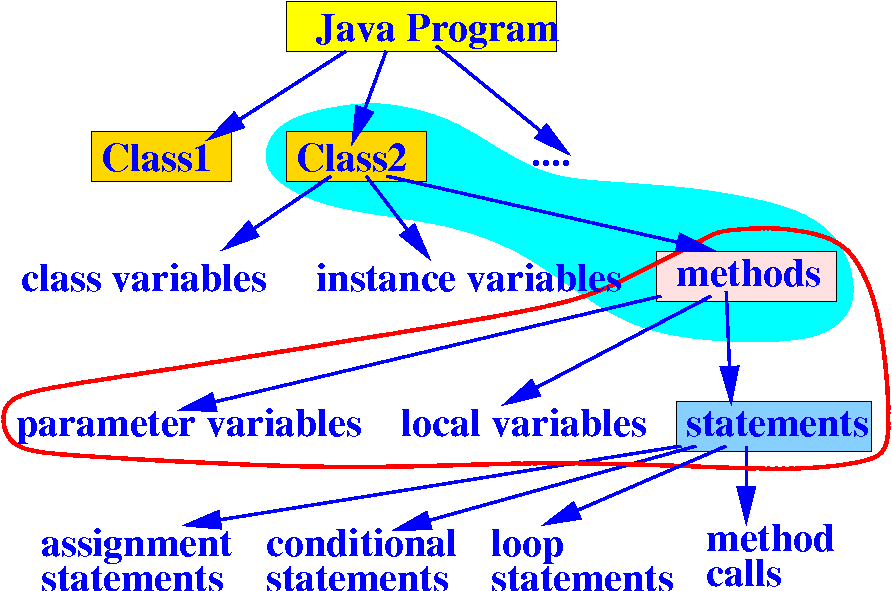
Java's Math class
|
Java's
Math class
|
How to
use a
method in Java's
Math class
|
DEMO: demo/04-Math+String/01-Math-class/MathMethods.java
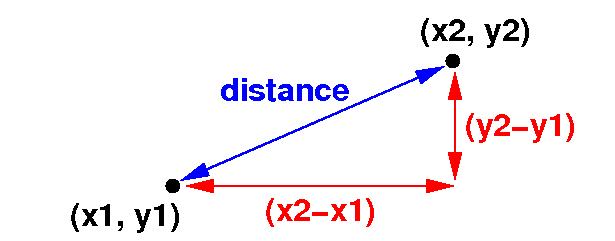
Compute the
distance
between 2 points
|
Compute the
distance between 2 points
|
DEMO: demo/04-Math+String/01-Math-class/Distance.java