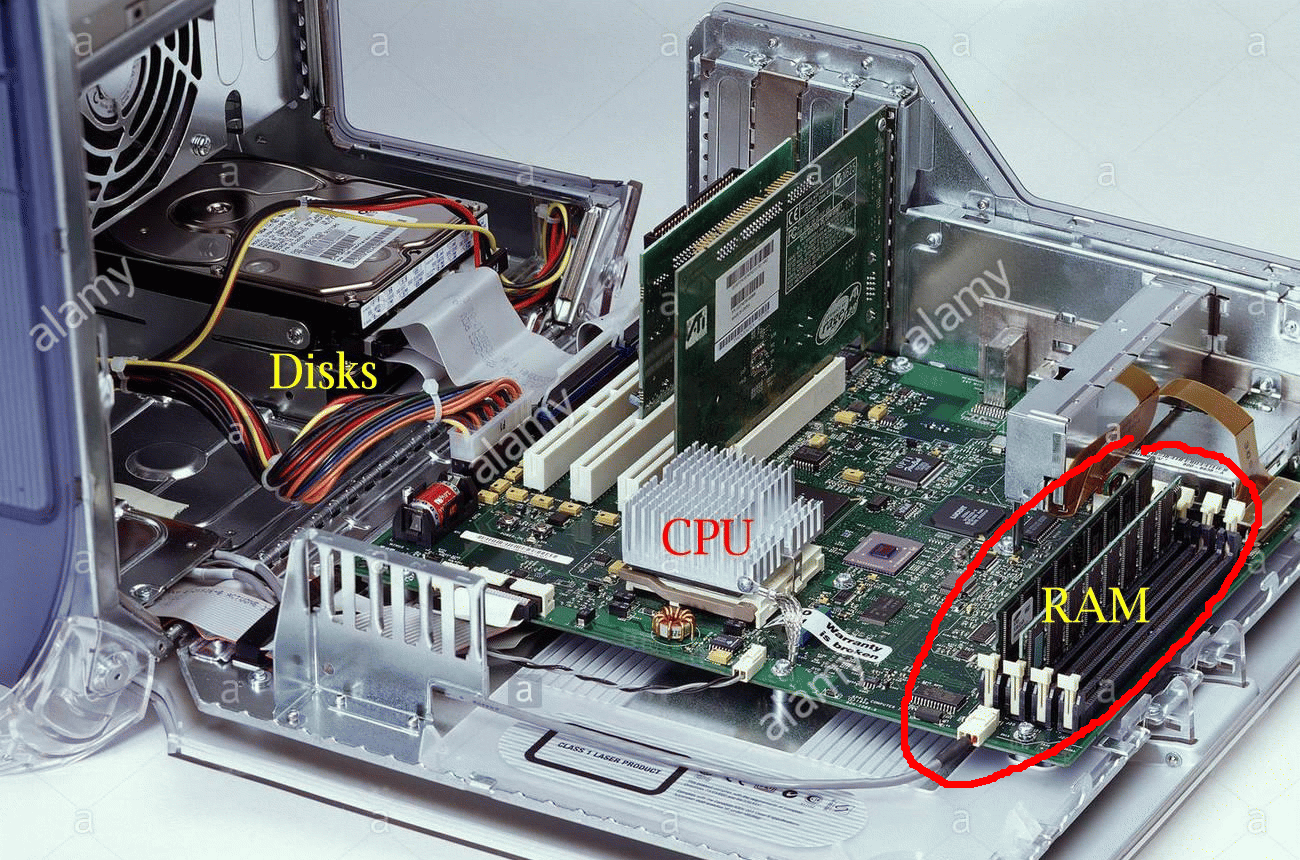
Review:
What a computer looks like from
inside
- The
RAM
(or Random Access Memory)
stores/contains
computer programs:
- A
computer programs
consists of:
- Program
instructions
- Program
variables
← Attention !!!
