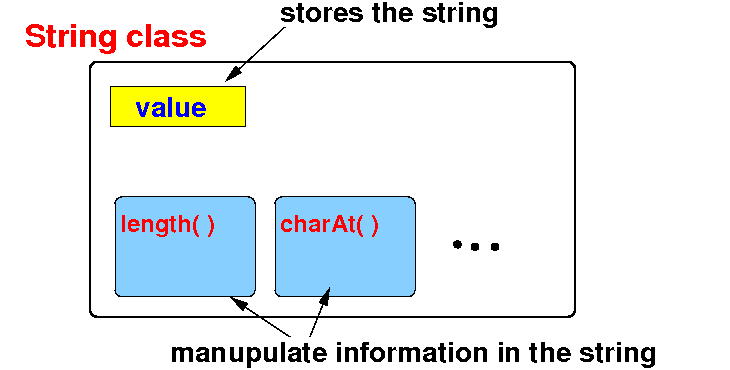
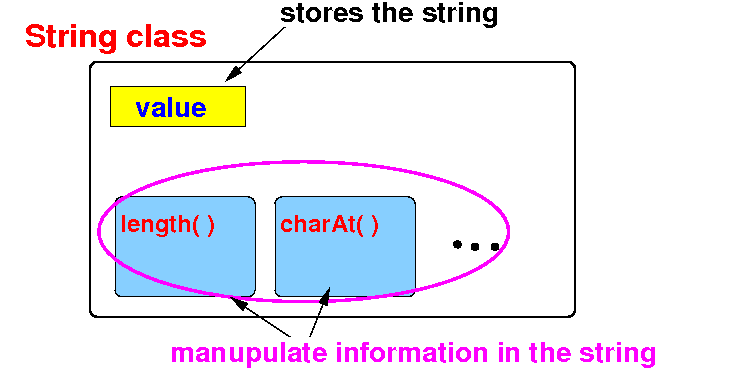
Java
String class
- String is
a class in the
Java library that
implement
strings
- A string
consists of a
sequence of
characters →
the
variables
- A string can be
manipulated
in certain
ways
→
the
methods
|
- Schematic
representation of the
String class:
- In this chapter, we
learn to
how to
use
the
String class
in the Java library
|
Defining and using
String typed
variables
- Syntax to
define a
String typed
variable:
Method 1: uninitialized
String varName;
// Later, you can assign a string
// to this variable with:
//
// varName = "Some string...";
Method 2: initialized
String varName = "initial string...";
|
Example:
String var1;
String var2 = "abcd";
|
|
DEMO:
04-Math+String/04-string/DefineStringVar.java
Reference
data types
and reference
variables
-
Reference
data type:
- All
Java classes are
reference
data types
(and vice versa)
|
- Since
String is
a Java
class:
- The
String
data type
is
not a
primitive
data type
- The
String
data type is
a
reference
data type
|
-
Reference
variables:
- Reference variables = a
variable
defined using a
class name
|
Example:
String var1; // var1 is a reference variable
|
- A
reference variable
always
stores a
reference (= address) of an
"object"
in Java
(next)
|
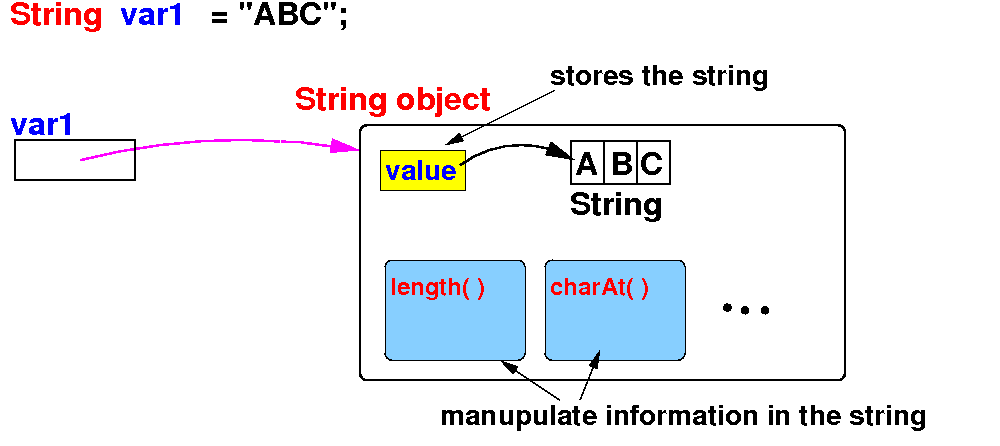
What happens when you
define and
assign to a
String typed
variable
What happens when you
define and
assign to a
String typed
variable
- Computer code that
creates a
String typed
variable and then
assigns to it:
String var1;
var1 = "ABC";
|
When the "
String
var1" is
executed, the
computer will
create the
variable
var1:

The variable
var1 will contain
the
default
value
null
(which means:
illegal reference)
|
What happens when you
define and
assign to a
String typed
variable
- Computer code that
creates a
String typed
variable and then
assigns to it:
String var1;
var1 = "ABC";
|
When the
assignment
"
var1 = "ABC" is
executed, the
computer will
(1) create a
String
object and
(2)
assign its
address (= reference)
to variable
var1:
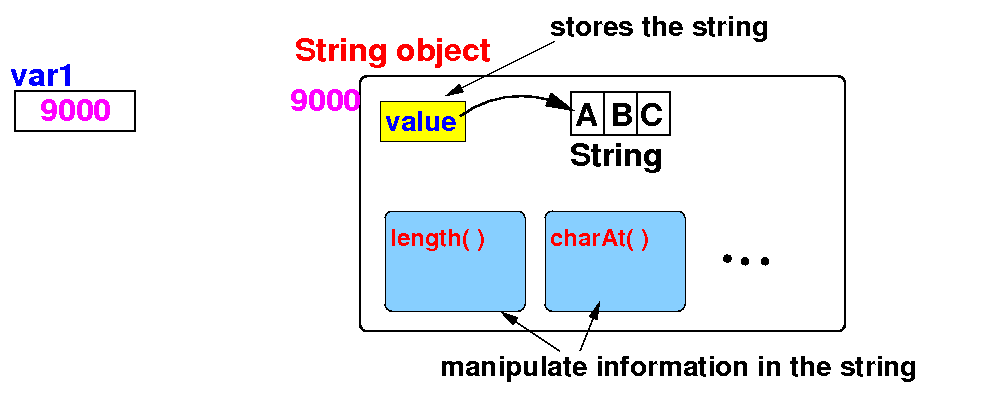
We can
now
use the
address in
the
variable
var1
to
find
the string
(stored in memory)
|
What happens when you
define and
assign to a
String typed
variable
- Computer code that
creates a
String typed
variable and then
assigns to it:
String var1;
var1 = "ABC";
|
We typically
use an
arrow to
represent the
fact that