|
|
More review:
analogy between
computer memory and
mail boxes
- The main memory
or RAM is
similar to
a collection of
mail boxes:

where:
- Each
mail box
is uniquely
identified
by an integer
mailbox number
(= address)
- Each
mail box contains
slip of paper
can store a
small number
|

|
How the Java compiler
works
- The Java compiler
translates
a Java program into
executable
machine code:
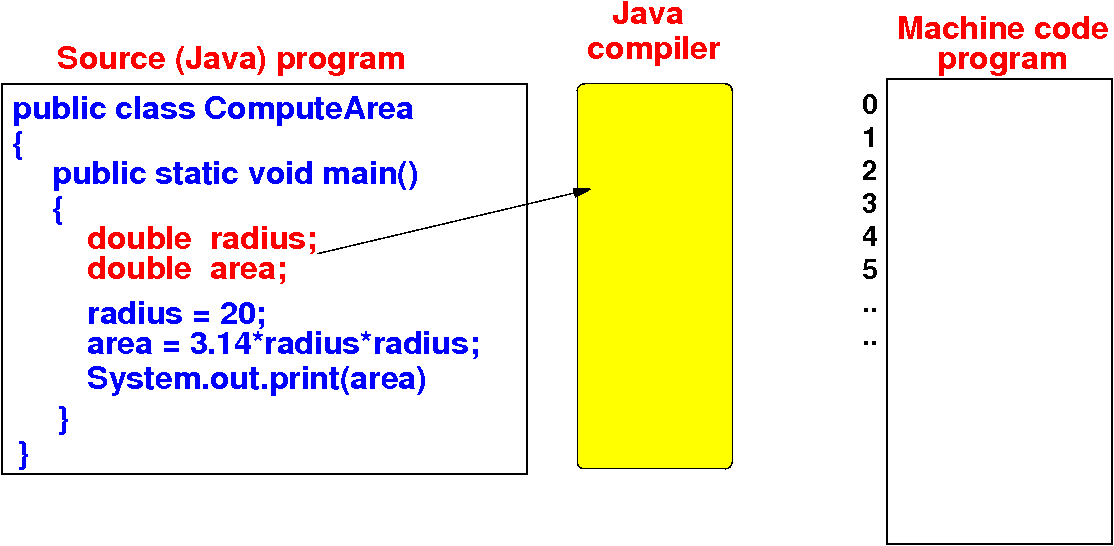
- The machine code will be
placed in
computer memory for
execution
- The items inside
the machine code
program will be
identified using
memory addresses
|
How the Java compiler
works
- When the Java compiler
finds a
variable definition,
it will
allocate (= reserve)
some memory cells
to store the
value:
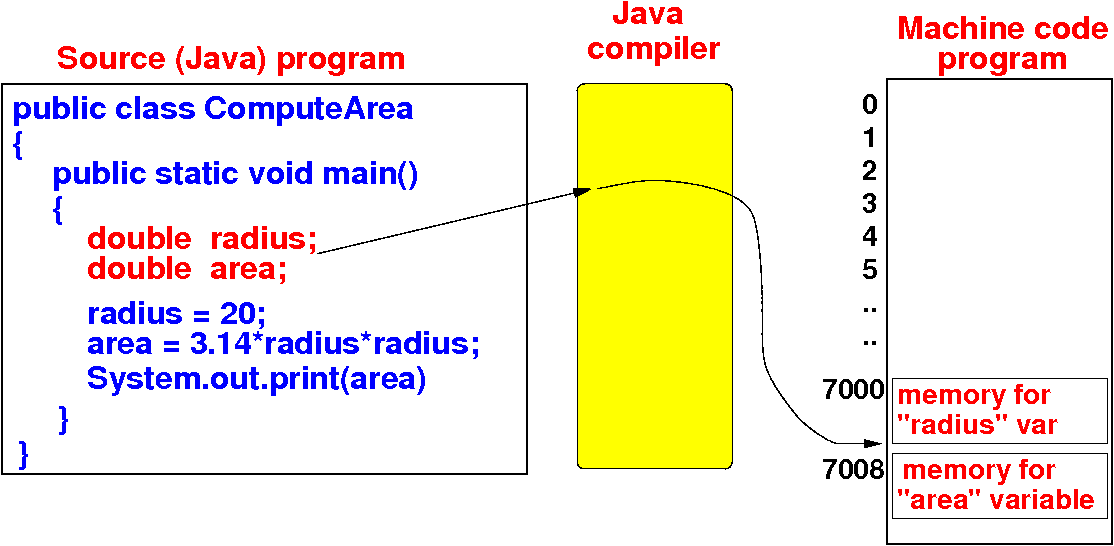
- These memory cells will be
identified using
memory addresses
- Example:
radius is placed
in memory address 7000 and
area in
memory address 7008
|
How the Java compiler
works
- The Java compiler will
remember
the placement of
the variables:
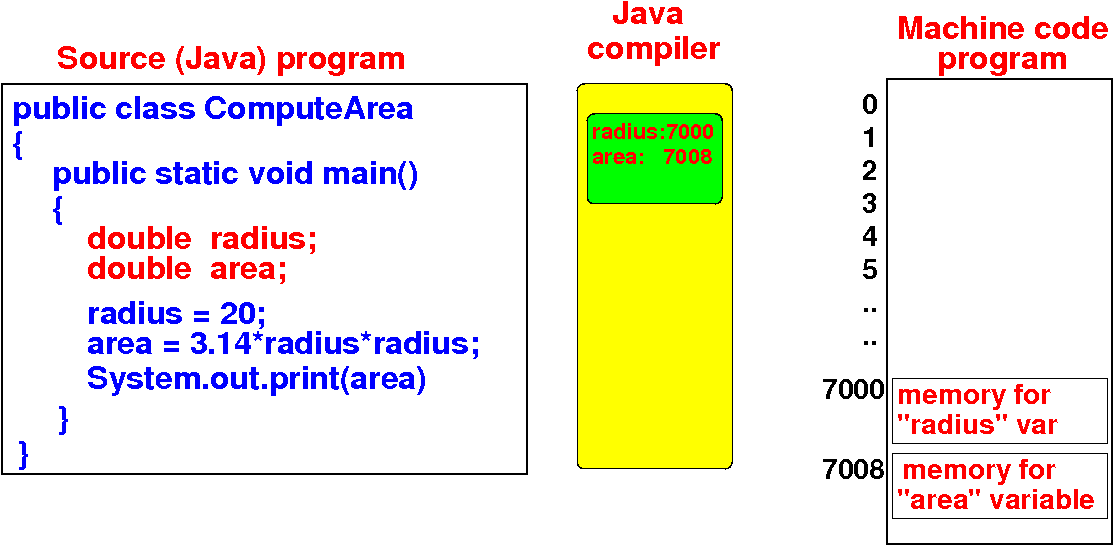
- The Java compiler
records the
variable placement in its
symbol table
- Example content of the
symbol table:
radius:
7000 and
area:
7008
|
How the Java compiler
works
- When a variable is