a (reference) variable stores
the address of
an object as
follows:
The
arrow indicates
that we will use the
object
pointed to by
the reference variable
|
DEMO:
04-Math+String/04-string/DefineStringVar.java
---
click on
ObjRef icon and
show content
Reference data types and objects
Summary
(1) String is a class or a reference data type in Java
(2) var1 is a reference variable
always contains a reference (= address) of an object
(3) "ABC" is a (String typed) object
(4) var1 references (points to) the "ABC" String object
|
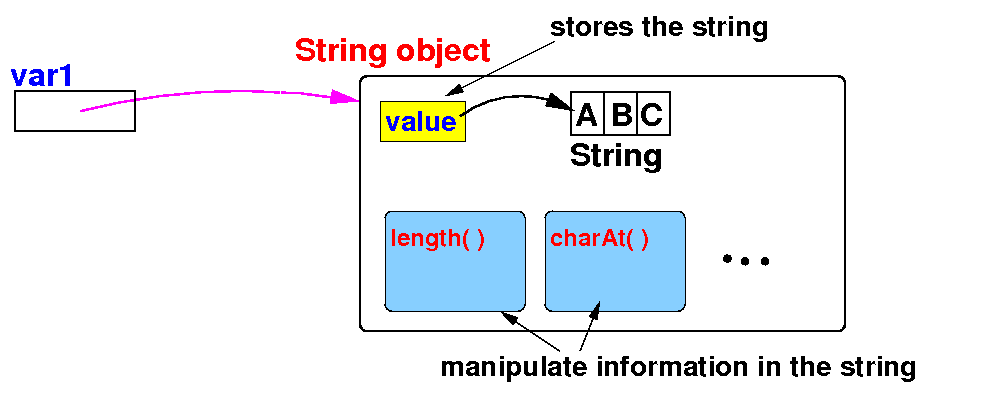
How to use
String objects:
instance methods
- Recall that
classes
contains
methods that
can
manipulate the
data
stored in the
class:
- The String
class in the
Java library
contains many
methods that
manipulate the
string:
|
Sample methods
inside the
String class
-
Sample methods defined
inside
the String
class that
manipulate
a
String object:
|
How to
apply
methods
inside the
String class
on
String objects
- Important fact:
- A class in
Java
is used to:
- Create
"object" with
certain
properties
and
also
- Provide
a set of
methods to
manipulate
the "object"
|
|
-
How to
apply
a method inside
the String class
(on a String object):
String var1; // (1) Define a String variable
// (to reference to a String object)
var1 = "abc"; // (2) Create a String object
// (we can use var1 to refer to this String object)
var1.length() // (3) Applies the length() method on the String object
that var1 is referencing
|
|
Example applying some
methods on
String objects
- In this program, we
create
2
String objects and
apply some
methods on
each of them:
public class ExampleString
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String s1 = "Hello 123"; // Create the first string
String s2 = " Good-bye "; // Create the second string
int x;
char c;
String result;
x = s1.length(); // the length of string s1
x = s2.length(); // the length of string s2
c = s1.charAt(1); // the char at pos 1 in string s1
c = s2.charAt(1); // the char at pos 1 in string s2
result = s1.toUpperCase(); // string s1 in uppercase
result = s2.toUpperCase(); // string s2 in uppercase
result = s1.concat(s2); // String s1 concatenated with string s2
result = s2.concat(s1); // String s2 concatenated with string s1
result = s2.trim(); // remove spaces before and after string s2
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
04-Math+String/04-string/UseString.java
❮
❯