used in the
program,
the Java compiler use the
location information
to translate the
instruction:
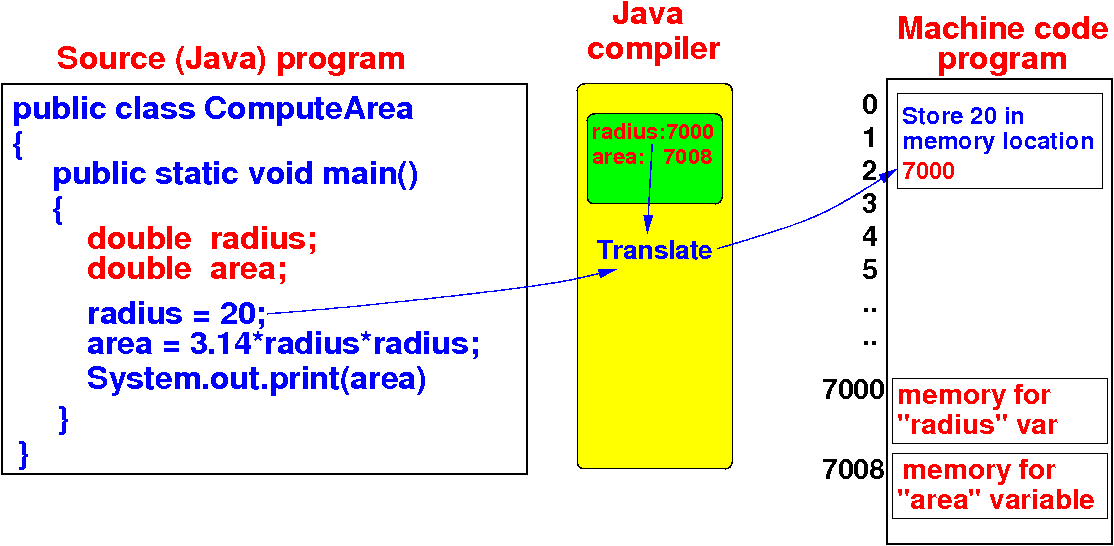
- The Java compiler
looks up the
memory address of the
variable using its
identifier
- Example translation:
radius = 20
⇒
machine code
that stores
20 into
mem addr
7000
|
How the Java compiler
works
- When the
Java program is
run/executed, the
effect of the
instruction
radius = 20 is:
store the
(binary) number 20
in memory location 7000:
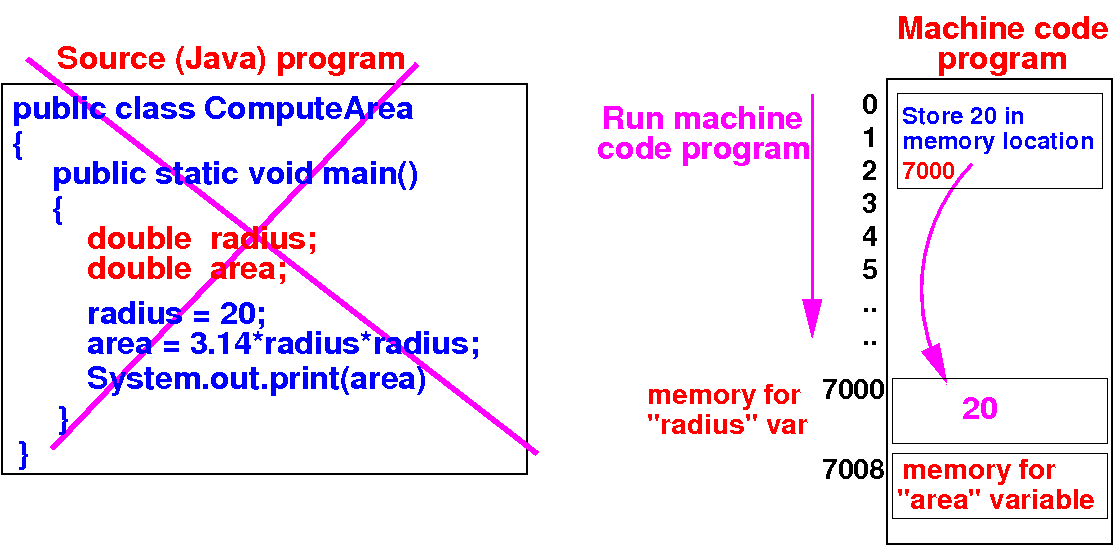
-
Only
the compiled
machine code is
used when a
program is
run
- The source code is
not used !
|
❮
❯







